When it comes to orthopedic care, precision is vital.
That's why integrating digital X-ray systems with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) has revolutionized how orthopedic conditions are diagnosed and treated. This advanced technology ensures accurate imaging, making it easier for healthcare providers to provide the best possible care for their patients.
This synergy is not just a technological leap; it's a transformative approach that enhances every aspect of orthopedic imaging.
Medical professionals now have access to a more precise and efficient way of diagnosing ailments thanks to the combination of digital X-rays and PACS. This allows for greater image clarity and detail while streamlining the diagnosis process.
As we delve into this topic, we'll explore how this integration optimizes image management and significantly improves patient care outcomes.
This integration marks a significant stride in orthopedic practice, offering insights into its profound impact on efficiency, diagnostic accuracy, and collaborative patient care in the healthcare industry.
Orthopedic imaging has undergone a remarkable transformation over the years, evolving from traditional methods to advanced digital technologies. This evolution has been pivotal in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and improving patient care in orthopedics.
Let’s journey through the historical context of imaging in orthopedics and explore the significant transition from traditional to digital X-ray systems.
Orthopedic imaging began with the discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen in 1895. Initially, X-ray imaging was a rudimentary process, producing images on photographic plates.
These early X-rays were revolutionary, allowing for the first time a non-invasive peek into the human body, specifically into the skeletal system. They became essential in diagnosing fractures, joint dislocations, and other bone-related conditions.
Over the years, traditional X-ray technology saw significant improvements. The introduction of film-screen systems enhanced image quality and reduced exposure times. However, these systems had limitations.
They required physical storage space for films, and the process of developing X-ray films was time-consuming. Moreover, the inability to manipulate images often led to the need for repeat scans, exposing patients to additional radiation.
The advent of digital radiography marked a turning point in orthopedic imaging. Digital X-ray systems emerged in the late 20th century and replaced traditional film-based methods.
These systems use digital X-ray sensors instead of traditional photographic film, resulting in immediate image capture and display.
Digital X-ray systems offer superior image quality with greater detail, which is crucial for accurate orthopedic diagnoses. They allow image manipulation, such as zooming and contrast adjustment, without requiring repeat exposures.
This capability improves diagnostic accuracy and reduces the patient's exposure to radiation.
The transition to digital X-rays streamlined the workflow in orthopedic practices. Digital images could be stored electronically, eliminating the need for physical storage space and the hassle of managing film archives.
This shift paved the way for easier and quicker access to patient images, enhancing the efficiency of orthopedic care.
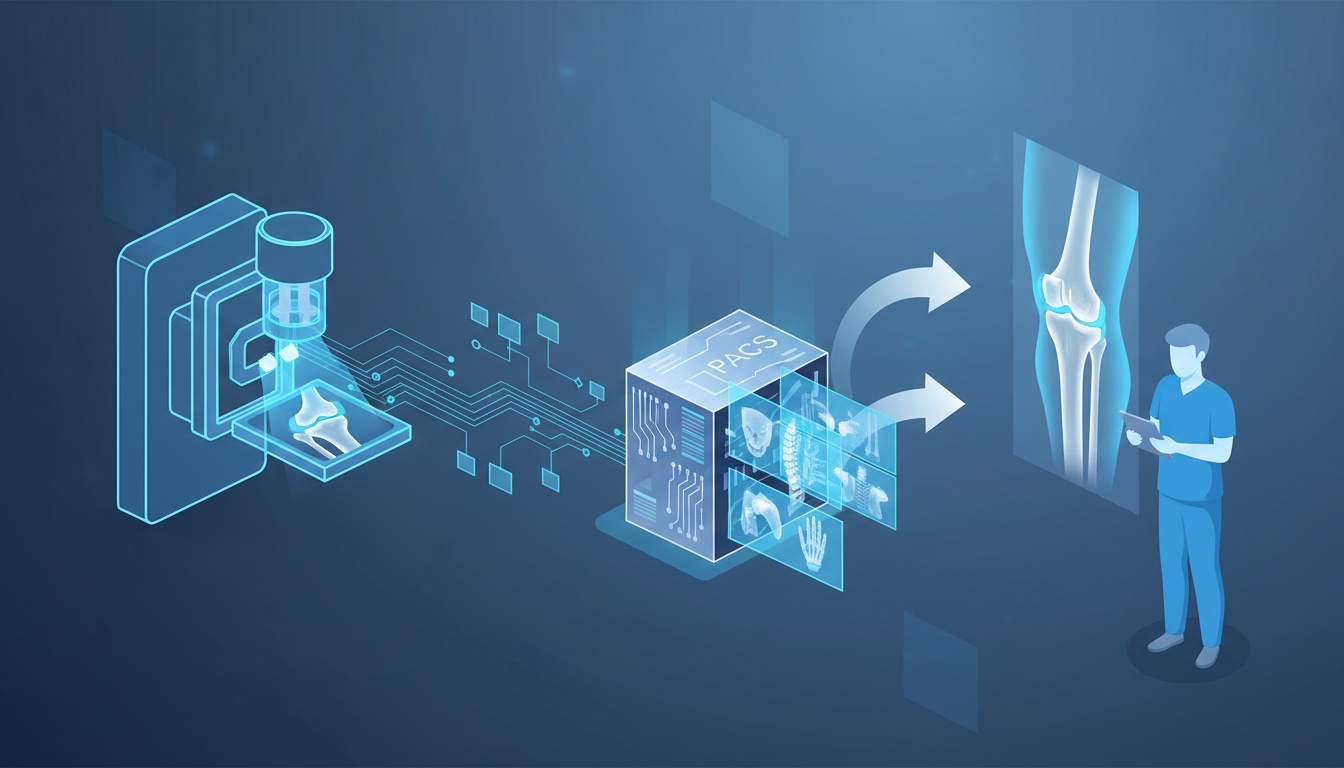
The integration of digital X-ray systems with PACS further revolutionized orthopedic imaging. PACS allowed centralized storage, easy retrieval, and efficient sharing of digital images
This integration meant that orthopedic surgeons could access patient images from any workstation within the healthcare facility, facilitating better collaboration and treatment planning.
A notable example of the impact of this evolution comes from a sports medicine clinic in California. The clinic transitioned to digital X-ray systems integrated with PACS, significantly improving its ability to diagnose and treat athletic injuries more effectively and efficiently.
Integrating digital X-ray systems with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) in orthopedics is a significant technological advancement, enhancing the quality and efficiency of imaging.
This integration reshapes how orthopedic conditions are diagnosed and managed, bringing a new level of precision to patient care. Let’s delve into this integration's process, technical aspects, and impact on orthopedic imaging.
Integrating digital X-ray systems into PACS involves several vital steps to ensure seamless functionality and compatibility.
Initially, it's crucial to ensure that the digital X-ray systems can produce images in the DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) format, the standard format PACS uses for medical imaging.
Once compatibility is established, the digital X-ray images are transmitted directly to the PACS server. This process requires a robust network infrastructure to handle the transfer and storage of large image files.
The PACS then stores these images in a centralized database, making them accessible to authorized personnel across the healthcare facility.
The integration of digital X-ray with PACS significantly enhances the quality and efficiency of orthopedic imaging:
Improved Image Quality: Digital X-ray systems provide high-resolution images, offering greater detail and clarity. This improvement is crucial for accurately diagnosing orthopedic conditions like fractures, joint disorders, and degenerative diseases.
Streamlined Workflow: With PACS, the time-consuming process of handling physical films is eliminated. Orthopedic surgeons and radiologists can access digital X-ray images instantly, reducing the time from image acquisition to diagnosis. This streamlined workflow is particularly beneficial in urgent care scenarios where quick decision-making is crucial.
Efficient Image Management: PACS allows for efficient organization and management of digital X-ray data. Orthopedic surgeons can easily compare current images with previous ones, track changes over time, and monitor the progression of orthopedic conditions.
Enhanced Collaboration: The integration facilitates better collaboration among healthcare professionals. Orthopedic surgeons can share digital X-ray images with other specialists within the facility or remotely, enhancing the multidisciplinary approach to patient care.
A notable example of the impact of this integration comes from an orthopedic clinic in New York. After integrating their digital X-ray systems with PACS, the clinic reported a significant improvement in diagnosing sports-related injuries.
The ability to rapidly access and analyze X-ray images allowed quicker and more accurate treatment plans.
Integrating digital X-ray systems with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) is revolutionizing patient care in orthopedics.
This synergy streamlines imaging processes and significantly impacts patient care, from diagnosis to treatment planning. Let's explore how this integration is enhancing patient care in orthopedic settings.
One of the most significant benefits of integrating digital X-ray with PACS in orthopedics is achieving faster and more accurate diagnoses.
Digital X-ray provides high-resolution images instantly available on PACS, allowing orthopedic specialists to quickly assess and diagnose conditions such as fractures, joint disorders, and bone diseases.
This rapid turnaround is crucial, especially in emergency situations where a timely diagnosis can significantly affect treatment outcomes.
For example, an orthopedic clinic in Toronto reported a notable decrease in the time taken to diagnose sports injuries after adopting this integration, leading to quicker initiation of appropriate treatments.
The integration also plays a vital role in treatment planning. With enhanced image quality and easy access to historical imaging data provided by PACS, orthopedic surgeons can plan surgeries and other treatments with greater precision.
They can assess the progression of a condition over time, making informed decisions about the most effective treatment approach.
A case in point is a knee replacement surgery at a hospital in Chicago, where the surgeon used historical and current digital X-rays from PACS to plan the surgical procedure precisely, resulting in a successful outcome and reduced recovery time for the patient.
In today’s digital age, the privacy and security of patient data are paramount. Integrating digital X-rays with PACS ensures that patient images and information are stored securely, with access restricted to authorized personnel only.
This system adheres to healthcare privacy laws like HIPAA, assuring patients that their sensitive health information is protected.
For instance, a healthcare network in California implemented advanced encryption and access control measures in their PACS, significantly enhancing the security of patient data and building trust among their patient community.
Integrating digital X-ray systems with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) in orthopedics is a significant step forward in medical imaging.
However, this integration can present challenges, from technical complexities to data migration issues. Let's explore these challenges and offer strategies for successful implementation, ensuring that healthcare providers can fully leverage the benefits of this integration.
One of the primary challenges in integrating digital X-ray with PACS is managing the technical complexities.
Ensuring compatibility between the digital X-ray systems and the PACS is crucial. This often involves configuring the X-ray systems to communicate effectively with the PACS, ensuring that images are correctly formatted and transmitted.
Solution: Work closely with IT specialists and vendors to ensure compatibility. Conduct thorough testing before full-scale implementation to identify and address any technical issues.
Migrating existing X-ray images and patient data to a new PACS can be daunting. It's essential to transfer this data accurately and securely to maintain historical records and ensure continuity of care.
Solution: Develop a detailed data migration plan. Start with a pilot migration of a small data set to identify potential issues. Ensure regular backups and establish a clear timeline for the migration process.
Another significant challenge is training staff to use the new integrated system effectively. It's crucial that all users, from radiologists to technicians, are comfortable and proficient with the new system.
Solution: Implement comprehensive training programs and hands-on workshops. Consider appointing 'super users' or champions who can provide ongoing support and guidance to their colleagues.
Stakeholder Engagement:Involve all stakeholders, including radiologists, orthopedic surgeons, and IT staff, in the planning process. Their input can provide valuable insights and help tailor the system to meet the department's specific needs.
Phased Implementation:Consider a phased approach to integration. Start with one department or a specific type of procedure before expanding to the entire orthopedic department.
Regular Feedback and Adjustments:Regularly collect user feedback and make necessary adjustments after implementation. Continuous improvement is critical to successful integration.
Prioritize Data Security: Ensure the integrated system complies with data security regulations. Implement robust security measures to protect patient data.
A hospital in Minnesota shared its success story of integrating digital X-rays with PACS.
They faced initial data migration and staff training challenges but overcame them through careful planning and stakeholder engagement. The result was a more efficient workflow and improved patient care.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
As we look toward the future of orthopedic imaging, the integration of digital X-ray systems with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) is set to evolve dramatically, influenced by emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
This evolution promises to enhance the capabilities of orthopedic imaging further, making it more efficient, accurate, and patient-focused. Let's explore the potential future trends and the impact of these emerging technologies in orthopedic imaging.
One of the most exciting prospects in orthopedic imaging is the integration of AI and machine learning with digital X-rays and PACS. AI algorithms can potentially analyze X-ray images for patterns and anomalies the human eye might overlook.
This can be particularly beneficial in the early detection of degenerative bone diseases or subtle fractures that are difficult to diagnose.
Example: A pilot program at a medical center in Boston used AI algorithms to analyze digital X-rays for early signs of osteoporosis, leading to earlier interventions and better patient outcomes.
Powered by machine learning, predictive analytics is poised to revolutionize how orthopedic conditions are managed.
By analyzing vast amounts of imaging data, these systems can predict the progression of orthopedic conditions, enabling personalized treatment plans based on individual patient data.
Impact: This approach could significantly improve the management of chronic conditions like arthritis, tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs and responses.
Future advancements in the integration of digital X-rays with PACS are likely to include more sophisticated image processing tools.
These tools could provide orthopedic surgeons with enhanced visualization capabilities, such as 3D reconstructions of skeletal structures from X-ray images, aiding in surgical planning and patient education.
Anecdote: An orthopedic surgeon in San Francisco used advanced 3D models generated from digital X-rays to plan a complex joint reconstruction surgery, resulting in a more precise and successful outcome.
Integrating digital X-ray and PACS with wearable technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) is another exciting future trend.
Wearable devices could monitor patient movements and bone health, with data being directly integrated into the PACS for comprehensive patient assessment.
Future Scenario: Imagine a scenario where a patient’s wearable device data is used in conjunction with their X-ray images to assess the recovery progress after a knee replacement surgery.
Integrating digital X-ray systems with PACS revolutionizes orthopedic imaging, offering enhanced diagnostic precision, streamlined workflows, and improved patient care.
As we look to the future, advancements in AI, machine learning, and predictive analytics promise to further elevate the field, bringing personalized treatment plans and more efficient management of orthopedic conditions.
Embracing these technological innovations is crucial for healthcare providers to stay at the forefront of orthopedic care. This integration signifies a technological leap and a commitment to delivering superior patient care.
As the landscape of orthopedic imaging continues to evolve, staying abreast of these changes will be vital to optimizing patient outcomes and advancing the practice of orthopedic medicine.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |