 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has carved a firm niche for itself in the world of medical imaging. Besides being radiation-free and, therefore, a safer form of medical imaging, it is also better suited for imaging non-bony anatomy of the body compared to the CT scan. MRI offers better images of soft tissues, organs, and blood vessels. In particular, it is useful in assessing blood flow to organs and blood vessel size. MRI scans play an important role in the diagnosis of musculoskeletal injuries, stroke, head trauma, and blood vessel conditions such as aneurysms.
However, the MRI is still being underutilized for diagnostic purposes. While a major limiting factor in its use is the cost, the traditional MRI machine also has other drawbacks that limit its use.
The MRI works by using the magnetic properties of human tissues. The human body, which is largely composed of water, has a huge number of protons in the form of hydrogen ions. When these protons are placed in a powerful magnetic field, they align themselves parallel to the field. High frequency radio waves are then applied within this field, which excite the protons. Once the waves are switched off, the protons realign themselves along the field and give off the excess energy as electromagnetic radiation. This is captured by the viewer in the form of an image. Since the protons largely come from water, MRI can principally distinguish between areas with high water content and high fat content.
The principle of the MRI demands the presence of high electromagnetic fields within an enclosed space for accuracy. It is necessary for the patient to lie down in this enclosed space, which resembles a wide, closed cylindrical tube, during the MRI scan. The scan can take anywhere from 15 minutes to 90 minutes and the patient must remain still for this duration in order to obtain accurate results. All these factors create several drawbacks from patients’ point of view:
The traditional MRI machine cannot accommodate patients who are well-built or obese. The traditional closed MRI machine is only about two feet (60 cm) in diameter. It would not accommodate patients who are obese.
The traditional MRI machine is not suitable for patients with claustrophobia. Since the space is enclosed, patients with claustrophobia may experience extreme anxiety. Even patients who do not have claustrophobia find it difficult to spend more than 15 minutes in the enclosed space of the scanning machine.
The traditional MRI can be a scary experience for children. The closed MRI machine makes a lot of noise during the scanning process. This, combined with the fact that they have to remain still within a narrow, confined space, can be a traumatic experience for young patients.
Accuracy depends on the patient’s complete cooperation. With the traditional MRI, patients have to lie absolutely still in order to obtain accurate images. This is difficult for anxious patients and children, who may end up fidgeting. If there is movement, the images may blur and the entire scan may have to be repeated again.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |
The open MRI machine was designed to overcome these drawbacks. So, what does an open MRI look like? What is the difference between an open and closed MRI?
As the name suggests, the open MRI machine consists of an ‘open’ tube rather than a closed one. Patients do not have to lie completely within an enclosed tube. All or at least part of the patient’s body is exposed to the external environment. This tends to calm the patient and reduce feelings of claustrophobia.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
Several types of open MRI scanners have been designed. Each scanner offers some unique design features and advantages:
Wide-bore MRI machines: These are not truly open MRI systems. The aperture of the MRI machine is wider than the traditional MRI system and is usually around 70 cm in diameter. While this may be able to accommodate obese and well-built patients, it does not really overcome the other drawbacks of the traditional system, such as claustrophobia.
Semi-open scanners: The scanner is only partially open. The patient lies on an examination table. The table includes a ‘tunnel’ which has a short width. It allows part of the body (which includes the region of interest) to be completely surrounded by the magnetic field. At the same time, since the rest of the body is not confined, feelings of discomfort and claustrophobia can be reduced. For instance, if an MRI of the abdominal region is required, the patient’s trunk alone rests within the tunnel, while the head and legs stick out and are exposed to the external environment.
Open MRI scanners: Instead of lying within a cylindrical tube, the patient lies on an examination table. There are large magnets positioned horizontally above and below the examination table which generate the magnetic field required for the examination. There is plenty of open space on the sides for the patient to feel comfortable. In some models, it is also possible to tilt the magnets relative to the examining table, so that angular planes of imaging can be obtained.
Open advanced MRI: These MRI scanners were specifically designed for patients who are physically unable to lie down or greatly prefer sitting or standing. The magnetic disks are vertically positioned with some space between them for the patient to sit or stand. The other two sides remain open. Since the patient can turn at will, the design allows imaging in angular planes. Open advanced MRIs are also preferred when weight-bearing on a joint is desired during imaging.
The surface area of the magnets is smaller in an open MRI machine, primarily because the magnets are placed on two opposing sides rather than circumferentially. So, is there a difference between open and closed MRI? In terms of tesla (the unit used to measure magnetic field strength), the open MRI has a much lower value compared with traditional MRI. Most open MRIs have a value of 0.3 to 0.7 T. The more advanced open MRI scanner has a maximum value of 1.2 T. However, closed MRIs are more powerful and have magnetic fields ranging from 1.5 to 3.0 T. Most of the disadvantages of open MRI are due to its lower magnetic field:
Lower resolution of images: In the open MRI machine, the magnetic field is not as strong as it is with the traditional MRI system. As a result, the images obtained from an open MRI do not have the same quality of resolution. This is especially significant while imaging smaller body parts.
Increased time: Since the magnetic field is weaker, acquiring images can take longer than it does with traditional MRI.
360° imaging may not be possible. Since the magnets are located only above and below the patient and not all around, it may not be possible to acquire images in all the planes.
It is obvious that both closed and open MRI systems have their own advantages and disadvantages. So how do you know which system to choose? Is an open MRI as accurate as a closed MRI? You need to be able to balance the comfort level of the patient with the accuracy of images needed. In general, the following tips may be useful when determining which MRI to go with:
Patients with claustrophobia should receive preferred open MRI as they are unable to tolerate 15 minutes of confinement in an enclosed tube. If a patient gives a history of claustrophobia or expresses discomfort at the idea of an MRI scan, it may be better to offer the option of an open MRI scanner.
Very young patients may benefit from open MRI. Pediatric patients find it difficult to follow instructions and remain still. The latest models of advanced open MRI scanners also allow parents to remain with their children and calm them during the course of the scan.
Avoid open MRI if you require high resolution images. If you need to do a detailed analysis of a tissue or organ, it is advisable to go for a high-field MRI which requires a closed MRI scanner.
Avoid open MRI if you want to image small areas of the body or deep tissues. The low magnetic field of open MRI may not give sufficient details for examining small or deep body structures. In these situations, consider using a semi-open high-field system instead of an open low-field MRI.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
We have seen that the main debate in using open or closed scanners is patient comfort vs. image quality. However, image quality does not depend only on the magnetic field, which is one area where closed scanners score over open scanners. The image quality also depends on two additional factors:
The skill of the technician taking the image
The quality of the software being used
While technical skill can be learned and developed with experience, it is equally important to invest in good quality software that allows technicians and doctors to handle high-resolution MRI images correctly. Here are some of the features that your software should have:
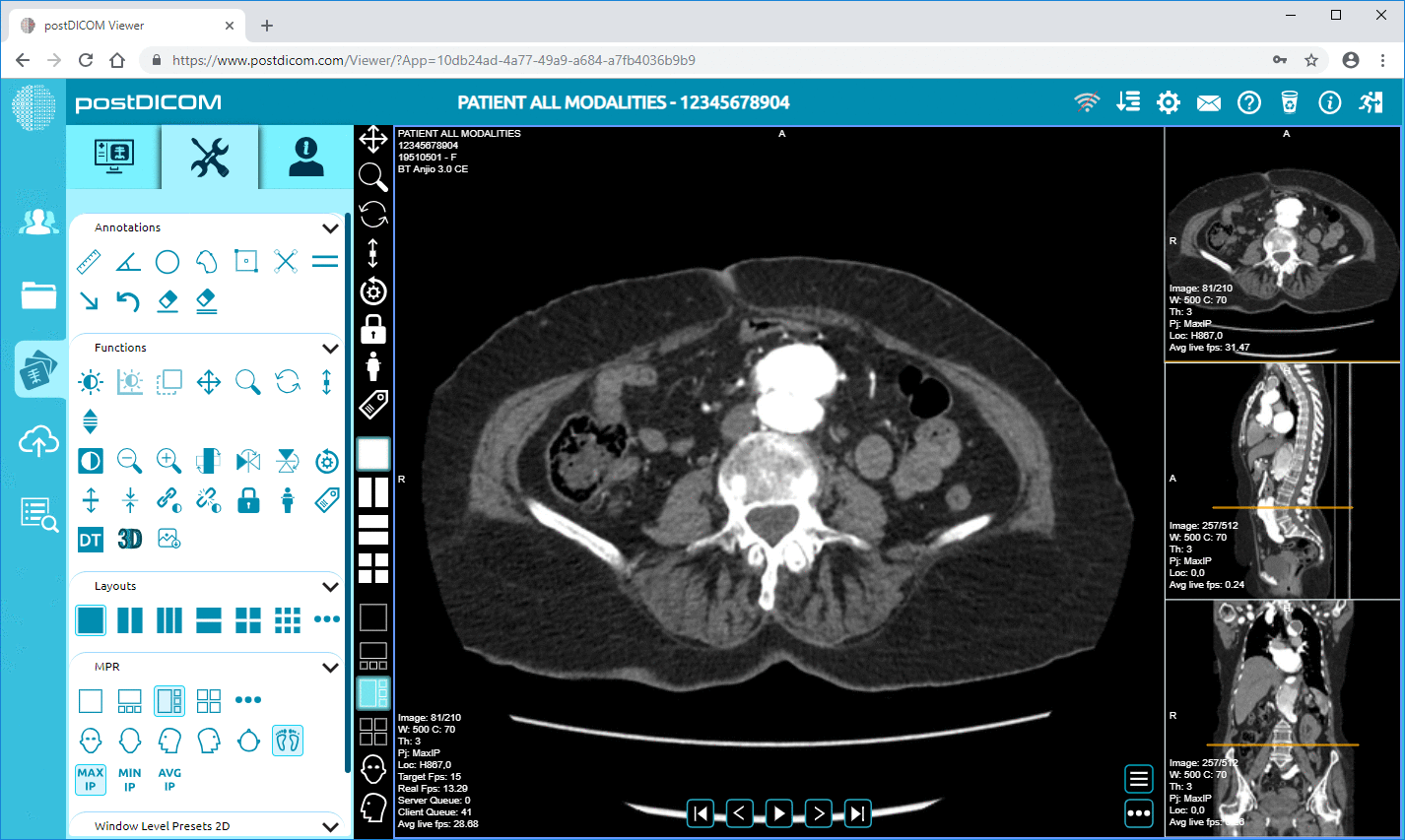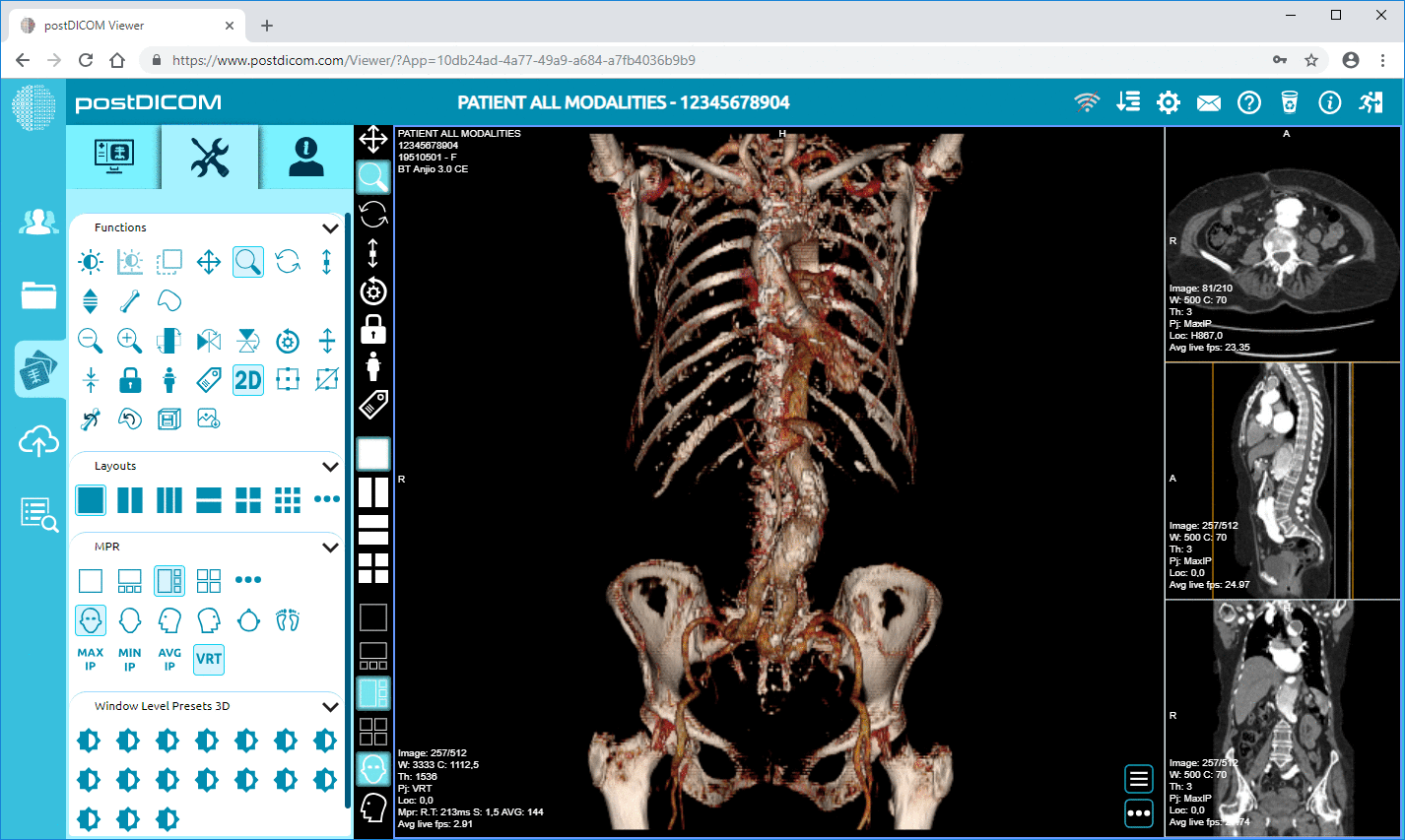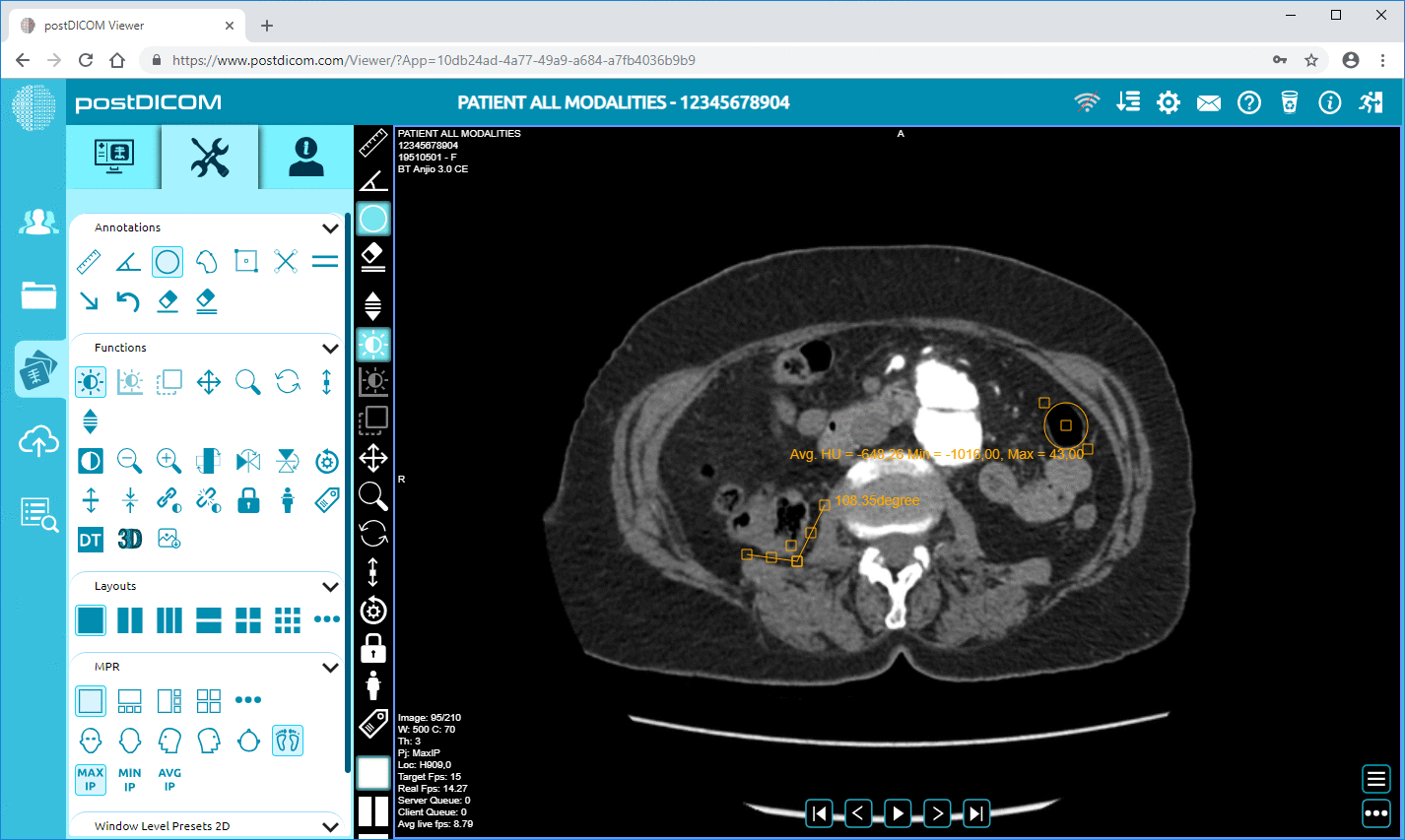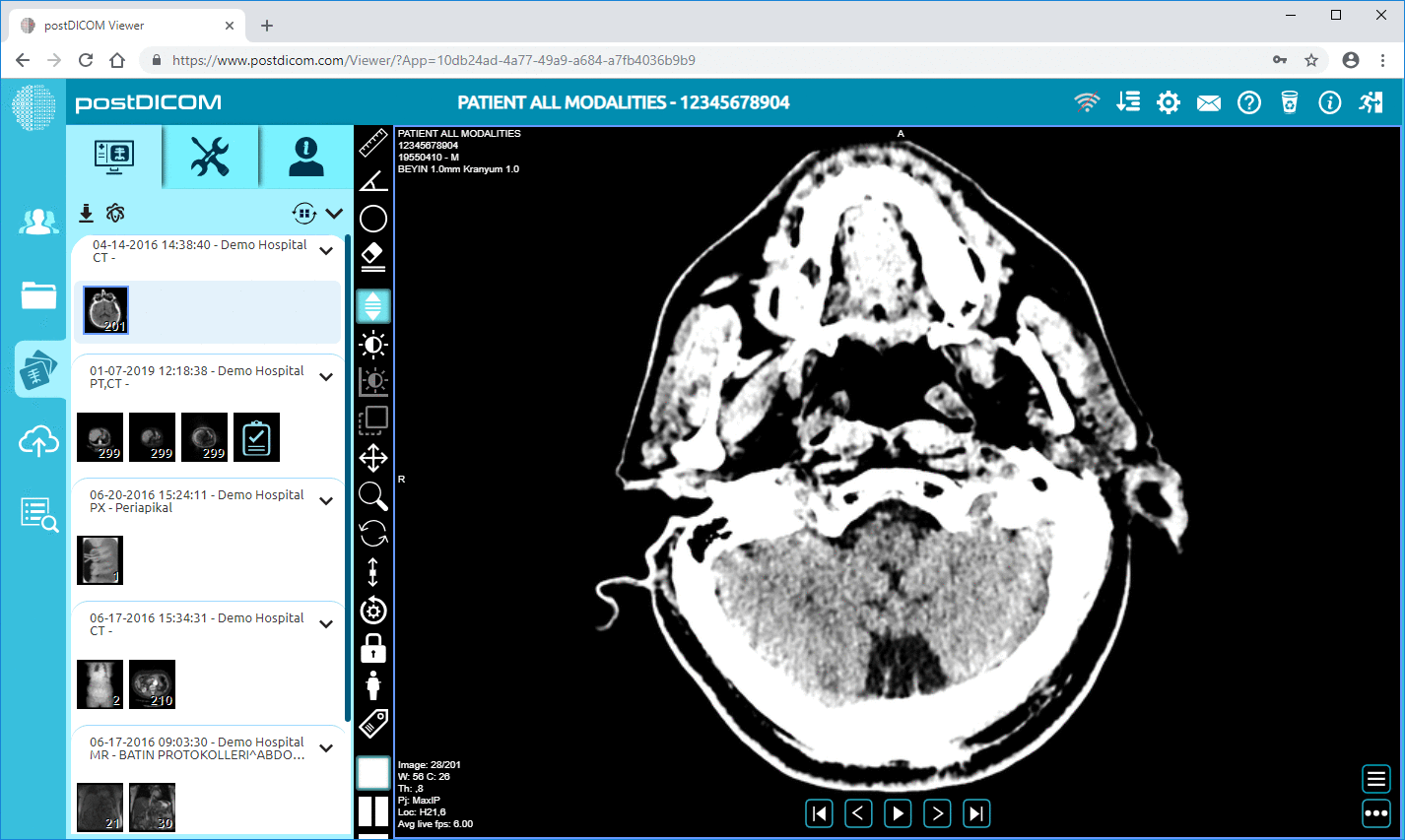
DICOM compatibility: DICOM, which stands for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine, is an internationally accepted format that enables you to view, store, retrieve, and share medical images. Since the images are of extremely high quality, they cannot be viewed using ordinary image viewers on your computer. It becomes necessary to invest in imaging software that specifically supports the DICOM format.
Basic editing tools: Your software should allow you to enhance the image by allowing you to alter its brightness, color, and contrast. It should permit you to zoom in on selected areas to study them without altering the image quality.
Advanced editing tools: Beyond basic image advancement, really good software helps you view the same images in new ways. For instance, advanced software tools can take a series of two dimensional images and convert them into a three dimensional structure. This allows the physician to have better anatomical orientation and identify any anomalies with more ease.
Storage and retrieval: Since MRI images are of high quality, they require ample storage space. Usually, each hospital has a PACS server (Picture Archiving and Communications System), which is like a virtual filing system. Patient MRI records can be stored in the PACS and retrieved when needed. It is essential for the software to be compatible with the PACS server.
Exporting and conversion: While these features are not strictly necessary for a clinical practice, it is useful if the software allows you to export images to other formats such as JPEG format. This enables use of the images in presentations and publications.
PostDICOM offers software solutions for both medical image viewing and storage. Irrespective of whether you acquire images using an open or closed MRI system, our free to try PostDICOM viewer ensures that you have an optimum image viewing experience. With all the basic and advanced editing tools available, you can extract maximum information from the MRI images. The DICOM viewer works on multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux, Mac OS and Android, so you can view these images from any device.
Storing and backing up those important MRI scans has never been easier with PostDICOM’s cloud-based PACS. With PostDICOM services, images viewed and edited in your DICOM viewer can directly be stored online and shared easily. The Cloud PACS also supports storage of clinical documents which are not in DICOM format. This ensures that the images truly become part of the patient’s medical record. Additional storage is available at a nominal cost.
To make sure that you get the best out of MRI image viewing and analysis, register for a PostDICOM account of Cloud PACS storage today!