
Telemedicine has rapidly moved from niche to mainstream, bringing healthcare directly to people instead of the reverse.
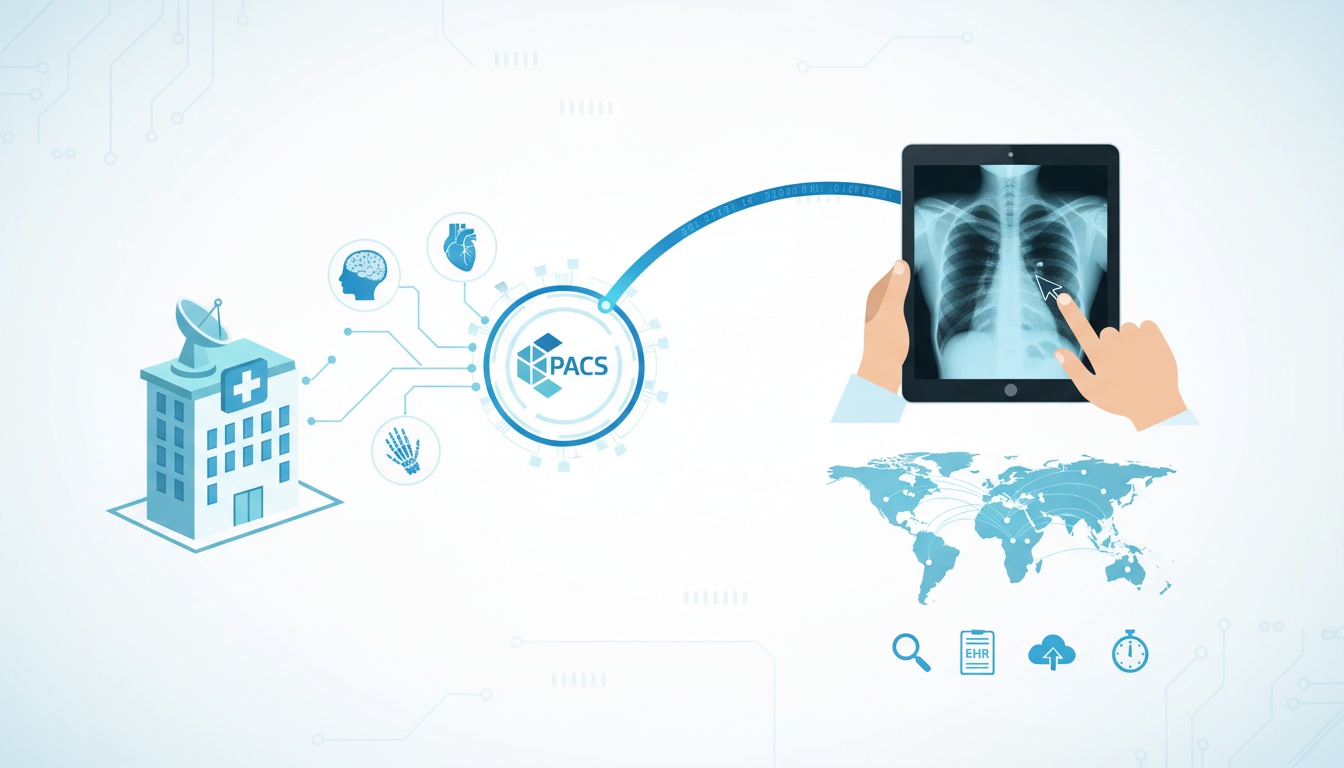
Yet diagnosing from afar hinges on accessing imaging studies with clarity. This is where Picture Archiving and Communications Systems (PACS) bridges the physical divide. PACS securely consolidates medical images to coordinate care and empower radiologists across vast distances.
We chart the evolution of this critical technology, which provides the backbone for remote consultations.
See how seamless integration with electronic records alongside diagnostic tools fosters efficient diagnoses unconstrained by geography. From case studies of mobile PACS revitalizing care post-disasters to pandemic workflows managing infection surges, the systems’ crisis stabilization roles come to light.
Optimized PACS in telehealth could unlock healthcare access for underserved communities by virtually transporting practitioners to a patient's side. Join us as we detail the strategy for implementation success and reveal the diagnostic possibilities.
Telemedicine, once a niche field within healthcare, has undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving into a vital component of modern medical practice, including treating chronic diseases and epidemics.
Its journey began several decades ago, leveraging early communication technologies to provide healthcare services over a distance. Initially, it primarily connected remote or rural populations with medical specialists in urban centers.
However, with the advent of the internet and digital communication tools, telemedicine has exponentially expanded its reach and capabilities.
Today, telemedicine encompasses a broad spectrum of services, from virtual consultations and remote patient monitoring to telediagnostics and e-prescriptions. Integrating advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and mobile health apps has further enhanced its scope and efficiency.
In the current healthcare landscape, telemedicine is not just an alternative but often a preferred mode of healthcare delivery, offering convenience, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility.
Recent global health crises, notably the COVID-19 pandemic, have acted as catalysts, accelerating the adoption and acceptance of telemedicine.
The necessity of social distancing and the strain on traditional healthcare systems have led both patients and providers to embrace remote healthcare services rapidly.
Telemedicine proved invaluable in offering continued medical care while minimizing the risk of virus transmission. It also demonstrated its potential in managing large-scale health emergencies, providing critical support in screening, monitoring, and managing patients.
At the heart of modern radiology lies the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), a technology that has become indispensable in the digital age.
PACS is a medical imaging technology that provides economical storage and convenient access to images from multiple modalities. It eliminates the need for manually filing, retrieving, or transporting film jackets, a significant limitation in the era of film-based imaging.
The core functionalities of PACS include capturing, storing, retrieving, and sharing radiological images electronically.
PACS is not just a standalone system; it is a comprehensive solution that integrates seamlessly with various aspects of telemedicine. This integration is crucial in a healthcare landscape where the boundaries between medical services are increasingly blurred.
PACS works with other telemedicine technologies, such as Electronic Health Records (EHR) and teleconsultation platforms, to provide a cohesive and efficient patient care experience.
For instance, radiologists who review an X-ray or MRI scan stored in PACS can easily share their findings with other specialists through telemedicine platforms, facilitating collaborative diagnosis and treatment planning.
The role and benefits of PACS in storing, managing, and transmitting radiological images are multifaceted.
Firstly, it provides a centralized repository for all imaging data, making it easily accessible to authorized personnel. This centralized storage is not just a convenience; it is a critical component in ensuring the continuity and consistency of patient care.
Secondly, PACS manages these vast datasets efficiently, ensuring quick and reliable image retrieval. This efficiency is particularly vital in emergency situations where time is of the essence.
Moreover, PACS plays a pivotal role in transmitting these images. In telemedicine, the ability to securely and swiftly transmit high-quality images across different locations is invaluable. It allows radiologists and other medical professionals to provide remote consultations and diagnostics, breaking down geographical barriers to healthcare access.
For medical businesses in North America, this capability is not just a technological advancement; it represents an opportunity to expand their reach and impact, especially in remote or underserved areas.
Integrating PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) into remote diagnostics has transformed radiology and telemedicine.
PACS enables radiologists and medical professionals to access and interpret medical images from virtually anywhere, breaking down the geographical barriers that once limited healthcare delivery. This capability is particularly crucial in remote diagnostics, where timely access to medical imaging can significantly influence patient outcomes.
One of the most significant advantages of PACS in telemedicine is its ability to enable remote consultations and diagnoses. Radiologists can review and interpret medical images sent from distant locations, providing their expertise without needing physical presence.
This aspect of PACS has been a game-changer, especially in rural or underserved areas with limited access to specialized radiological expertise.
For instance, a small clinic in a remote area can send digital images to a radiology center in a city, where specialists can quickly analyze the images and provide a diagnosis, often within the same day.
Several case studies highlight the effectiveness of PACS in remote diagnostics. For example, a healthcare network in rural North America implemented PACS across its facilities, allowing for the centralization of radiology services.
This implementation enabled radiologists located in a central hub to provide timely and accurate diagnoses to patients across various remote clinics, significantly improving the network's efficiency and patient care quality.
Another example involves a tele-radiology service that utilizes PACS to offer around-the-clock radiological consultations. Hospitals without 24-hour in-house radiology support can send images to this service, ensuring patients receive timely diagnoses, regardless of the time or day.
The impact of PACS on the quality and speed of remote medical diagnostics cannot be overstated. With PACS, the time to deliver radiological reports has drastically reduced, leading to quicker treatment decisions and better patient outcomes.
The quality of diagnostics has also improved, as PACS allows for better image resolution and manipulation, aiding radiologists in making more accurate interpretations.
Moreover, PACS has a significant role in reducing diagnostic errors. The ability to access previous images and reports for comparison enhances the accuracy of diagnoses, especially in complex cases.
This aspect is particularly beneficial in chronic disease management, where tracking the progression of a condition is crucial.
Global health crises, such as pandemics, have underscored the critical role of Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) in managing radiology services.
Healthcare systems are often overwhelmed during such times, and the need for efficient, remote medical services becomes paramount. In this context, PACS emerges not just as a tool for convenience but as a necessity for continuity of care.
One of the most significant challenges during health crises like pandemics is the limited in-person visits to healthcare facilities. PACS plays a vital role in this scenario by facilitating the remote access of medical images and reports.
This capability ensures that radiologists and physicians can continue to provide diagnostic services without being physically present at a hospital or clinic.
For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many radiologists shifted to remote work, relying on PACS to access patient scans and provide timely diagnostics, thereby maintaining the continuity of essential radiology services.
PACS has proven to be an essential component in healthcare delivery in real-world crisis situations. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals and medical centers utilized PACS to manage the surge in chest X-rays and CT scans, which were crucial for diagnosing and monitoring the disease.
PACS enabled the rapid sharing of these images with specialists, regardless of location, facilitating swift decision-making in treatment plans.
Another scenario where PACS proved invaluable was in the aftermath of natural disasters. In such situations, healthcare infrastructure can be severely disrupted. PACS allows for the quick setup of temporary, remote radiology services, ensuring that medical imaging services remain uninterrupted.
This aspect was particularly evident in areas affected by hurricanes or earthquakes, where mobile units equipped with PACS provided critical radiological services amidst the chaos.
PACS also enhances remote collaboration among healthcare professionals. During health crises, when quick and coordinated responses are necessary, PACS enables different specialists to review and discuss medical images in real time, fostering a collaborative approach to patient care.
This collaboration is crucial, especially when dealing with novel or rapidly evolving health challenges, where shared expertise can significantly impact patient outcomes.
Integrating Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) with telemedicine platforms presents a unique set of challenges. These challenges span technical, regulatory, and security domains, each requiring careful consideration and strategic planning.
One of the primary technical challenges lies in ensuring seamless compatibility between PACS and various telemedicine platforms. This integration often involves synchronizing different software systems, each with its protocols and specifications.
To address this, choosing PACS solutions known for their interoperability and compliance with industry standards like DICOM is essential. Additionally, working with experienced IT professionals specializing in healthcare technology can help navigate these technical complexities.
They can assist in customizing solutions that ensure smooth integration and functionality across different platforms.
Regulatory compliance is another significant challenge, especially given the stringent laws governing patient data and privacy. In North America, compliance with regulations such as HIPAA is non-negotiable.
To ensure adherence, medical businesses should choose PACS providers who clearly understand and implement these regulations. Regular audits and system updates in accordance with changing laws can help maintain compliance.
Given the sensitive nature of diagnostic data, security concerns are paramount. Data breaches and unauthorized access are real threats in the digital age.
Implementing robust security measures is crucial to mitigate these risks. This includes data encryption in transit and at rest, using secure VPNs for remote access, and implementing multi-factor authentication for users.
Regular security training for staff and periodic risk assessments can also fortify the system against potential breaches.
Effective implementation of PACS in telemedicine requires a strategic approach. This includes conducting thorough needs assessments to understand the specific requirements of the medical business.
Tailoring the PACS solution to these needs while allowing scalability and future upgrades is essential. Additionally, investing in staff training is crucial to ensure that the team uses the system efficiently.
Focusing on user experience is critical for North American medical businesses looking to optimize PACS for telemedicine. The system should be intuitive and user-friendly, minimizing the learning curve for medical staff.
Regular feedback sessions with users can provide insights into potential improvements or additional training needs.
Furthermore, leveraging cloud-based PACS solutions can enhance accessibility and collaboration, allowing healthcare providers to access diagnostic data from anywhere at any time. This is particularly beneficial in telemedicine, where timely data access can significantly impact patient care.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
Selecting the right Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) for telemedicine involves understanding the unique needs of a medical business. Check out PostDICOM's state-of-the-art cloud PACS service at an affordable price.
This decision is pivotal in ensuring that telemedicine services are efficient, secure, and patient-centric. The choice of PACS can significantly influence the quality of remote diagnostics and the overall patient experience.
When choosing a PACS for telemedicine, several key features are essential for effective remote diagnostics.
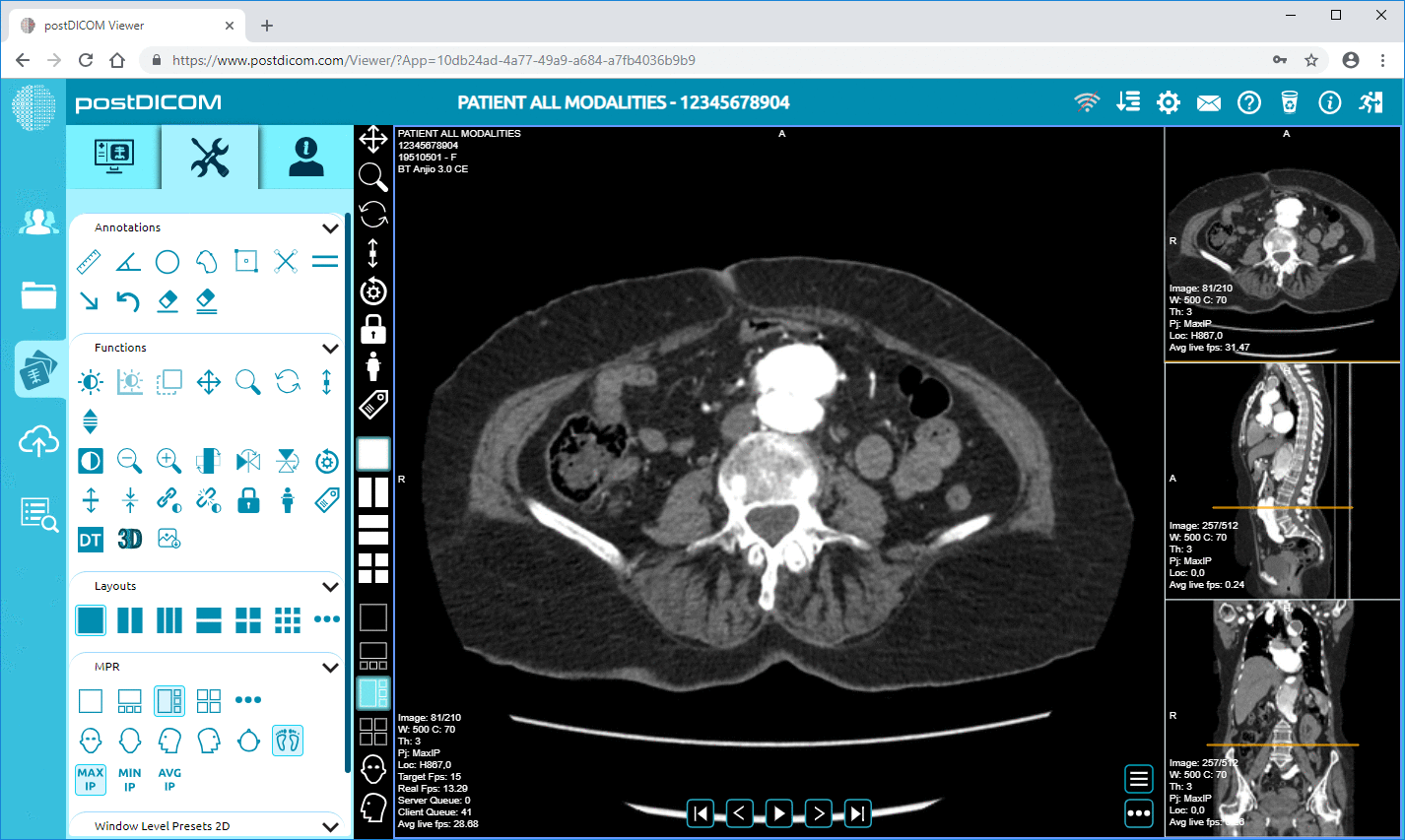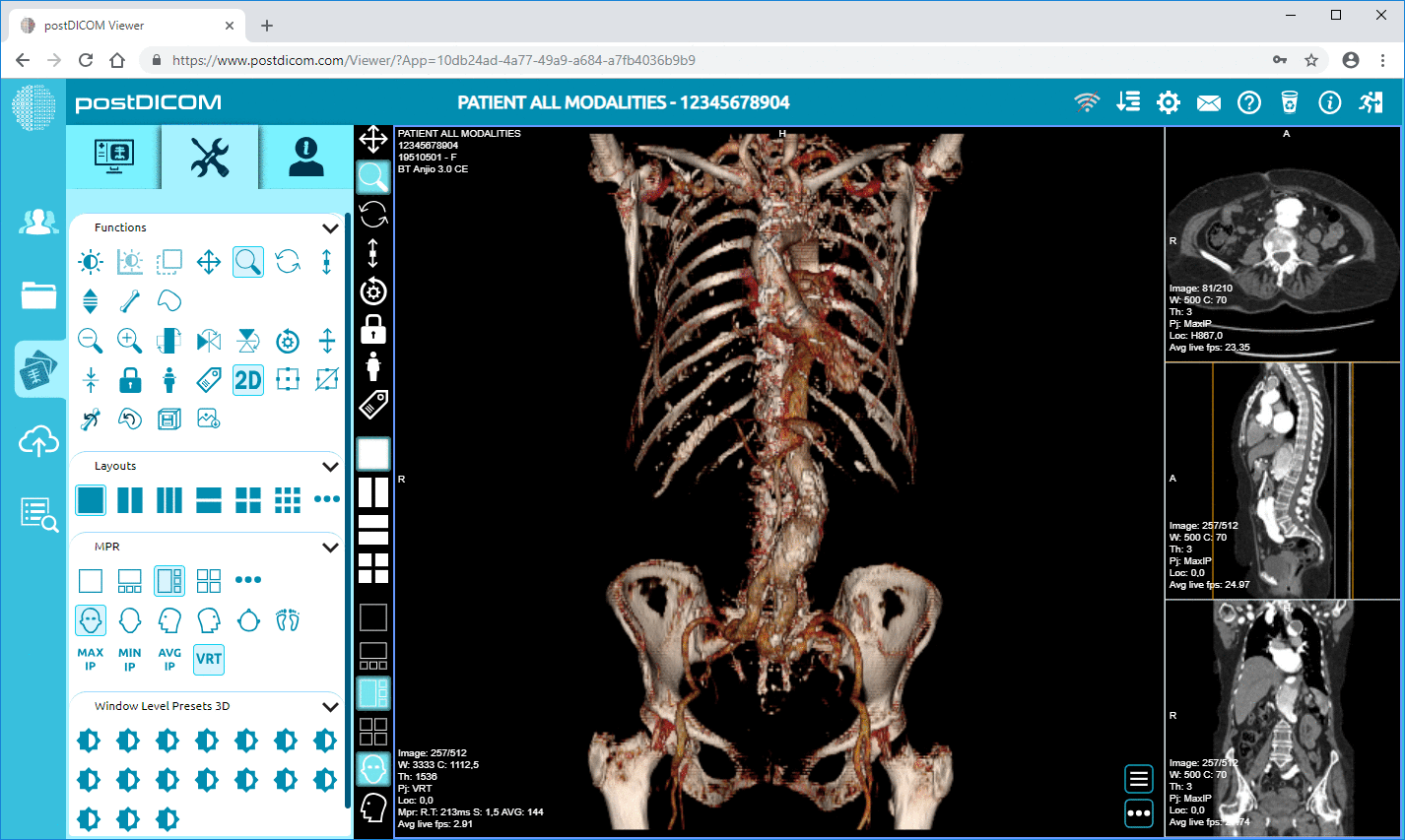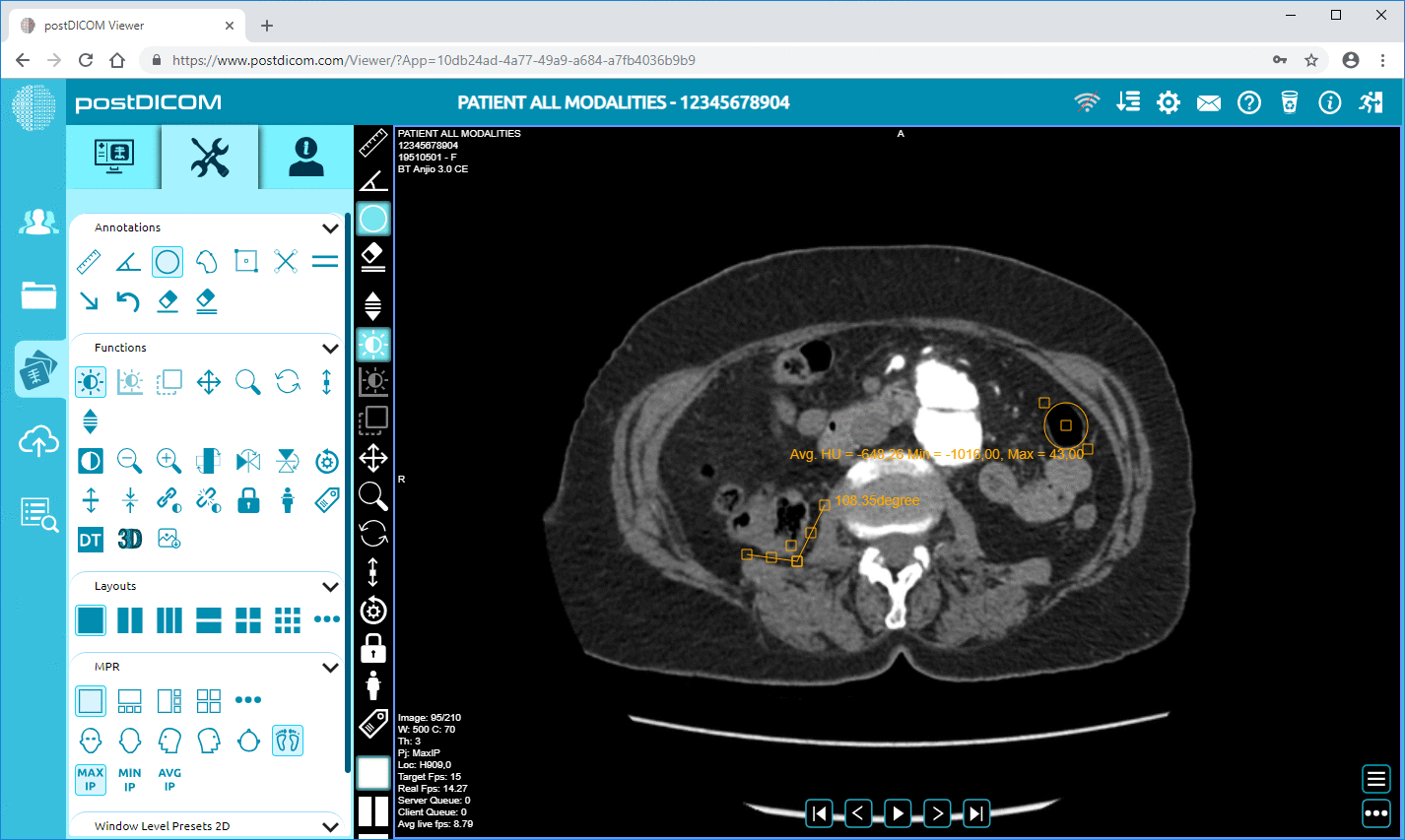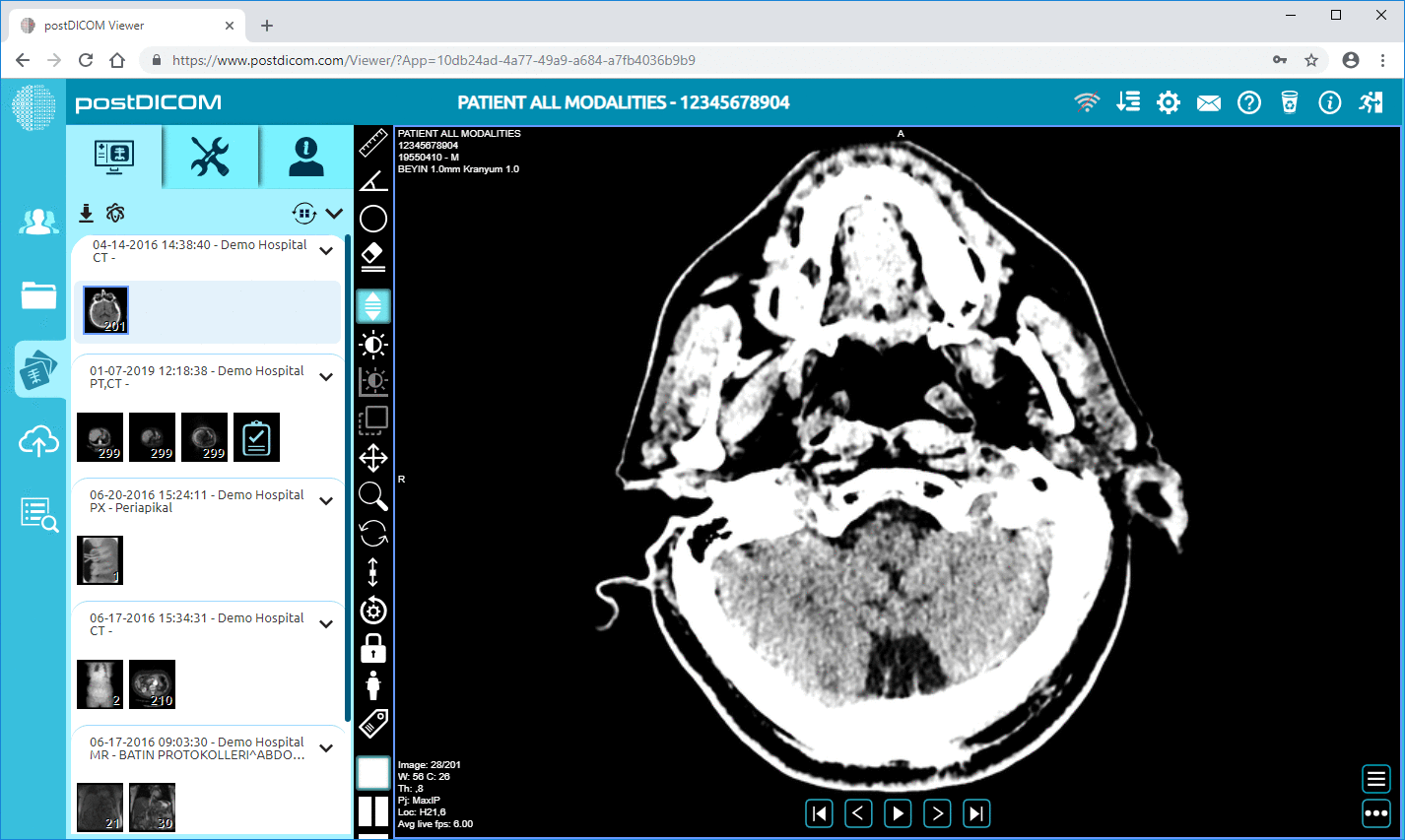
Firstly, the system should offer high-quality image rendering. Clear and precise images are crucial for accurate diagnostics, especially when consultations are conducted remotely.
Another essential feature is the ease of integration with other telemedicine platforms and electronic health records (EHR). This integration ensures that patient data and diagnostic images are easily accessible in one place, streamlining the diagnostic process.
The system should also offer robust data compression and transfer capabilities. Efficient data transfer is critical in telemedicine, where time is often of the essence, and large diagnostic files need to be transmitted quickly and securely over the internet.
Scalability is a crucial consideration. The chosen PACS should meet current needs and grow with the medical business. This means it can handle an increasing volume of data and accommodate new functionalities as technology advances and the practice's needs evolve.
Interoperability is another critical factor. The PACS should be able to seamlessly communicate with various diagnostic tools and software systems used in telemedicine. This interoperability for DICOM and PACS is essential for ensuring that the workflow is smooth and that there are no technical barriers that could impede the efficiency of remote diagnostics.
Compliance with regulatory standards, such as HIPAA in the United States, is non-negotiable. The PACS must ensure the privacy and security of patient data. This includes having strong encryption protocols, secure access controls, and the ability to audit trails. Regular updates and compliance checks are necessary to keep up with evolving regulations.
The integration of PACS into telemedicine has been transformative, catalyzing a new era of healthcare delivery unbounded by geography. As telehealth permeates medical practice with advanced efficiency, security, and mobility, optimized PACS underpins diagnostic success by condensing the distance between specialists and those needing care.
We have seen how thoughtful implementation meeting technical, regulatory, and collaborative demands has elevated standards across institutions. While barriers persist in uninsured communities, the proliferation of these information hubs represents hope for closing persistent access gaps.
Telemedicine powered by PACS offers the potential for early interventions by pooling expertise that saves lives. As virtual consults and AI capacities continue enhancing what’s possible, secure data transmission will be the channel enabling it all. By converging technologies with boundless medical promise at their fingertips, providers everywhere can profoundly transform outcomes.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |