 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
The ultrasound remains one of the most important diagnostic tools available in medical imaging. This stems from the fact that it is faster and cheaper than other methods of medical imaging, such as the CT scan or MRI. It also has the advantage of being safer than both modalities, as it does not involve the use of ionizing radiation or magnetic fields. Despite these advantages, the ultrasound still remains underused as a medical diagnostic tool. At present, the ultrasound medical device is only used extensively in three major clinical specialties, namely radiology, cardiology and obstetrics. However, this is about to change with the introduction of new generation portable ultrasound devices.
When ultrasound systems were first introduced, they were bulky devices that could not be easily transported. Therefore, each department that used the ultrasound had its own imaging system in place. This played a huge role in restricting the use of ultrasound as an imaging system. Portability makes it possible to make ultrasound a point-of-care (POC) diagnostic test. This means that the test can be carried out at the patient’s bedside, where medical care is actually being delivered, rather than at a medical laboratory or imaging room. The introduction of the handheld ultrasound device has several proven benefits, which include the following:
Accuracy of diagnosis: Studies have shown that in one out of every three patients, adding the handheld ultrasound device to routine clinical examination has changed, added to, or confirmed an important diagnosis. This makes the use of ultrasound devices indispensable for diagnostic purposes.
Quicker diagnosis and treatment: Because an ultrasound device at the bedside eases workflow, not only can a diagnosis be made faster but treatment can be initiated immediately as well. This improves patient outcomes.
Reduced need for invasive testing: By helping confirm a diagnosis at the bedside, it is possible to avoid further investigations, which were previously required to arrive at a diagnosis.
Peripheral usage: Handheld devices are especially useful away from the hospital, when medical camps are being conducted in remote areas or when treatments are carried out at low-income centers.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
Abdominal screening: FAST (Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma) is one of the standard protocols in trauma management. It is a rapid bedside ultrasound that is used in the emergency department. It is used to screen for the presence of blood around the heart or abdominal organs. The examination can also be extended to the lungs in order to screen for the presence of pneumothorax.
Portable ultrasound has also proven effective in the detection of abdominal aortic aneurysm. It is as effective as traditional ultrasonography, and the portable ultrasound device can also be used to measure the maximum diameter of the abdominal aorta.
Bladder volume: Residual urinary bladder volume is measured when investigating for urinary incontinence or evaluating urinary tract infections. Usually this is done by catheterization, which is invasive, unpleasant and carries the risk of infection. A handheld ultrasound device offers a convenient alternative to measure bladder volume, and has proven to be almost as accurate.
Cardiovascular applications: While the traditional echocardiography console is still the gold standard in most cardiology units, there are instances where quicker results are required. This can be achieved with the help of a portable ultrasound device. The portable device can assist in screening for cardiovascular diseases. For instance, carotid artery stenosis is often not detected at the primary healthcare center while a duplex ultrasound or an MRI is ordered only in cases of an acute event (such as an infarction or stroke). However, if the portable ultrasound device were used in primary care, it would help identify patients who are at a higher risk of stroke. The device can help dictate proper management of risk factors and it can help select candidates who would benefit from therapeutic procedures, such as endarterectomy.
The handheld ultrasound device can also help screen patients who have clinically suspected deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Prompt detection and management of DVT can help avoid fatal outcomes, such as those associated with pulmonary embolism. The handheld ultrasound device has also been used to detect varicose veins, both primary and those that recur after treatment.
Obstetrics: As with cardiology, the traditional console is most commonly used for obstetrics. As of today, the traditional console cannot be replaced by the portable device, especially for anomaly scans and 4D scans that are used to assess the health of the fetus. However, the portable ultrasound device does have a role to play in obstetrics in the emergency setting. If a pregnant patient presents with bleeding or ruptured membranes, the portable ultrasound device can be used to determine fetal viability and fetal positioning, which can help detect a miscarriage. The amniotic fluid volume can also be measured and management strategies can be planned accordingly.
Musculoskeletal problems: The handheld ultrasound device can be applied in the outpatient clinic to diagnose various musculoskeletal problems. Studies have shown that the handheld ultrasound device can be almost as sensitive as arthroscopy in detecting partial or complete rotator cuff tears of the shoulder. Using ultrasound can help avoid unnecessary MRIs in these patients, which lead to both financial and time savings. The handheld ultrasound device has been used in knee joints to exclude meniscal tears. The portable ultrasound device is also used in the emergency department to screen for swollen joints. This can help exclude a diagnosis of joint effusion.
Ultrasound-guided treatment: The portable ultrasound device can be used to guide treatment in the operating room. Regional anesthetic blocks can be given under ultrasound guidance. Portable ultrasound devices are also useful to detect lesions and masses prior to taking an ultrasound-guided biopsy. In vascular surgery, a handheld ultrasound device may be used to identify blood vessels relevant to the procedure.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |
Several ultrasound system manufacturers have come up with their own handheld ultrasound device. Here we list some of the best handheld ultrasound devices developed by various ultrasound machine manufacturers:
Sonosite: This is marketed by Fujifilm. Sonosite is a hardy line of portable ultrasound devices that are proven to be accurate as well as reliable. The Sonosite Edge II is a portable laptop unit that is embedded with steel to make it durable. It can survive all types of weather conditions and any drops. The Sonosite i-viz is a portable seven-inch tablet that offers high quality image resolution. The i-viz also offers embedded learning tutorials and an ultrasound education app.
Vscan: This was developed by GE healthcare. It is a pocket-sized device that can easily fit in the palm of your hand. The Vscan Extend model and the VScan dual probe model have two transducers in one probe. With a monitor that resembles a smartphone, it is easy to use and can increase information available at the point-of-care. It provides both black and white anatomic images as well as color blood flow images in real time. The Vscan Extend can integrate with the hospital’s wireless network and can then be used to transfer information to the hospital’s PACS for easy documentation and reporting.
Acuson P10: Developed by Siemens Medical Solutions, this product claims to be the world’s smallest ultrasound device. It is lightweight, weighing only 1.6 pounds and has an LCD display of 3.7 inches. It has a touch screen interface and a menu that is easy to navigate. It was primarily designed for diagnostic use in emergency medicine, cardiology and obstetrics.
Viamo: This is a portable laptop unit marketed by Canon Medical Systems. It claims to have diagnostic precision and productivity that equals a standard cart ultrasound device. With Advanced Dynamic Flow technology, it offers high quality ultrasound images, especially for color flow. The transducers that come with the Viamo unit are lightweight and shaped in a way so that they offer maximum efficiency. It also comes with highly flexible cables for ease of use.
Philips CX50 ultrasound system: While this ultrasound system is slightly larger than the laptop-sized and handheld units, this is still a compact portable system that can be transported anywhere in the hospital. It has a high resolution monitor and incorporates PureWave technology that allows it to give fast and superior performance. It can be connected through wired or wireless networks to the PACS server. The monitor and cart are combined into a single lightweight unit, with adjustable height.
Prosound C3CV: This monitor developed by Hitachi is a laptop unit that can be converted into a cart unit. The highlights of this device are its fast Fusion processor and easy to use Windows graphical interface. It can be used with a variety of transducers.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
Ultrasound is no longer just a diagnostic imaging modality, it can be used for therapy as well. Low intensity ultrasound devices, which deliver sound waves between 1 MHz to 3 MHz, have been shown to promote tissue healing. These low intensity ultrasound devices have been in use for a long time in physiotherapy units, where they are primarily used for pain relief. Current research has shown that ultrasound can aid in faster healing of wounds and fractures.
Therapeutic ultrasound devices are available for home use and therefore are usually portable. An ultrasound device for home use can provide relief for patients who have chronic pain and can help with faster convalescence after an injury. The best home ultrasound device must be of clinical grade quality, should have a sufficiently large probe so that you can use it over a wider area of the body.
With the advent of handheld ultrasound, several areas of medicine that did not previously use ultrasound are likely to do so in the future. However, one significant challenge in expanding the use of the portable ultrasound device is the lack of adequate specialist knowledge. Several physicians and primary healthcare providers may not have sufficient training to be able to interpret the ultrasound images with ease and precision. Performing the ultrasound scan may also require certain technical skills which need to be acquired.
Some ultrasound machine manufacturers are looking towards artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning (DL) techniques as a possible solution to the above challenges. By incorporating image recognition techniques, the portable ultrasound manufacturers enable the device to offer users guidance on organ detection and probe placement. Philips Healthcare, for instance, has developed an ‘AI breast’ system that helps the sonographer identify key anatomical landmarks. This helps in reaching a correct diagnosis. AI systems are currently under research for detecting abnormalities within images and reaching a diagnosis. QView medical, for example, is testing a software solution that is capable of detecting suspicious areas of breast tissue and highlighting areas which might possibly be malignant.
AI solutions are also being developed for ultrasound-based quantification. Ultrasound-based imaging analysis software is being used to incorporate deep learning techniques for measurements. Ejection fractions can be calculated and analyzed using DiA’s ultrasound analysis tools. It is also possible to quantify the fetal brain using GE healthcare’s SonoCNS fetal brain system.
The future goal is to combine detection tools with quantification tools, so that a quicker and more accurate patient diagnosis can be made.
We have entered the world of convenience by using the latest portable systems produced by various ultrasound device manufacturers. The software needed for reading, editing and analyzing the ultrasound images must be equally versatile. Just as it is now possible to acquire the image at the bedside, it would be ideal if the DICOM imaging software edited and analyzed the image at the bedside as well.
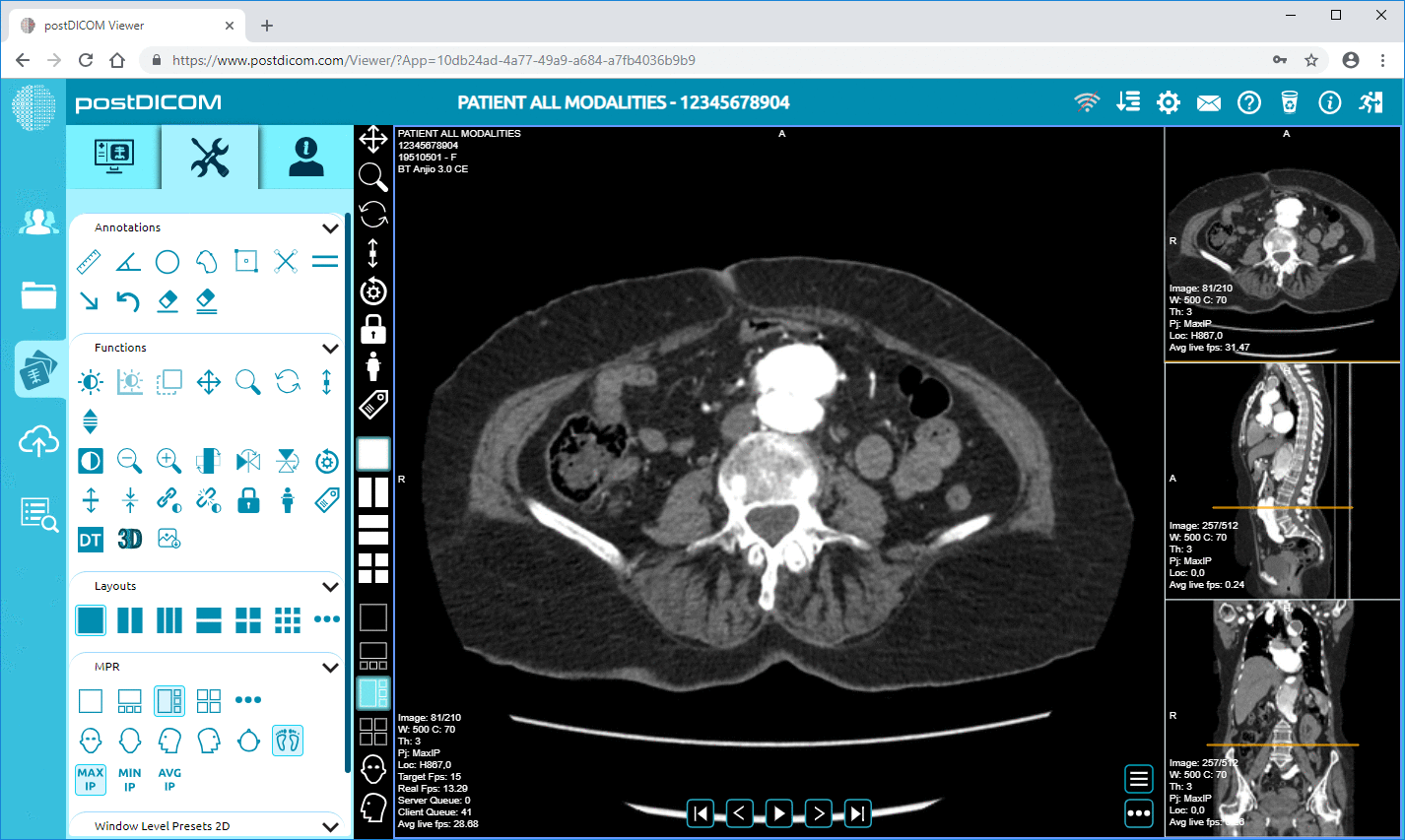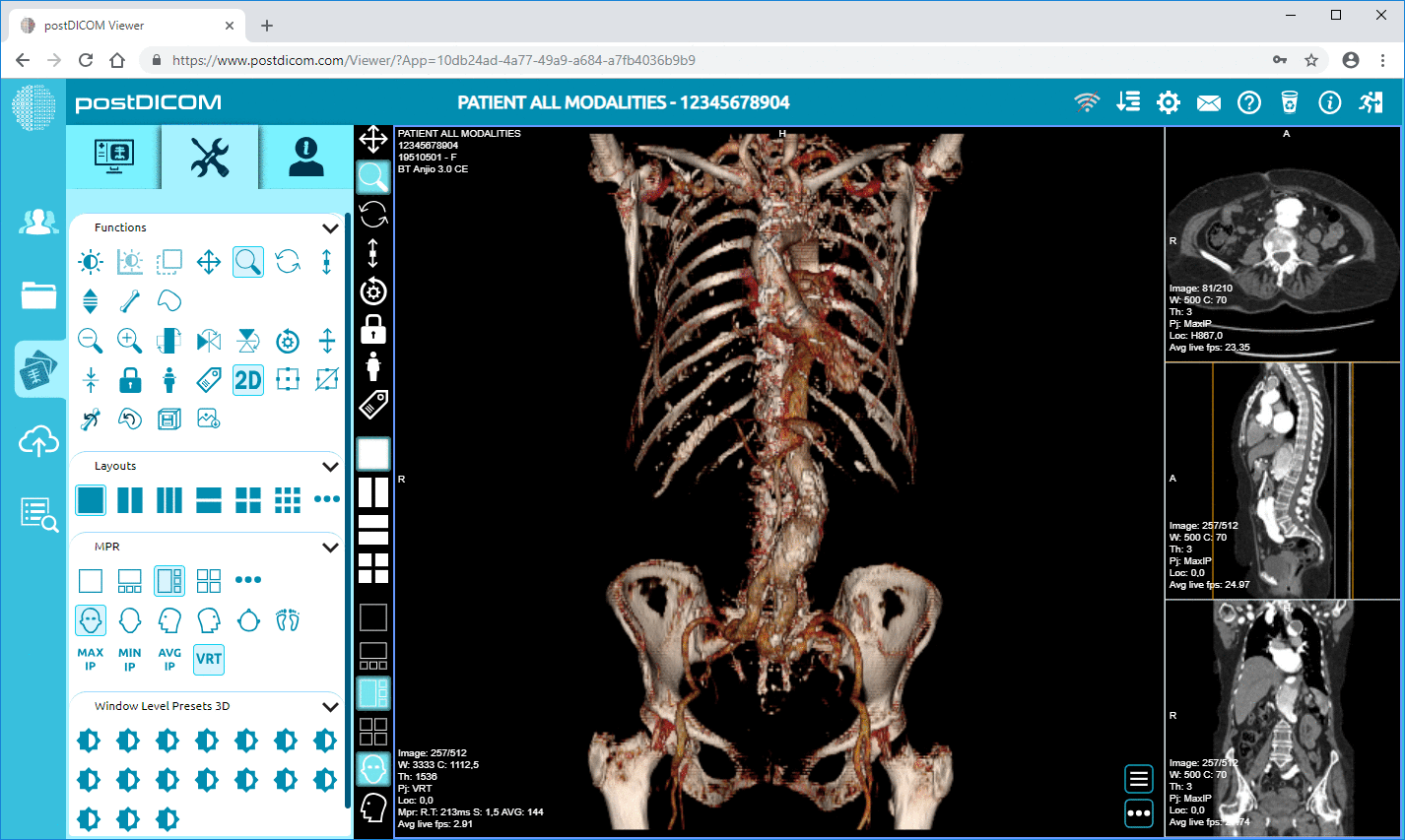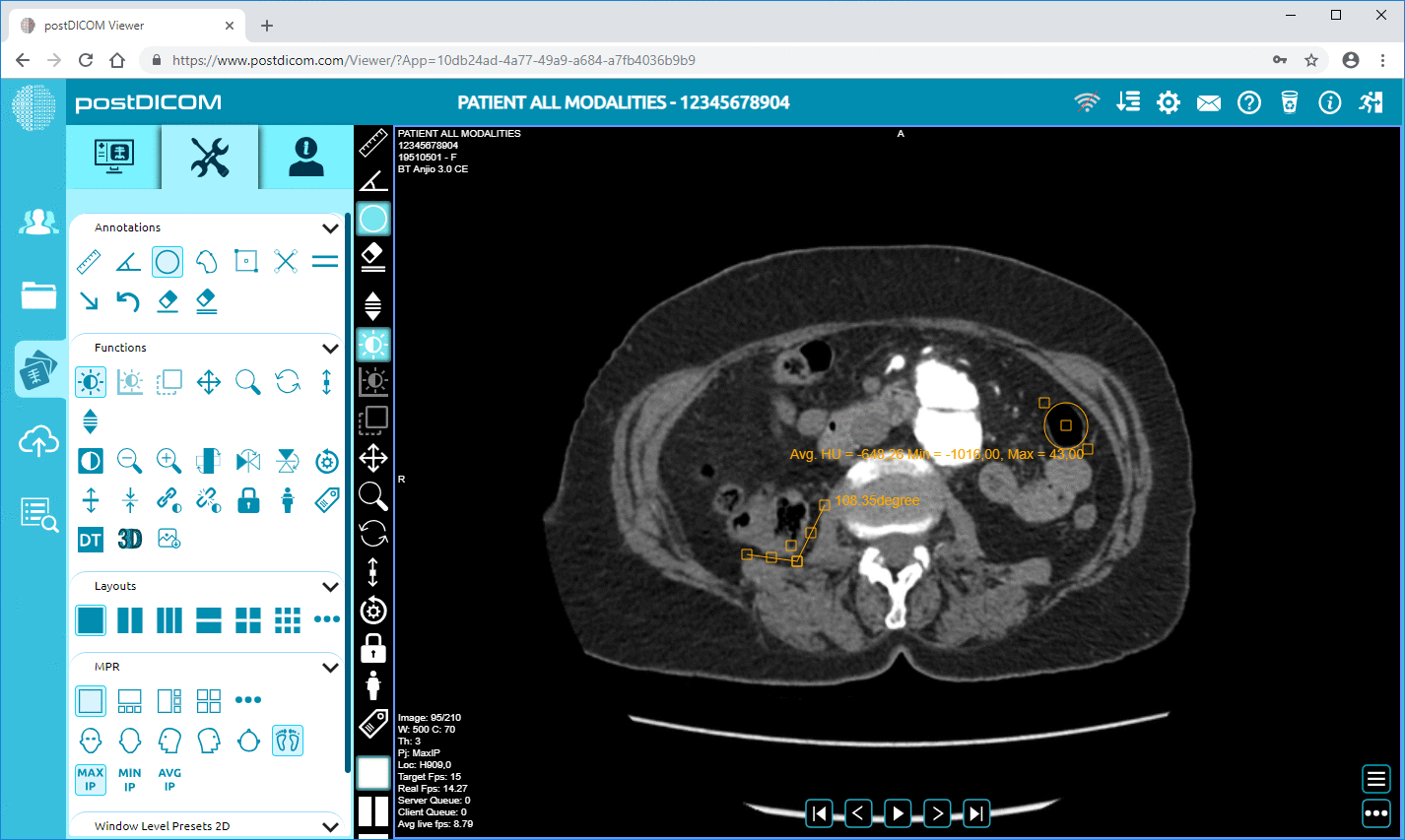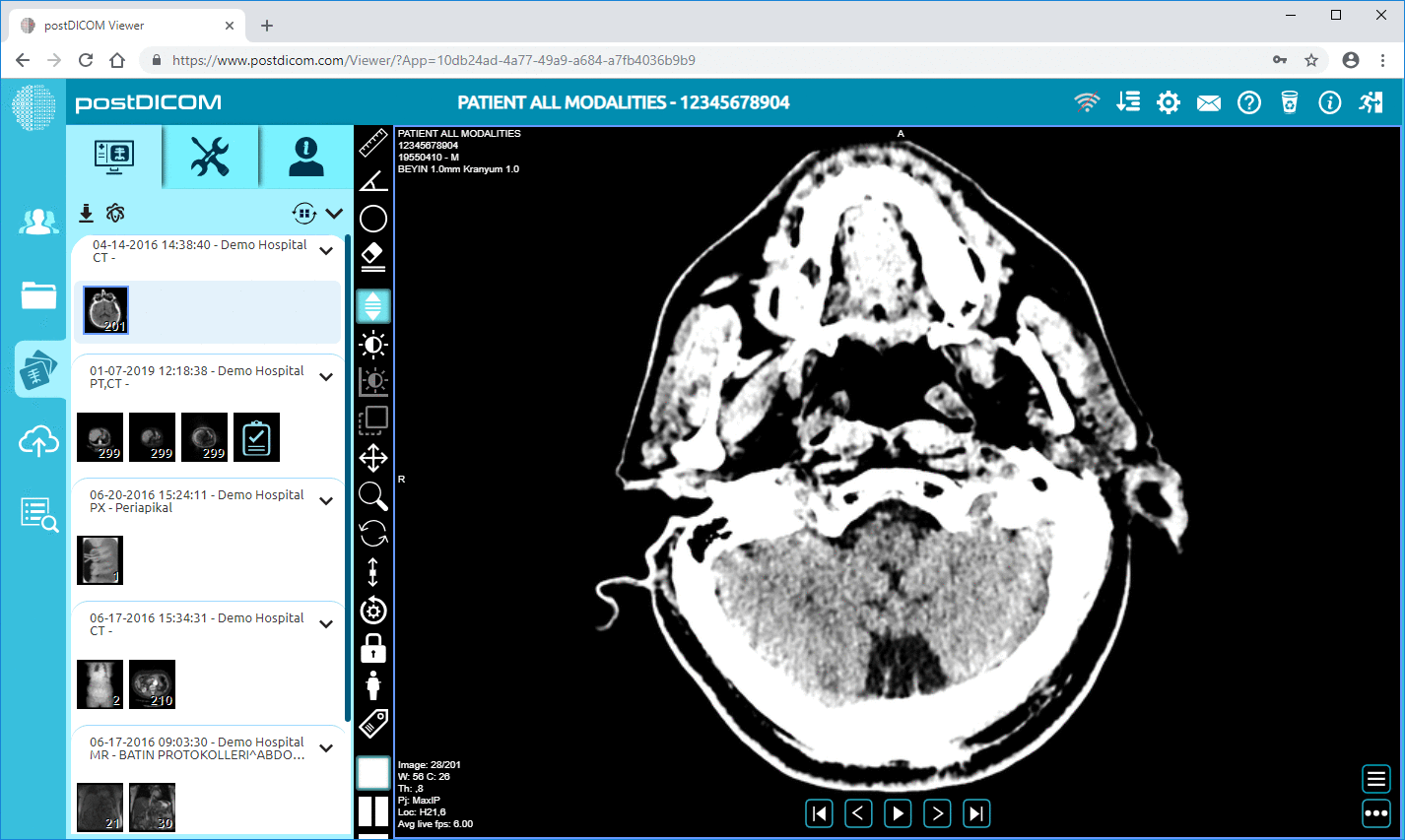
PostDICOM’s cloud-based DICOM imaging software provides such features on the cloud! Our multimodality online imaging viewer supports ultrasound images in the DICOM format. It allows editing and analytic features such as measurements of angles, volumes and lines. The viewer is compatible with Android, Mac OS, Windows and Linux — so you can access the viewer from any device, at any time! PostDICOM offers free trial to cloud storage as well, so you don’t have to save images to your hospital PACS server. If you have a handheld ultrasound device or are planning on getting one, make sure that you register for your PostDICOM image viewer to go with it!