 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
The ultrasound is an imaging technology that is even older than traditional X-ray imaging. However, it was adapted for use in the medical field much later. Its first recorded use is in obstetrics in the 1950s. Since then, the use of ultrasound has expanded to cover other areas of medicine, and ultrasound medical imaging technology has made several advances over the years. This article discusses the progress of ultrasound over time and how it is being used in healthcare today.
As the name suggests, it works by employing sound waves. Ultrasound imaging devices generate high frequency sound waves, usually between 1 to 5 MHz. These sound waves are transmitted into the body using a handheld probe. The sound waves travel uninterrupted inside the body, until they hit the interface between two tissues (for example, between muscle and bone or between fluid and soft tissue). Depending on the kind of tissue present, the sound waves may either get reflected back or continue to travel further. The waves that are reflected back (called echoes) get relayed back to the ultrasound imaging device. Based on the time of each echo’s return and the speed of sound in the tissue, ultrasound medical imaging device calculates the distance between the probe and each structure. The distance and intensity of all the echoes is transformed into a two-dimensional image which appears on the ultrasound imaging screen.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
The biggest advantage of ultrasound is that unlike most other imaging techniques, it does not use ionizing radiation. It is, therefore, safe for patient populations who are susceptible to the effects of radiation exposure, like pregnant women and children. It captures soft tissues much better than X-rays and CT scans, and is ideal for viewing internal organs. During the same sitting, multiple imaging planes can be obtained without changing the position of the patient; just moving the handheld probe suffices. In addition to the fact that it does not use radiation, another key advantage to the use of ultrasound in medical setups is the low cost. It is far less expensive than CT scans and MRI imaging.
On the other hand, traditional ultrasound cannot provide the detailed imaging accuracy that is available with advanced techniques, such as the CT scan. It cannot adequately visualize bone and hard tissues. The ultrasound imaging session takes longer than other imaging modalities. While a CT scan can be obtained in 30 seconds, an ultrasound would take 15 to 30 minutes.
A medical ultrasound imaging system can be used to visualize the structure of any of the body’s internal organs in real-time. By applying the Doppler effect (which is a change in the frequency of sound as the object moves towards/away from the source), the flow of blood through vessels can also be tracked. A few applications of ultrasound medical imaging are listed below:
Obstetrics/Gynecology: Ultrasound can be used to evaluate the female reproductive system as well as the developing fetus in the womb. This is very useful in detecting possible fetal anomalies before birth.
Abdomen and pelvic sonogram: Solid organs, such as the liver and pancreas in the abdomen or the bladder and uterus in the pelvis, may be visualized. It is difficult to look at the bowel cause abdominal gas often obstructs sound waves.
Neurosonography: It helps visualize the brain and detect anomalies in blood flow to the brain.
Vascular ultrasound: This is used to assess the amount and rate of blood flow in vessels and to detect the presence of constrictions or stenosis.
Echocardiography: This ultrasound is specifically for the heart and its major blood vessels, including the aorta and pulmonary artery.
Therapeutic applications: By using ultrasound to obtain /images of organs in real time, guided interventions can be performed. For instance, ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration involves using ultrasound to guide the needle into a deep abscess or cyst in order to aspirate its contents. The Doppler ultrasound can also be used to detect veins prior to venipuncture or to detect blood vessels prior to raising a surgical flap for reconstruction.
Manufacturers of ultrasound imaging equipment have always strived to overcome the limitations of the traditional ultrasound. This has led to several innovations. There has been an improvement in the ultrasound imaging system itself, including better hardware and transducer systems. Ultrasound diagnostic imaging system manufacturers have worked hard to achieve improvements in the acquisition, storage and interpretation of ultrasound /images. Some of the notable advancements in ultrasound imaging that have led to significant advancements in healthcare are discussed below:
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM /images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |
Digitalization: Just like radiographs, ultrasound acquisition has moved into the digital era. As compared to conventional analog ultrasound, digital ultrasound diagnostic imaging system is more reliable and tends to produce better /images. This is because the digital ultrasound has better features, which include the following:
Digital beam production: Ultrasound diagnostic imaging system manufacturers have introduced devices in which the sound wave beam can be controlled by digital means. Controlling the image beam can improve spatial resolution and reduce artefacts. This improves the image contrast.
Improved signal-noise ratio and signal acquisition: These allow for better transmission and reception of the sound wave. This leads to a better image display.
Better storage and archiving: Digital /images are automatically stored in the ultrasound imaging system. Archiving /images is also made easier because it can be done electronically. This means that there is a reduced likelihood of misplacing patients’ records.
Portability: The ability to pack large amounts of information on to small microchips has allowed the once bulky ultrasound devices to shrink in size. This allows the ultrasound imaging equipment manufacturer to provide an important advantage to healthcare professionals—portability. New ultrasound devices are handheld, and can be carried by the physician easily to different examination rooms and to the operation theatre. Handheld devices often contain a multipurpose ultrasound imaging system, which may be used for any purpose. For instance, screening for fluid collection in the abdomen, analyzing blood flow, and detecting fetal heart beats can be done with the same device.
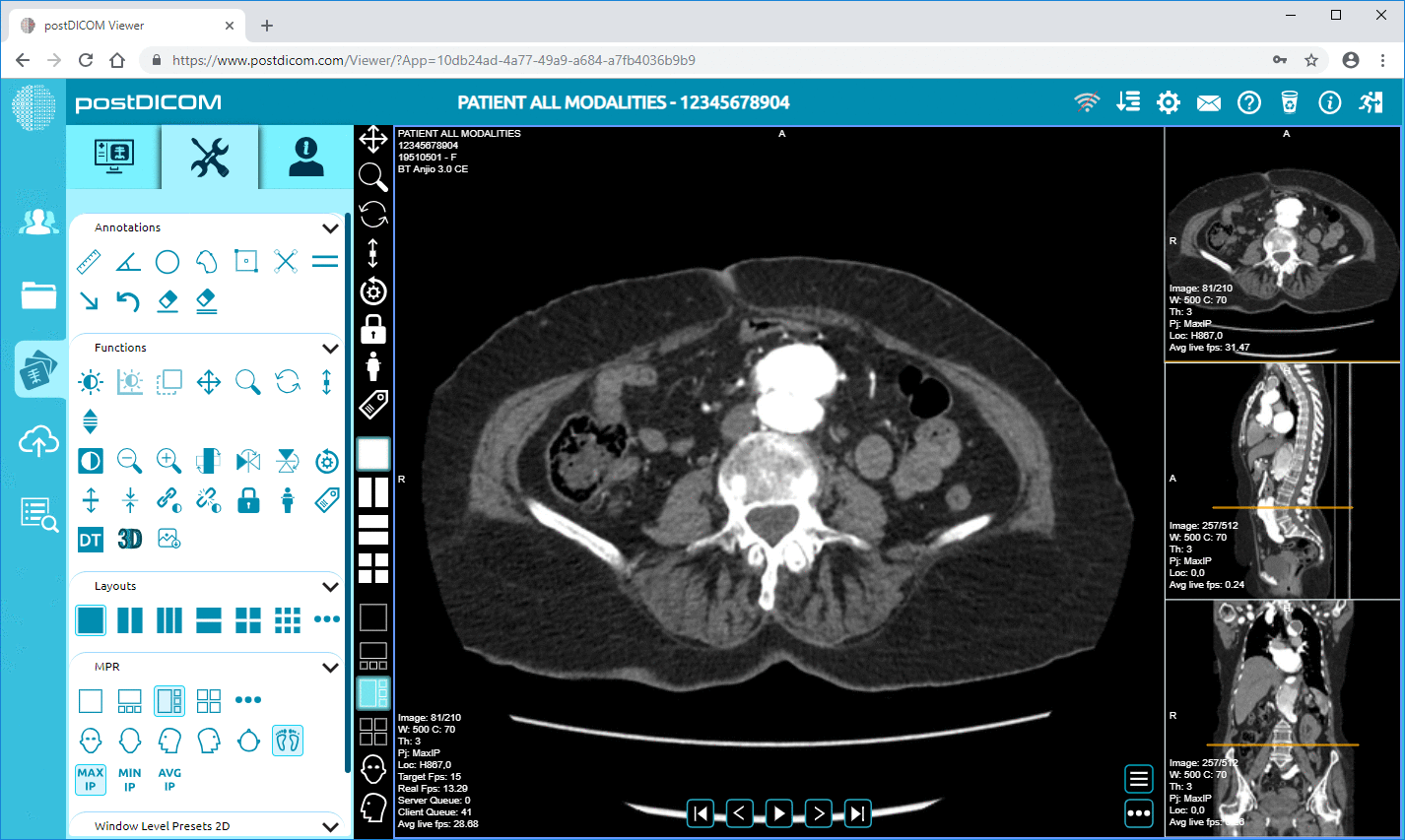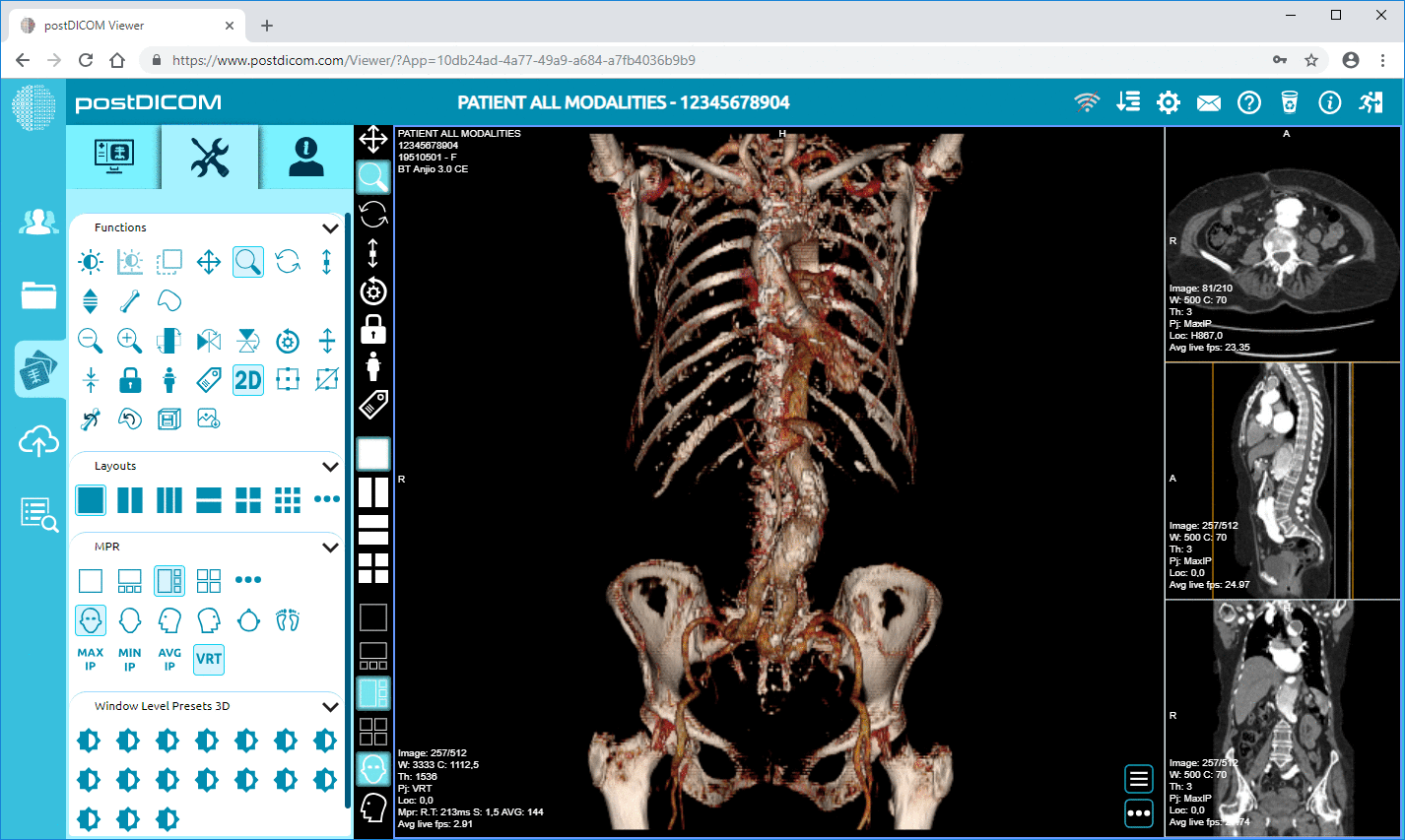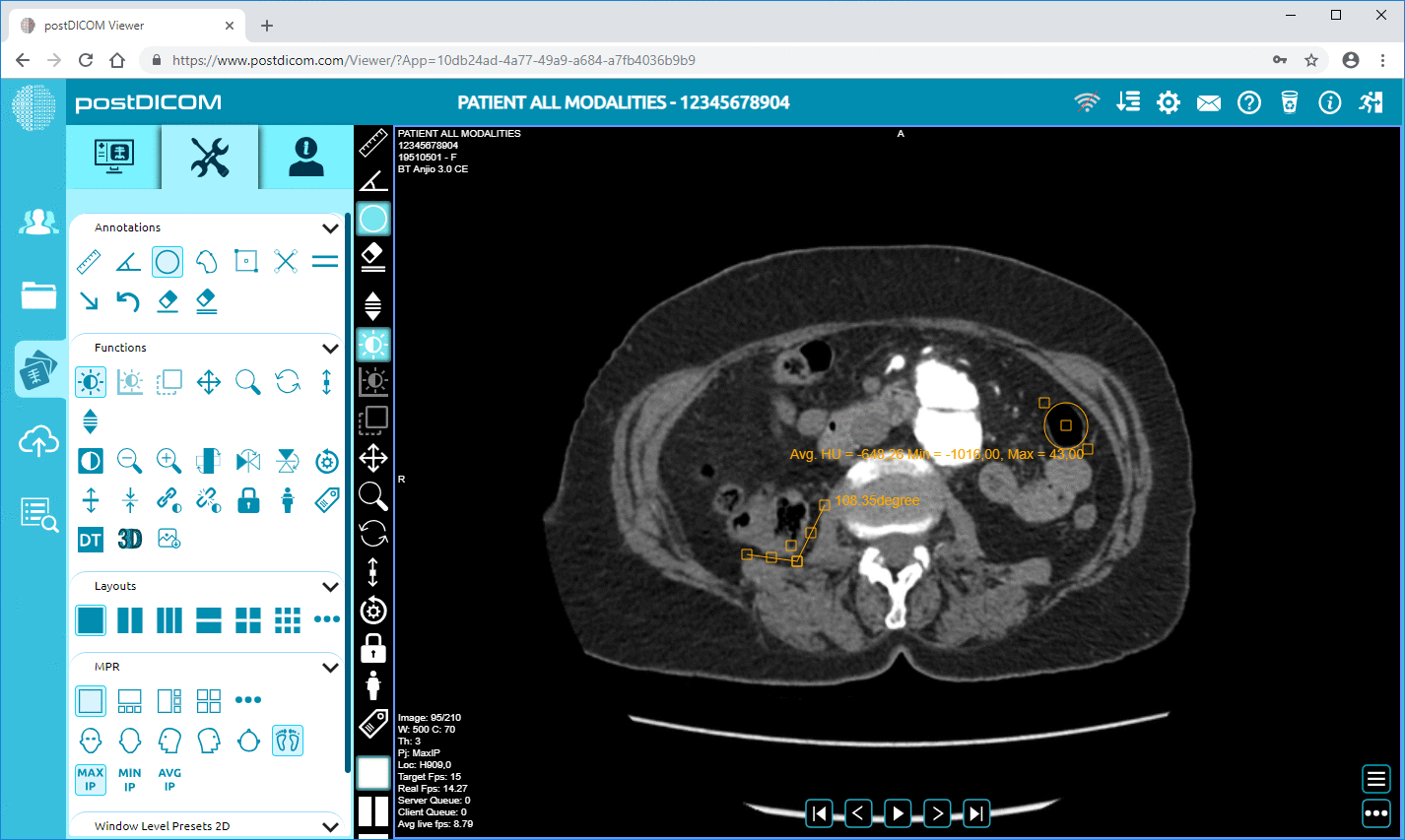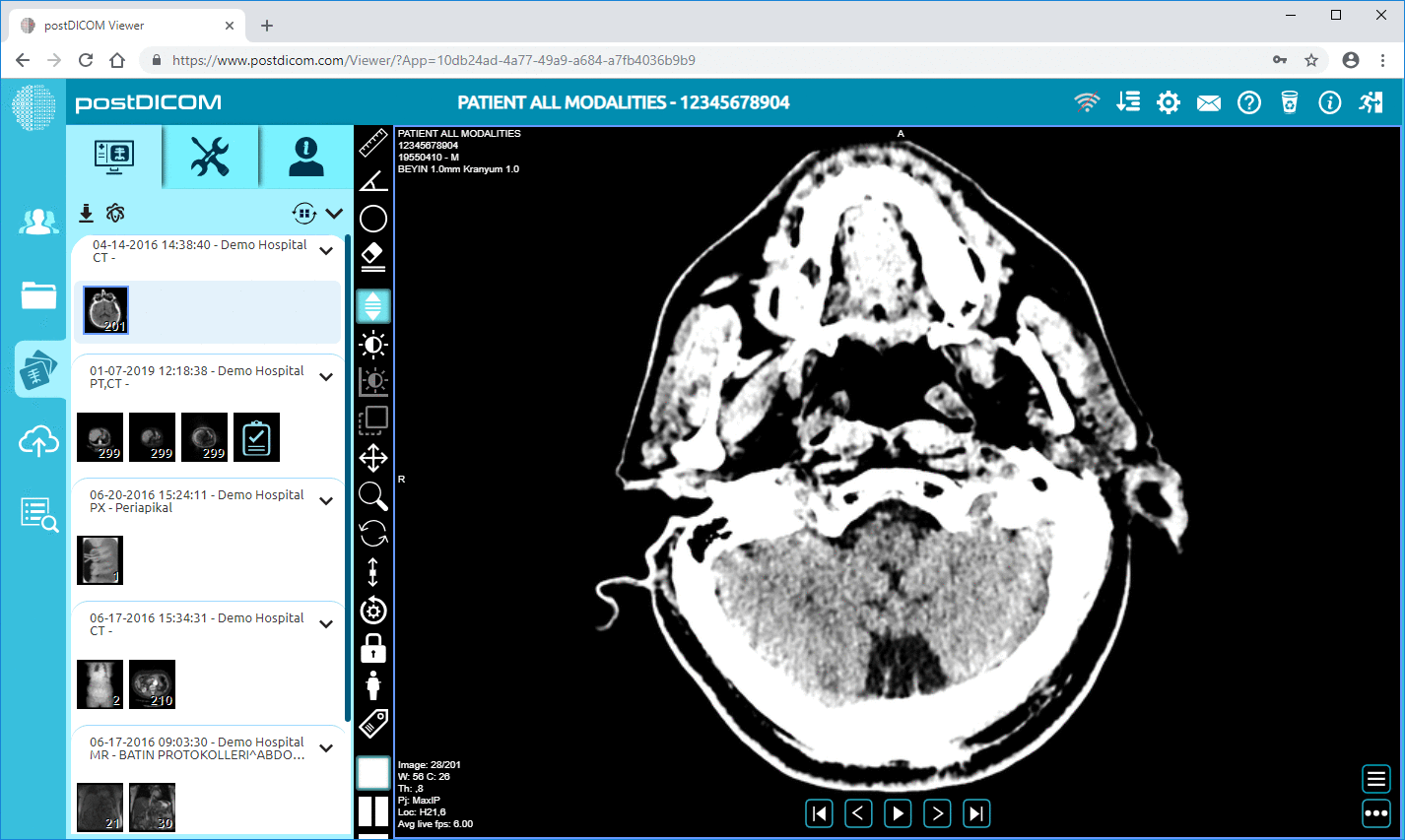
3D and 4D ultrasounds: The main limitation of the traditional ultrasound is its two dimensional nature. The physician needs to understand the structural and spatial relationships between various anatomical structures and must attempt to ‘assemble’ the /images in their mind for proper orientation. Nowadays, however, 3D ultrasound /images can be obtained by reconstructing a series of two dimensional /images. The main advantage of this technique is that it can aid in volumetric measurements. For instance, with 3D echocardiography, quantification of atrial and ventricular volume can be done. Three dimensional visualization of anatomy can also help diagnose conditions such as valvular heart diseases.
4D ultrasound has also been developed as part of the medical ultrasound imaging system. In 4D imaging, the physician can visualize the reconstructed /images in the same way as in 3D ultrasound /images, but they can also evaluate function in real time. For example, by using 4D ultrasound in obstetrics, it is possible with 4D imaging to visualize the fetus opening its eyes or sucking on a thumb.
Methods to evaluate the physical properties of tissues: Conventionally, ultrasound and other diagnostic imaging techniques for tissues allow for inspection and not palpation. So while we can ‘see’ the tissue or organ under study, we cannot ‘feel’ it. However, advancements in ultrasound medical imaging methods have made this possible:
Elastography: Certain diseases can cause a change in tissue elasticity. The degree of elasticity or stiffness of tissues can be measured through the modulus of elasticity (Young’s modulus). This is done by applying compression on the tissues through the transducer and measuring the degree of distortion of the tissue under this compressive force. This can be applied for various conditions. For example, it can be used to detect fibrosis of the liver, analyze the cause of enlarged lymph nodes, and identify thyroid nodules. It can also be used to screen for tissue malignancy.
Vibro-acoustography: This technique involves the use of two ultrasound beams to focus on the region of interest. Both the beams have differing frequencies and tend to interfere with each other. This causes the object of interest to vibrate at a low frequency. The vibration is captured by a microphone and converted into an image. This is useful for detecting harder masses within soft tissue, like calcified masses. For instance, salivary stones or breast microcalcifications can be detected using this technique.
Contrast ultrasound: Contrast agents have been successfully applied in other imaging techniques, such as CT scans and MRI imaging. Contrast agents are typically radioactive dyes that are injected into the blood vessels to help monitor the pattern of blood flow through them. Contrast agents for ultrasound were introduced quite recently. These are not radioactive dyes, but microbubbles of high molecular weight gases encapsulated within an elastic shell. In a normal ultrasound, blood vessels cannot be distinguished from the surrounding normal tissue easily. However, when microbubbles are introduced into circulation, the gas bubbles oscillate in response to the sound waves. Therefore, the echo received from the blood vessels may be distinguished from the surrounding tissue. Today, microbubbles as small as 10 µm in diameter are available. Due to their microscopic size, they can even cross capillary beds, which allows physicians to have a detailed view of the vascular network. This technique is particularly useful in echocardiography and can be used to assess left ventricular function and blood flow through the great vessels.
Endoluminal ultrasound: The development of smaller ultrasound transducers has allowed their inclusion in endoscopic devices. Therefore, it is possible to obtain better quality /images of internal organs with endoscopes. Endoluminal ultrasound has been used for guided biopsies of lesions located in areas such as the tracheobronchial tree, urogenital tract, or biliary tract. It has also been used in the intravascular region to guide procedures such as angioplasty.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
The traditional transducer probe (which makes use of piezoelectric crystals) may be on its way out. Researchers and entrepreneurs have found a way to incorporate artificial intelligence on to a microchip, which forms the new transducer probe. This sleek, handheld probe can simply be attached to the user’s smartphone and /images can be viewed on the device. The “ultrasound on a chip” brings down hardware costs and can also be used to monitor patients at home.
With today’s modern digital ultrasound diagnostic imaging system, physicians also require high quality image viewing software so that the ultrasound /images can be viewed with high resolution and clarity. With the advent of the DICOM standard, all acquired digital ultrasound /images are stored in the DICOM format. So, the software must be capable of reading and editing /images in this format. An ideal software would also allow physicians to obtain information from the /images through various techniques, such as volume rendering and reconstruction. The software would enable image fusion. This means that the ultrasound image can be superimposed on another imaging modality, such as the CT scan. This allows medical experts to gain anatomical orientation as well as functional assessment at the same time.
It is also essential for the image viewing software to be combined with an equally efficient storage system. This is because digital ultrasound /images need ample storage space, and you would need a server that allows you to accommodate several imaging files from patients. Such a storage system can allows you to retrieve those files from the archive when required.
PostDICOM offers a free multimodality online DICOM viewer, which serves all the purposes discussed above. It comes with advanced features such as volume rendering, 3D reconstruction, and length, density and angle measurements. You can save images to retrieve or view them later! Compatible with Windows, Mac OS, Linux and Android systems, you can view your ultrasound /images from any device, at any time. Signing up to use PostDICOM’s online viewer is hassle-free. So get your free DICOM viewer today!