Over a century has passed since Wilhelm Röntgen’s revolutionary discovery of X-rays. This breakthrough enabled visualizing the body’s inner workings, though early film-based methods faced substantial limitations.
As medical imaging advanced from analog to digital platforms, new obstacles arose – from data silos to workflow inefficiency. Yet solutions were essential with medical discovery predicated on sharing precise scan results.
The Picture Archiving and Communications System (PACS) emerged as the catalyst for change by securely consolidating study storage, distribution, and display. We chart PACS’ transformation from conceptual inception to widespread integration with hospital systems benefiting top North American institutions.
Learn how cloud-based iterations with enhanced diagnostics via algorithms are transforming radiological capabilities.
Join us on an imaging technology tour that depicts where we’ve been, offerings in the present, and a peek into the future. When images freely flow, patient trajectories can shift.
The story of radiology began in 1895 with Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen's groundbreaking discovery of X-rays, a moment that forever changed the medical world. This discovery opened the door to the internal visualization of the human body, a previously inconceivable concept.
Read more to know the future of medical imaging technology.
In the early 20th century, X-ray technology rapidly became integral to medical diagnostics. The primary medium for capturing these images was photographic film, a method that dominated for nearly a century.
Film-based radiology involves exposing a film to X-rays, which, after chemical processing, produce a static image of the body's internal structure. This revolutionary method allowed doctors to enter the human body without invasive surgery.
For North American medical businesses in the early and mid-20th century, film-based radiology was a significant advancement, offering a new dimension to patient care and diagnosis.
Despite its revolutionary nature, film-based radiology was not without its challenges, many of which impacted the efficiency and effectiveness of early medical practices:
Storage Issues: Film radiographs required physical storage space, which became a significant issue as the volume of X-rays grew. Hospitals and medical facilities had to dedicate entire rooms or buildings to store these films, increasing operational costs and space constraints.
Physical Degradation: Over time, films could degrade, suffer from wear and tear, or become damaged due to environmental factors like humidity and temperature. This degradation risked the loss of critical patient data and historical medical records.
Accessibility and Sharing: Retrieving and sharing film-based radiographs was a time-consuming process. If a patient needed to consult with multiple specialists, the physical films had to be manually transported, leading to delays in diagnosis and treatment. For medical businesses, this meant slower workflows and increased logistical challenges.
Environmental Concerns: The chemical processing of films was time-consuming and environmentally harmful. The toxic chemicals used required careful disposal, adding another layer of complexity to film-based radiology.
The reliance on film-based imaging had a profound impact on early medical practices and patient care:
Diagnostic Delays: The time required to develop, store, and retrieve films could lead to delays in diagnosis, impacting patient care, especially in urgent cases.
Limited Collaboration: The difficulty in sharing films hindered collaborative efforts among healthcare professionals, often limiting the scope of patient care to the expertise available within a single facility.
Cost Implications: The costs associated with film production, storage, and disposal were significant. For medical businesses, especially smaller practices, these costs could be a substantial portion of their operating expenses.
Patient Experience: The physical limitations of film-based radiology meant that patients often had to wait longer for results and endure multiple exposures if films were lost or damaged.
The radiology landscape began a significant transformation with the advent of digital imaging in the late 20th century. This shift marked a pivotal moment, as it promised to address many of the limitations inherent in film-based methods.
Digital imaging in radiology first emerged in the 1980s, introducing a new era where images could be captured, stored, and viewed electronically.
The initial foray into digital radiology involved techniques like Computed Radiography (CR) and, later, more advanced methods such as Digital Radiography (DR). CR used a cassette-based system where the imaging plate contained photostimulable phosphor, which was then read by a scanner to create a digital image.
On the other hand, DR utilized a more direct approach, capturing images electronically and immediately rendering them in a digital format.
These early digital techniques offered several advantages over traditional film:
Enhanced Image Quality and Manipulation: Digital images provided clearer details and could be easily enhanced for better visualization, aiding in more accurate diagnoses.
Reduced Radiation Exposure: Digital systems were more sensitive to X-rays, meaning lower doses could be used, benefiting patient safety.
Instant Access and Distribution: Digital images could be viewed immediately after capture and easily shared electronically with other healthcare professionals, facilitating quicker, more collaborative decision-making.
Efficient Storage and Retrieval: Digital images require no physical storage space and can be retrieved quickly and easily, significantly improving workflow efficiency.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Time: While the initial investment was higher, digital systems reduced ongoing costs related to film processing, storage, and disposal.
Despite these advantages, the transition to digital radiology was not without its challenges:
High Initial Investment: The cost of digital radiology equipment was substantially higher than traditional film-based systems, posing a significant barrier for many medical businesses, especially smaller practices.
Learning Curve and Training Needs: The shift to digital required significant training for radiologists and technicians. Adapting to new technology and leaving familiar processes behind was a considerable hurdle.
Technical Limitations and Reliability Concerns: Early digital systems had limited resolution and image quality compared to mature film-based methods. There were also concerns about the reliability and longevity of digital technology.
Data Storage and Management: The shift to digital has introduced new challenges in data storage and management. Medical businesses had to invest in digital storage solutions and manage larger volumes of data.
Skepticism Among Professionals: Many radiologists and medical professionals were initially skeptical about the efficacy and reliability of digital imaging. This skepticism was rooted in their unfamiliarity with the new technology and deep trust in the established film-based methods.
For North American medical business owners, transitioning to digital imaging was complex, weighed down by financial, operational, and cultural considerations.
However, as technology advanced and the benefits became more apparent, the medical community gradually began to embrace digital radiology, setting the stage for a new era in medical imaging.
This transition promised enhanced patient care and heralded a significant change in how medical businesses operated and managed radiological services.
The Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) represents a technological revolution in medical imaging. Initially conceptualized in the early 1980s, PACS is a medical imaging technology that provides economical storage, rapid retrieval, and convenient access to images from multiple modalities (source machines).
Essentially, PACS breaks down the physical and time barriers associated with traditional film-based image retrieval, distribution, and display.
PACS emerged as a solution to the growing challenges of film-based and early digital imaging systems. For film-based methods, PACS offered a way to digitize images for easy storage and access, eliminating the need for physical space and reducing the risks associated with film degradation.
In the realm of early digital imaging, PACS addressed issues of image distribution and accessibility. It allowed for the centralized storage of digital images and enabled healthcare professionals to access them from various locations, facilitating better collaboration and efficiency in patient care.
Several vital technological advancements drove the growth and development of PACS:
Advancements in Digital Imaging: The evolution of digital imaging technologies, such as CR and DR, provided higher-quality images conducive to digital storage and retrieval. This advancement was crucial in the initial stages of PACS development.
Improvements in Computer Technology: The rapid advancement in computer technology, including increased processing power, larger storage capacity, and improved display monitors, made it feasible to store and view large volumes of high-resolution images, a fundamental requirement of PACS.
Development of Network Systems: The expansion and enhancement of network systems, including the advent of the Internet and intranet technologies, facilitated the efficient transmission of digital images across different hospital departments or geographical locations. This capability was essential for the widespread adoption of PACS.
Standardization Efforts: The development of standards like DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) played a pivotal role in the growth of PACS. DICOM provided a universal protocol for the handling, storing, printing, and transmitting medical images, allowing different systems and devices to communicate seamlessly.
Integration with Hospital Information Systems (HIS) and Electronic Health Records (EHR): The ability to integrate PACS with other hospital systems, such as HIS and EHR, streamlined the workflow, making patient data and images readily available within a unified system.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
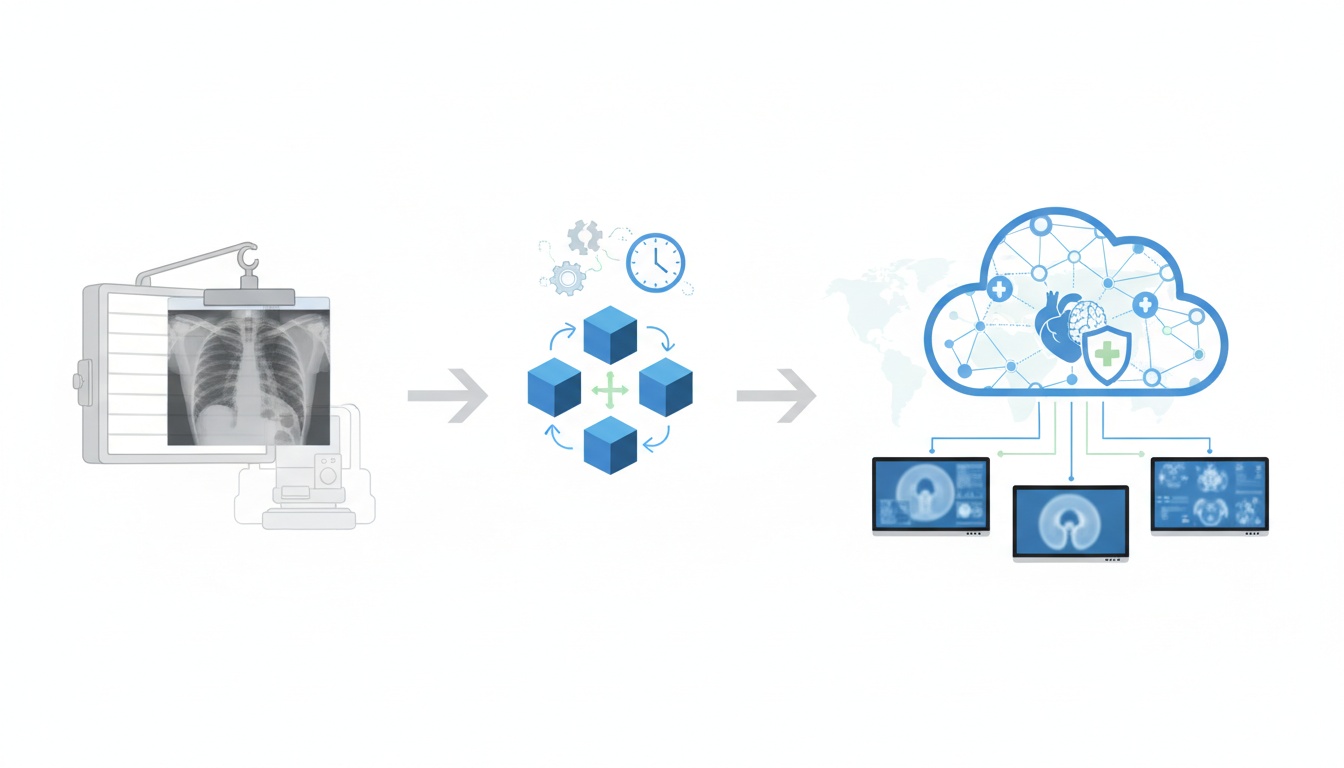
The introduction of PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) in radiology marked a paradigm shift in how medical images were managed, stored, and shared.
This technology revolutionized three key areas: data storage, transmission, and presentation.
Data Storage: PACS replaced the need for physical film storage with digital storage solutions. This shift saved physical space and enhanced the longevity and integrity of medical images. Digital storage systems, often employing advanced solutions like cloud storage, allow vast data to be stored securely and accessed easily.
Transmission: PACS enabled the rapid transmission of medical images across various departments within a healthcare facility and even between different locations. Advancements in network technology facilitated this capability, allowing for the quick and secure sharing of patient data and images, which is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Presentation: With PACS, radiologists and other medical professionals could view images on high-resolution monitors, offering greater detail and clarity than traditional film. The ability to manipulate these images (zoom, rotate, adjust brightness/contrast) further enhanced diagnostic capabilities.
The adoption of PACS brought numerous benefits to medical businesses, including:
Efficiency: PACS significantly streamlined the workflow in radiology departments. The time taken for retrieving, sharing, and viewing images was drastically reduced, leading to quicker diagnosis and treatment planning.
Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial setup cost for PACS could be high, the long-term savings were substantial. Reductions in film, chemical processing, storage space, and transportation costs contributed to these savings.
Improved Diagnostic Capabilities: The enhanced image quality and manipulation capabilities provided by PACS led to more accurate diagnoses. Additionally, the ability to easily compare current and past images improved the quality of patient care.
Enhanced Collaboration: PACS facilitated better collaboration among healthcare professionals. Specialists could access and review images remotely, leading to more comprehensive and coordinated patient care.
Several North American medical facilities have successfully implemented PACS, demonstrating its transformative impact:
Johns Hopkins Hospital: This renowned institution implemented PACS and observed a significant improvement in radiology service delivery. The system enabled faster turnaround times for radiological reports and improved radiologists' efficiency by allowing them to work remotely.
Mayo Clinic: Known for its innovative approach to healthcare, Mayo Clinic adopted PACS and integrated it with its EHR system. This integration resulted in a seamless workflow, where clinicians could access patient images and records simultaneously, leading to more informed decision-making and patient care.
Massachusetts General Hospital: As one of the early adopters of PACS, this hospital saw a drastic reduction in the use of film, leading to cost savings and a decrease in environmental impact. The ability to quickly access historical patient images also enhanced their research capabilities.
The Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) has evolved significantly since its inception, adapting to the ever-changing landscape of medical technology.
Modern PACS solutions are not just storage and communication tools but comprehensive, integrated systems that enhance every aspect of radiological practice. Key capabilities and features include:
Advanced Image Processing: Modern PACS offers sophisticated image processing tools, allowing for enhanced visualization, 3D reconstructions, and detailed analyses that were impossible with earlier systems.
Interoperability: Today's PACS is designed to integrate seamlessly with various hospital information systems (HIS), electronic health records (EHR), and other diagnostic tools, ensuring a unified workflow and centralized access to patient data.
Cloud-Based Solutions: Many PACS now leverage cloud technology, offering scalable storage solutions, enhanced data security, and remote access to images and reports from any location.
Mobile Access: With the advent of mobile technology, PACS can now be accessed through smartphones and tablets, allowing healthcare professionals greater flexibility and immediate access to patient data.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and machine learning algorithms into PACS has begun to transform diagnostic radiology, aiding in quicker and more accurate image interpretation.
In the current healthcare environment, PACS plays a central role in medical workflows and patient care:
Efficient Workflow Management: PACS streamlines the entire radiology workflow, from image acquisition to interpretation and reporting. This efficiency reduces patient wait times and accelerates the diagnostic process.
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: The high-quality imaging and advanced analytical tools provided by modern PACS contribute to more accurate diagnoses, leading to better patient outcomes.
Collaborative Care: PACS facilitate easier collaboration among healthcare professionals, regardless of their location. This capability is particularly crucial in complex cases requiring multidisciplinary input.
Patient Engagement: Some PACS now offer portals where patients can access their images and reports, fostering greater transparency and engagement in their healthcare journey.
Compliance with regulatory standards is a critical aspect of PACS:
HIPAA Compliance: In the United States, compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is essential. Modern PACS ensure the security and confidentiality of patient information, adhering to HIPAA regulations.
DICOM Standards: Compliance with the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard ensures imaging equipment and PACS interoperability. This standard allows for the seamless exchange and management of medical images and related data.
Other Regulatory Standards: PACS must also comply with other national and international standards, ensuring they meet the highest levels of quality and safety.
The medical imaging landscape has been radically reshaped since the advent of PACS, enabling enhanced diagnostics and multidisciplinary collaboration. As this technology advances in sync with AI and cloud capabilities, so will patient care through early intervention and personalized treatment plans.
Stay abreast of the newest features and continual upgrades PACS now regularly offers for North American medical businesses. Consider how expanded potentials can augment workflows, research endeavors, and patient experiences via portals on personal devices. Though optimal integration requires financial investment, recognize that efficiency gains and elevated standards of care translate to lives impacted.
Look back at the origins of X-ray film that laid the groundwork for digitization. With patient data now integrated, accessible, and equipped for machine learning analysis, the future is undeniably bright. PACS has redefined radiology by conquering previous obstacles - transforming your practice for the better.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |