Radiology information systems (RIS) are computer systems that manage medical imaging data and related information within a healthcare organization.
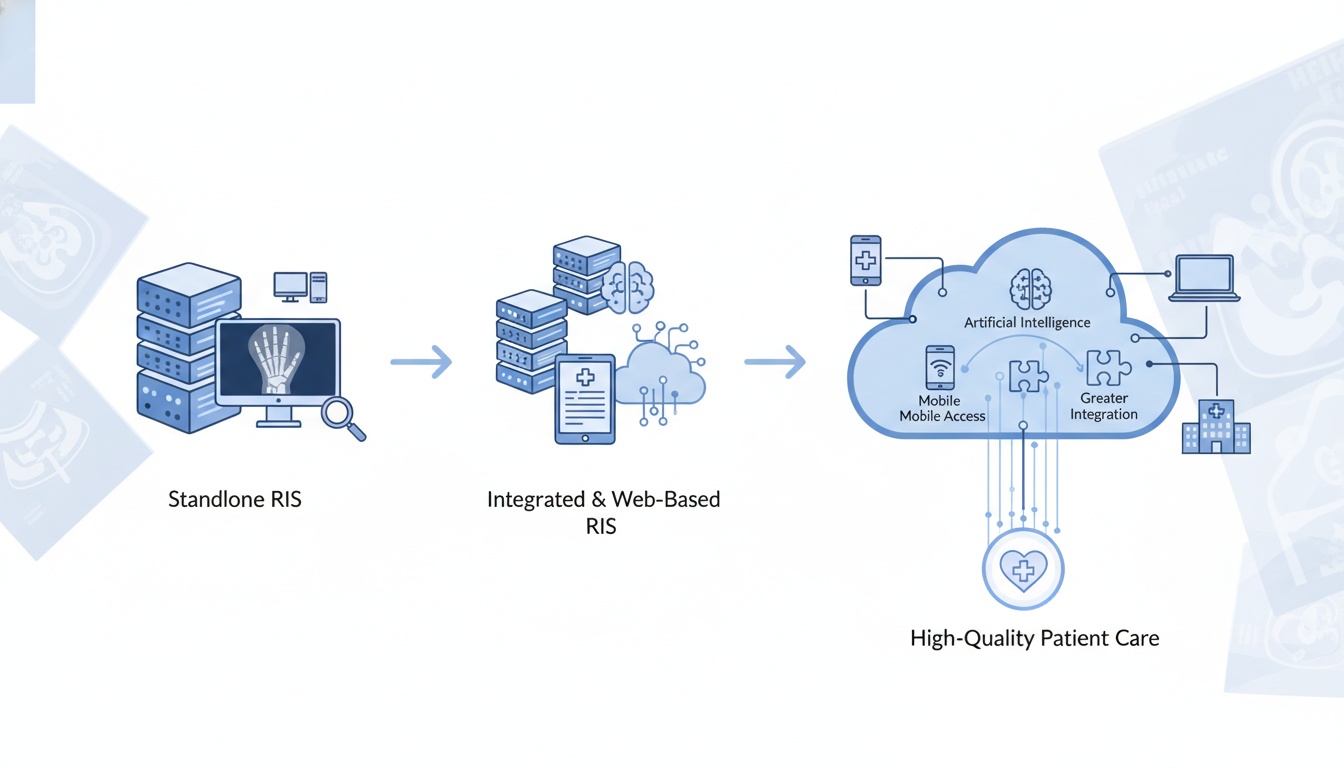
Several types of RIS exist, including standalone, integrated, web-based, cloud-based, and mobile systems. Every kind of RIS has unique features and capabilities, and the choice of system will depend on the needs and goals of the healthcare organization.
As healthcare technology continues to evolve, the future of RIS will likely involve a combination of artificial intelligence, cloud-based platforms, mobile access, and greater integration with other healthcare systems. These advances will help to improve the quality, efficiency, and accessibility of radiology services and support the delivery of high-quality patient care.
In this article, we have compiled the segments of RIS systems, their implications, and the future evolution of the technology that will shape medical data management. Stay with postDICOM for more information and affordable services.
Radiology information systems (RIS) are computer systems that manage medical imaging data and related information within a healthcare organization. There are several different types of RIS, including:
These systems are designed to handle the scheduling and tracking of radiology exams and patient information management within a single department or facility.
These systems are designed to integrate with other healthcare information systems, such as electronic medical record (EMR) systems and picture archiving and communication systems (PACS), to provide a more comprehensive view of a patient's medical history and care.
These systems use a web browser to access the RIS system, allowing users to access the system from any location with an internet connection.
These systems are hosted on remote servers and accessed through the internet, allowing healthcare organizations to outsource the management and maintenance of the RIS system to a third party.
These systems are designed for use on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, and allow users to access and manage radiology information while on the go.
Radiology information systems (RIS) have several functions designed to support the workflows and processes of radiology departments and other healthcare facilities. Some standard functions of RIS include:
Scheduling and appointment management: RIS can schedule radiology exams, manage patient appointments, and track staff availability, equipment, and other resources.
Patient registration and demographics: RIS can capture and store patient information, such as contact details, insurance information, and medical history.
Exam tracking and management: RIS can track the progress of radiology exams and manage the ordering, reporting, and billing of these exams.
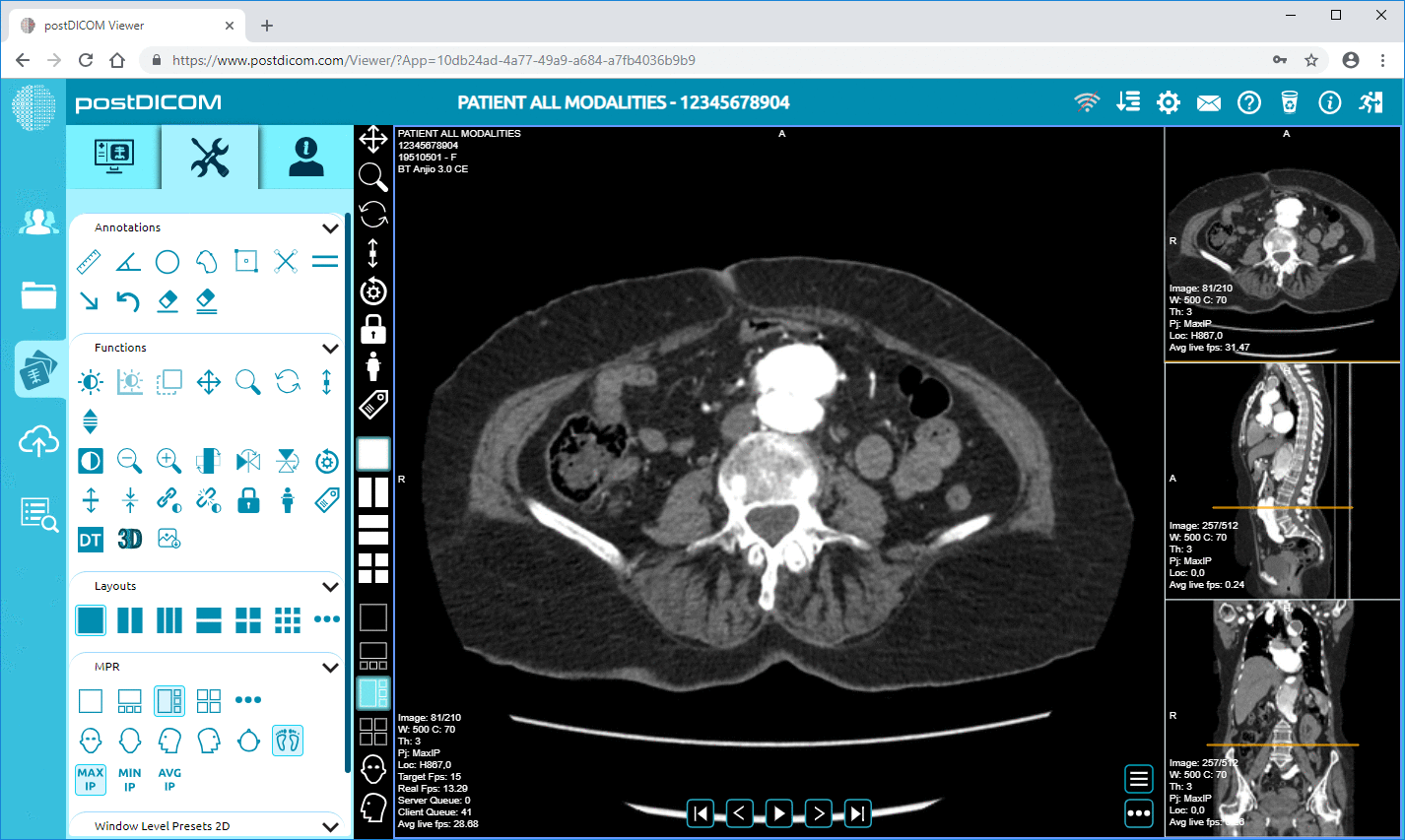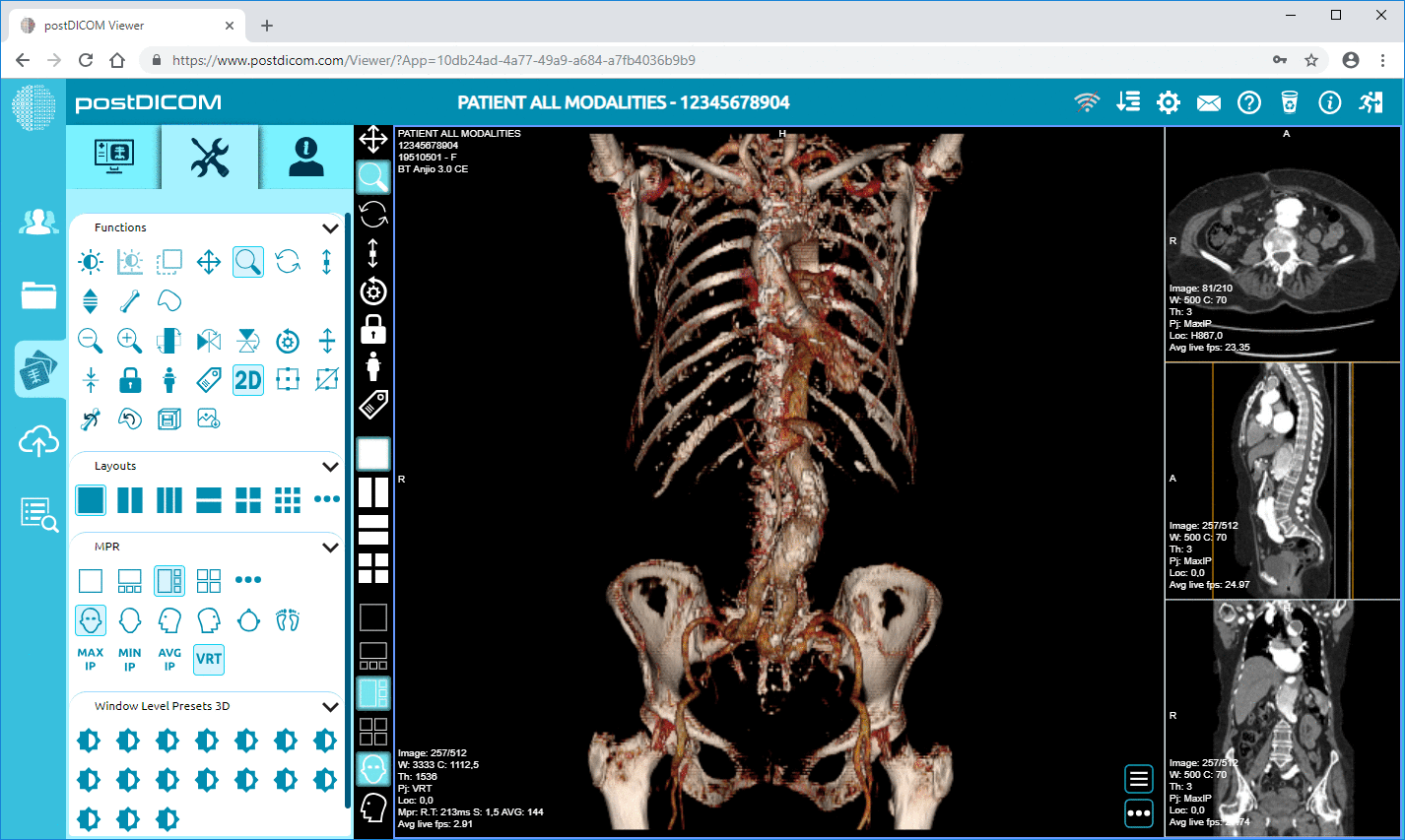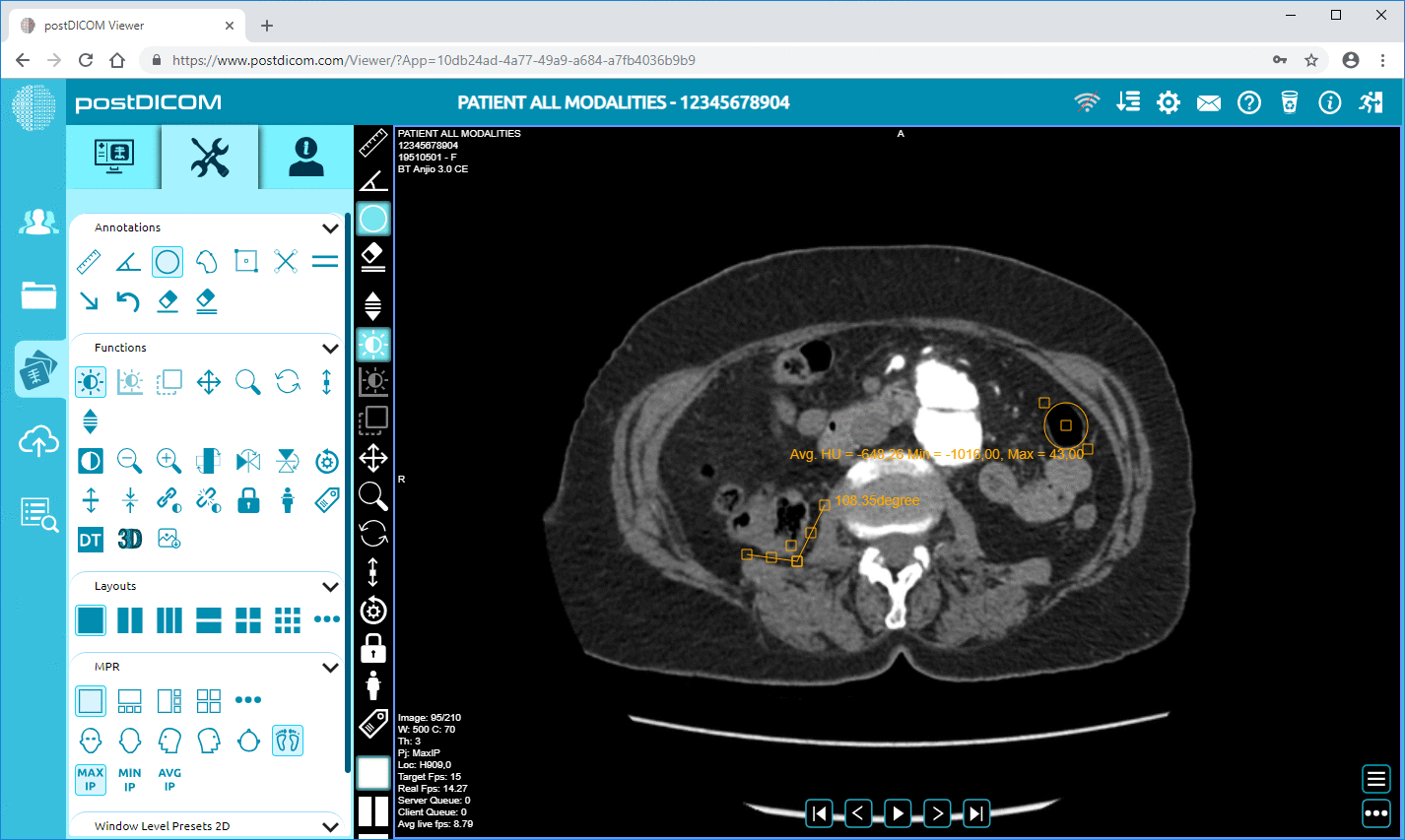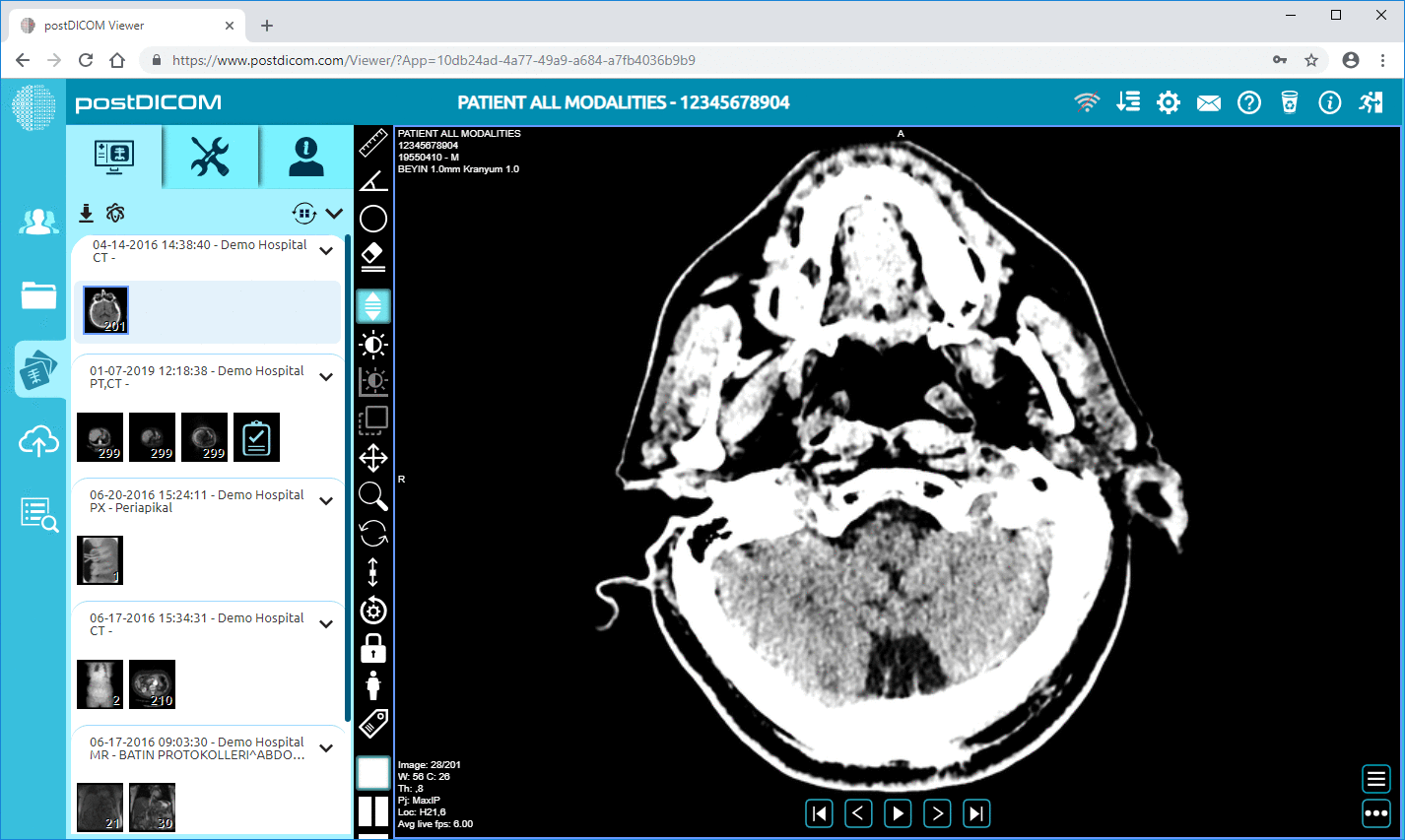
Image management: RIS can store medical images and related data, such as radiographic reports and diagnostic information.
Order entry and management: RIS can manage the ordering and scheduling of radiology exams and related procedures.
Reporting and data analysis: RIS can be used to generate reports and perform data analysis to help improve the efficiency and effectiveness of radiology services.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
There are several benefits to using a radiology information system (RIS) in a healthcare setting. Some of these benefits include:
Improved patient care: RIS can help improve the quality of patient care by providing a comprehensive view of a patient's medical history and care, including medical images and diagnostic information.
Enhanced efficiency: RIS can streamline the workflows of radiology departments and other healthcare facilities, helping to reduce errors and improve the efficiency of services.
Improved communication: RIS can facilitate the exchange of information between different healthcare providers, helping to improve communication and coordination of care.
Enhanced data management: RIS can provide a central repository for storing and managing medical images and related data, helping to reduce the risk of lost or misplaced information.
Reduced costs: RIS can help reduce healthcare costs by streamlining processes and improving the efficiency of radiology services.
Improved patient safety: RIS can help reduce the risk of medical errors by providing a comprehensive view of a patient's medical history and care, including alerts for allergies and contraindications to specific procedures.
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) and RIS (Radiology Information System) differ. While they are used in managing medical imaging data and related information, they have different functions and are often used in conjunction with one another in a healthcare setting.
PACS is a system that stores, retrieves, and distributes medical images and related data. Radiologists and other medical professionals typically use it to view and interpret medical images, such as x-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
On the other hand, RIS is a system used to manage radiology services' administrative and logistical aspects. It is used to schedule appointments, track the progress of exams, manage patient information, and perform billing and reporting functions.
In many cases, PACS and RIS are integrated to provide a comprehensive view of patient care and streamline radiology departments' workflows and other healthcare facilities.
The future of radiology information systems (RIS) will likely involve continued technological advancement and greater integration with other healthcare information systems. Some of the trends and developments that are likely to shape the future of RIS include
RIS may incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies to improve image analysis, diagnostic accuracy, and efficiency.
RIS may increasingly be delivered through cloud-based or web-based platforms, allowing for more flexible and scalable systems.
RIS may be designed for mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, and may support remote access to allow healthcare providers to access and manage radiology information while on the go.
RIS may become more closely integrated with electronic health records (EHRs) and other healthcare information systems to provide a more comprehensive view of patient care.
RIS may become more interoperable with other healthcare information systems and devices, allowing for the seamless exchange of medical images and related data.
Overall, the future of RIS will likely involve continued technological advancement and greater integration with other healthcare systems to improve the quality, efficiency, and accessibility of radiology services.
For healthcare organizations looking to upgrade their RIS systems, PostDICOM offers state-of-the-art DICOM and cloud PACS services.
These services provide a secure, reliable, scalable solution for storing, managing, and accessing medical images and related data. By choosing postDICOM, healthcare organizations can use the latest technologies and support delivering high-quality patient care.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |