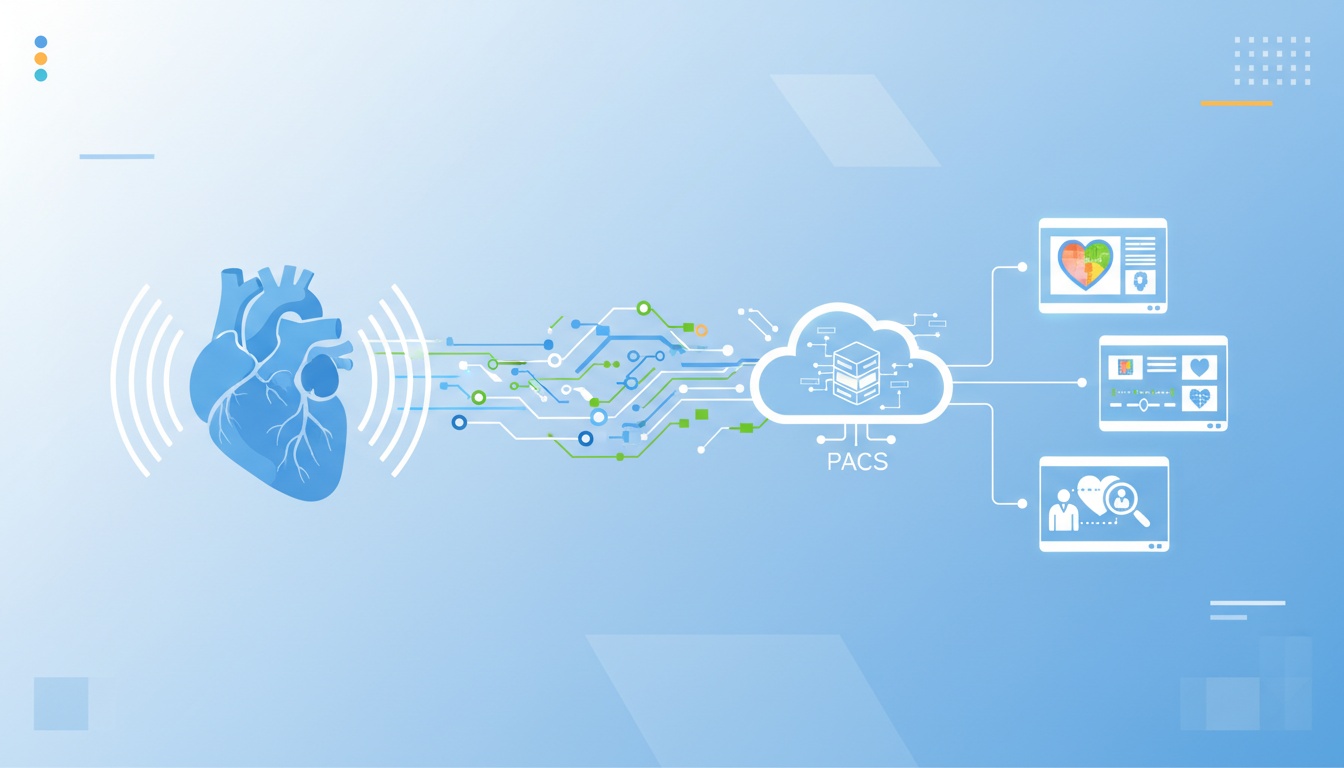
Echocardiography stands as a critical tool for diagnosing heart conditions. Integrating this vital imaging technique with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) is revolutionizing how cardiologists view, analyze, and store these essential images.
This synergy between echocardiography and PACS is not just a technological advancement; it's a significant leap forward in enhancing cardiac imaging and patient care. By streamlining the storage, retrieval, and sharing of echocardiographic data, PACS empowers medical professionals to make more informed decisions faster.
As we delve into this topic, we'll explore how this integration shapes the future of cardiac imaging, offering insights into its profound impact on efficiency, diagnostic accuracy, and collaborative patient care in the healthcare industry.
Echocardiography has become indispensable in cardiac care, offering a non-invasive yet detailed glimpse into the heart's structure and function. Let's explore the pivotal role of echocardiography in diagnosing and managing heart conditions, highlighting the various types of echocardiographic procedures and their applications in cardiac care.
Echocardiography uses sound waves to create images of the heart, allowing cardiologists to assess its size, structure, and function. It's precious in diagnosing heart diseases, monitoring heart conditions, and guiding treatment decisions.
For instance, in a clinic in Boston, echocardiography played a crucial role in detecting a patient's heart valve disease, leading to timely surgical intervention.
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE): The most common type, TTE, is a non-invasive procedure where a transducer is placed on the chest to obtain heart images. It's widely used for initial cardiac assessments.
Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE): In TEE, a flexible probe with a transducer is guided down the throat into the esophagus, providing a closer and more precise view of the heart. It's beneficial for examining heart valve function and detecting blood clots.
Stress Echocardiogram: This test combines echocardiography with exercise or medication-induced stress to assess how the heart functions under physical strain. It's essential for diagnosing coronary artery disease.
Doppler Echocardiography: Doppler techniques measure the speed and direction of blood flow in the heart, helping to identify abnormal blood flow patterns indicative of heart problems.
Echocardiography has a broad range of applications in cardiac care:
Diagnosing Heart Conditions: Echocardiograms can detect heart conditions such as valve diseases, cardiomyopathy, and congenital heart defects.
Evaluating Heart Function: It assesses the heart's pumping strength, which is crucial for patients with heart failure.
Guiding Treatment: Echocardiography helps plan surgeries, such as valve repair or replacement, and guides non-surgical procedures like balloon angioplasty.
Monitoring Treatment Efficacy: Regular echocardiograms are used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments for heart conditions.
Echocardiography's impact on patient care is profound. A cardiologist in New York shared a case where echocardiography detected a small tear in a patient's heart muscle post-heart attack, which was critical in tailoring the patient's treatment plan.
In the dynamic field of medical imaging, Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) have emerged as a cornerstone technology, especially in specialties like echocardiography.
We will define PACS and explore its primary functions in medical imaging departments, highlighting how it benefits image storage, retrieval, and sharing.
PACS is a medical imaging technology that systematically stores, retrieves, and manages medical images electronically.
PACS replaces traditional film-based methods with a digital framework, allowing for more efficient imaging data handling. This system is particularly beneficial in echocardiography, where detailed heart images require precise and careful analysis.
Digital Storage: PACS enables the storage of large volumes of imaging data in digital format. This capability is crucial in echocardiography, where high-resolution images can occupy significant storage space.
Efficient Retrieval: With PACS, retrieving past and current echocardiograms becomes a matter of a few clicks. This efficiency is vital for cardiologists who need quick access to patient images for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Image Management: PACS allows for the organization and management of imaging data, making it easier for healthcare providers to track patient progress and compare images over time.
Enhanced Image Quality and Accessibility: PACS provides high-quality digital images that authorized personnel can easily access. In cardiac care, this means that cardiologists can view detailed echocardiograms with clarity, aiding in accurate diagnoses.
Streamlined Workflow: The integration of PACS streamlines workflow in medical imaging departments. For instance, a cardiac imaging center in California reported a significant reduction in the time taken to process and analyze echocardiograms after adopting PACS.
Improved Collaboration: PACS facilitates better collaboration among healthcare professionals. Cardiologists can share echocardiographic images with other specialists for consultations, providing more comprehensive patient care.
Remote Access and Telemedicine: With PACS, echocardiograms can be accessed remotely, which is invaluable for telemedicine initiatives. This feature was particularly beneficial during the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing cardiologists to continue providing care while maintaining social distancing.
A heart center in New York shared how PACS integration transformed their echocardiography services. The ability to quickly access and share echocardiograms across departments led to faster decision-making and improved patient outcomes, especially in emergencies.
The integration of echocardiography with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) is a significant advancement in cardiac imaging.
This fusion not only streamlines processes but also enhances the quality and efficiency of cardiac care. Let's explore the technical aspects of this integration and how it's reshaping cardiac imaging in healthcare facilities.
Integrating echocardiography with PACS involves several technical steps to ensure seamless compatibility and functionality. The first step is providing the echocardiography equipment that can interface with the PACS.
This usually involves configuring the ultrasound machines to transmit images in the DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) format, the standard format PACS uses for medical imaging.
Once the echocardiography machines are configured, the images are transmitted directly to the PACS server. Here, they are stored in a centralized database, making them accessible to authorized personnel across the healthcare facility.
This process requires a robust network infrastructure to handle the large file sizes of echocardiographic images and ensure quick transmission and retrieval.
The integration of echocardiography with PACS significantly enhances the quality and efficiency of cardiac imaging:
Improved Image Quality: PACS provides high-resolution digital images, allowing cardiologists to view detailed echocardiograms with enhanced clarity. This improvement in image quality aids in more accurate diagnoses of heart conditions.
Streamlined Workflow: With PACS, the time-consuming process of handling physical films is eliminated. Cardiologists can access echocardiographic images instantly, reducing the time from image acquisition to diagnosis. This streamlined workflow is particularly beneficial in urgent care scenarios where quick decision-making is crucial.
Efficient Image Management: PACS allows for efficient organization and management of echocardiographic data. Cardiologists can easily compare current images with previous ones, track changes over time, and monitor the progression of heart conditions.
Enhanced Collaboration: The integration facilitates better collaboration among healthcare professionals. Cardiologists can share echocardiographic images with other specialists within the facility or remotely, enhancing the multidisciplinary approach to patient care.
Integrating Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) with echocardiography is not just a technological advancement; it's a significant leap in patient care in cardiac imaging.
This integration brings numerous benefits impacting patient experience, from faster diagnosis and treatment planning to enhanced data privacy. Let's explore these patient-centric advantages in detail.
One of the most immediate benefits for patients is the expedited diagnosis process. Traditional echocardiography methods, reliant on physical films, could lead to delays in diagnosis. With PACS, digital images are instantly available for review, significantly reducing the time from scan to diagnosis.
For a patient awaiting echocardiogram results, this reduced wait time can alleviate anxiety and stress. Moreover, early diagnosis is crucial in heart disease treatment, often leading to better outcomes.
A cardiac center in Chicago noted a decrease in the time to diagnosis by over 40% after integrating PACS, directly impacting patient prognosis and treatment success.
Repeat scans are not just inconvenient; they can also be a source of additional stress and exposure to radiation for patients.
The clarity and detail provided by PACS-integrated echocardiography reduce the likelihood of inconclusive results, thereby minimizing the need for repeat scans.
A patient at a health clinic in Texas shared how the clarity of her digital echocardiogram on PACS led to a quick diagnosis, sparing her the anxiety and discomfort of undergoing multiple scans.
Data privacy and security are paramount concerns for patients in the digital age. PACS systems are designed with robust security protocols to protect sensitive health information. This includes secure data encryption, access controls, and compliance with healthcare privacy laws like HIPAA.
Patients can rest assured that their personal health information is safeguarded against unauthorized access, giving them one less thing to worry about during their healthcare journey.
The real-world impact of integrating echocardiography with PACS is profound. A heart center in New York shared how PACS integration transformed their echocardiography services.
The ability to quickly access and share echocardiograms across departments led to faster decision-making and improved patient outcomes, especially in emergencies.
Integrating echocardiography with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) can revolutionize cardiac imaging, but it's not without its challenges.
From technical complexities to data migration issues, let's navigate these challenges and provide actionable solutions to ensure a smooth transition and effective integration.
One of the primary challenges in integrating echocardiography with PACS is the technical complexity involved.
Ensuring compatibility between echocardiography equipment and the PACS, especially from different manufacturers, can be daunting. The solution lies in thorough research and careful system selection. Choosing a PACS known for its interoperability is crucial and can seamlessly integrate with various echocardiography machines.
Consulting with IT specialists with medical imaging technology experience can provide valuable insights. For example, a hospital in Atlanta overcame this challenge by involving its IT team from the outset, ensuring that the selected PACS was compatible with their existing echocardiography equipment.
Migrating existing echocardiographic images and patient data to a new PACS can be another significant challenge. This process requires careful planning to avoid data loss or corruption. A structured approach to data migration is essential.
Start by categorizing and backing up existing data. It's often helpful to run a pilot migration with a small data set to identify potential issues before migrating the entire database. A clinic in Seattle successfully migrated years of echocardiographic images using this phased approach, minimizing disruptions to their daily operations.
Effective use of PACS requires specialized training for cardiologists, technicians, and other staff members. Comprehensive training programs, hands-on workshops, and continuous support are critical.
It's also beneficial to identify 'super users' within the team who can provide peer support and guidance. A medical center in Texas implemented a 'train-the-trainer' program, where selected staff were extensively trained and then tasked with training their colleagues, ensuring a widespread understanding of the new system.
Involve Stakeholders Early: Engage cardiologists, technicians, and IT staff in the decision-making process to ensure the selected PACS meets the needs of all users.
Prioritize Data Security: Ensure the new PACS complies with data security regulations and includes robust encryption and access controls.
Plan for Downtime: Schedule the integration during low activity to minimize the impact on patient care.
Seek Feedback Post-Integration: Regularly gather user feedback after integration to identify areas for improvement.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
As we look toward the future of cardiac imaging, the integration of Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) with echocardiography is poised to embrace groundbreaking technological advancements.
This integration is expected to evolve significantly, influenced by emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Let's explore the potential impact of these technologies and predict future trends in cardiac imaging.
One of the most exciting prospects in the future of cardiac imaging is the integration of AI and machine learning with PACS and echocardiography. AI algorithms can potentially analyze echocardiographic images for patterns the human eye might miss.
For instance, AI can assist in identifying early signs of heart disease, such as subtle changes in heart muscle movement or early indicators of valve dysfunction.
A clinic in San Francisco recently piloted an AI program that analyzed echocardiograms to predict the likelihood of heart failure in patients. The results were promising, demonstrating AI's potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
Predictive analytics, powered by machine learning, is set to revolutionize how cardiologists approach patient care.
By analyzing vast amounts of echocardiographic data, these systems can predict the progression of heart conditions, enabling proactive management of diseases. This approach improves patient outcomes and optimizes resource allocation within healthcare facilities.
Future advancements in PACS and echocardiography integration will likely include more sophisticated image analysis tools.
These tools could provide cardiologists with enhanced visualization capabilities, such as 3D heart reconstructions or real-time analysis of heart function during stress tests. This level of detail will allow for more precise diagnoses and tailored treatment plans.
Integrating PACS and echocardiography is also expected to bolster telemedicine capabilities in cardiac care.
With high-quality echocardiographic images accessible through PACS, cardiologists can offer remote consultations and second opinions, making specialized cardiac care more accessible, especially in underserved areas.
Cloud-based PACS solutions are anticipated to become more prevalent in cardiac imaging. These solutions offer scalable storage options, enhanced data security, and access to echocardiographic images from any location.
This flexibility benefits multi-site healthcare systems, allowing seamless collaboration and consultation across different facilities.
The integration of PACS with echocardiography marks a transformative era in cardiac imaging, offering unparalleled efficiency, accuracy, and patient care benefits. This synergy streamlines workflows, enhances diagnostic capabilities, and fosters better collaboration among healthcare professionals.
Incorporating advanced technologies like AI and machine learning promises to revolutionize cardiac imaging further, making it more predictive, personalized, and accessible. As we embrace these advancements, the future of cardiac care looks brighter, with improved patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare delivery on the horizon.
For medical service providers, staying updated with these technological strides and adapting to them is crucial for delivering top-tier cardiac care. Integrating PACS and echocardiography is a technical upgrade and a step towards a more informed, efficient, and patient-centric approach to cardiac imaging.
|
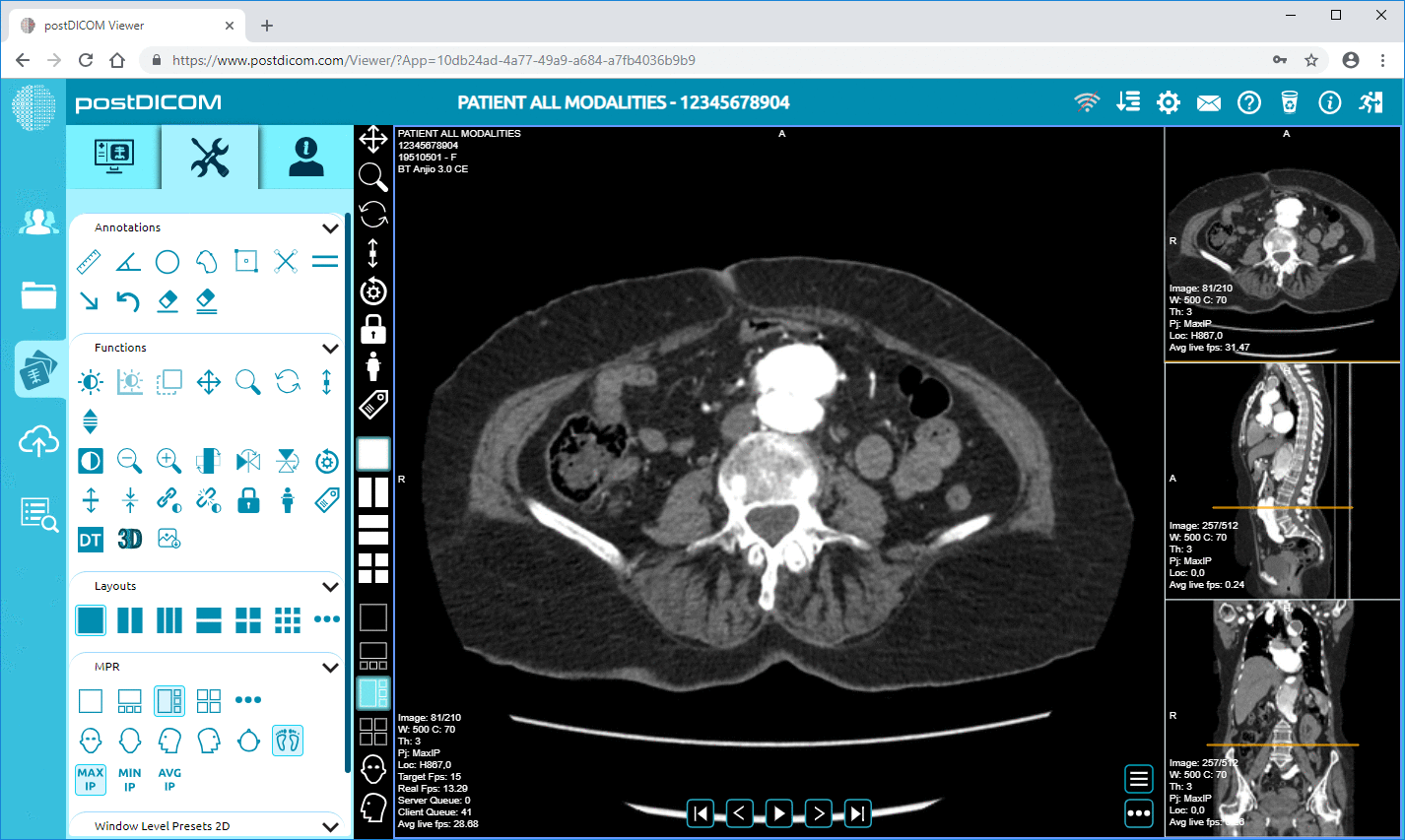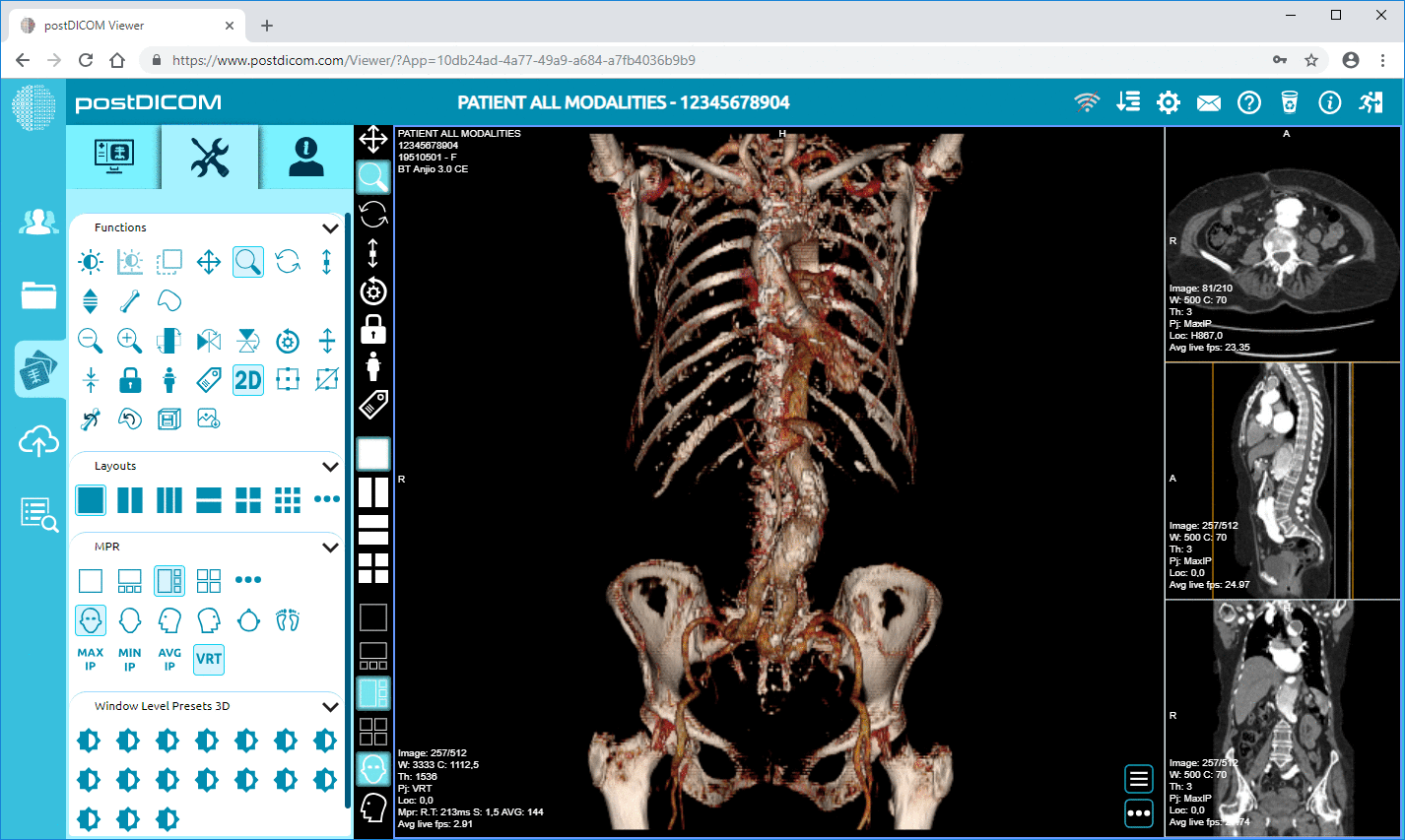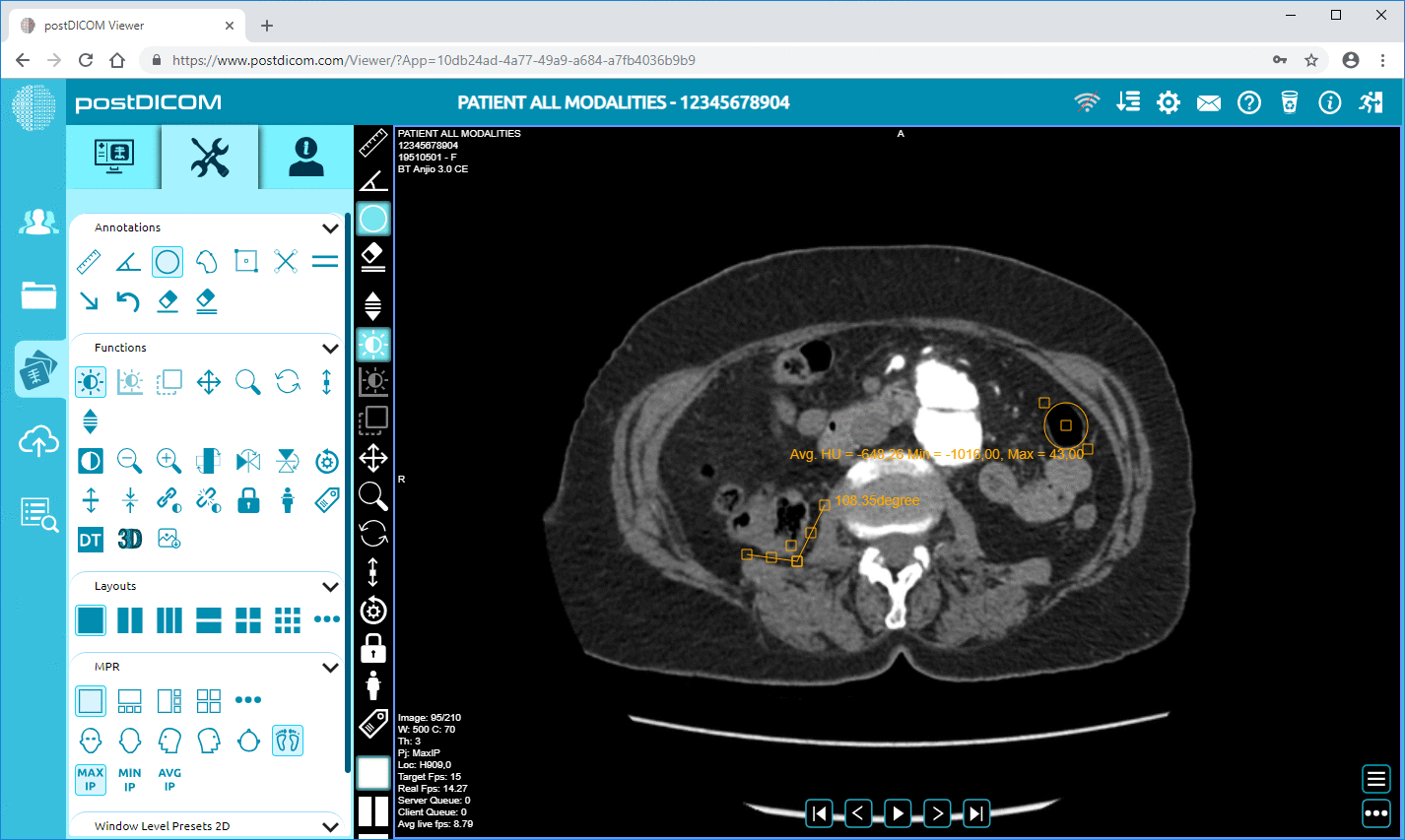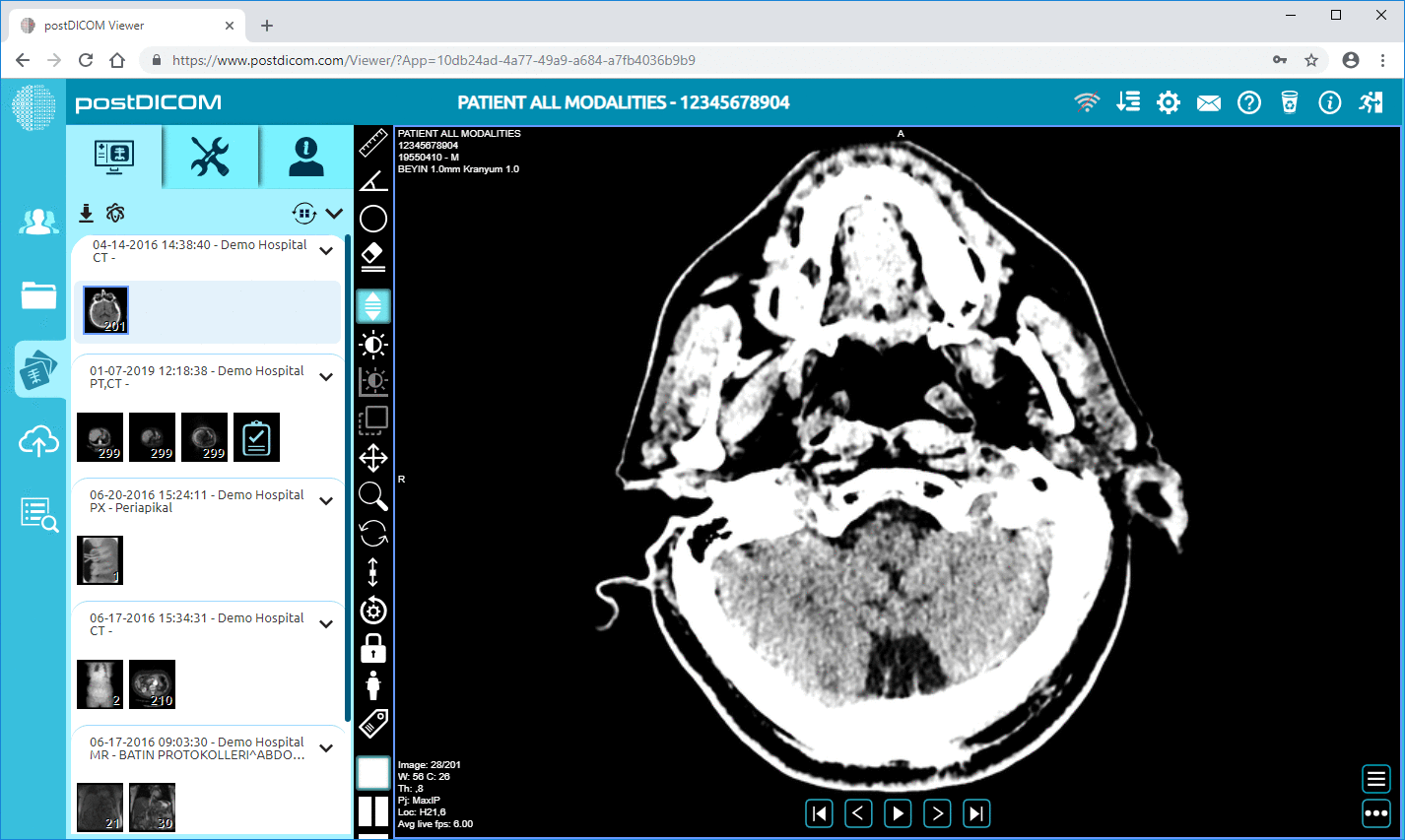
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |