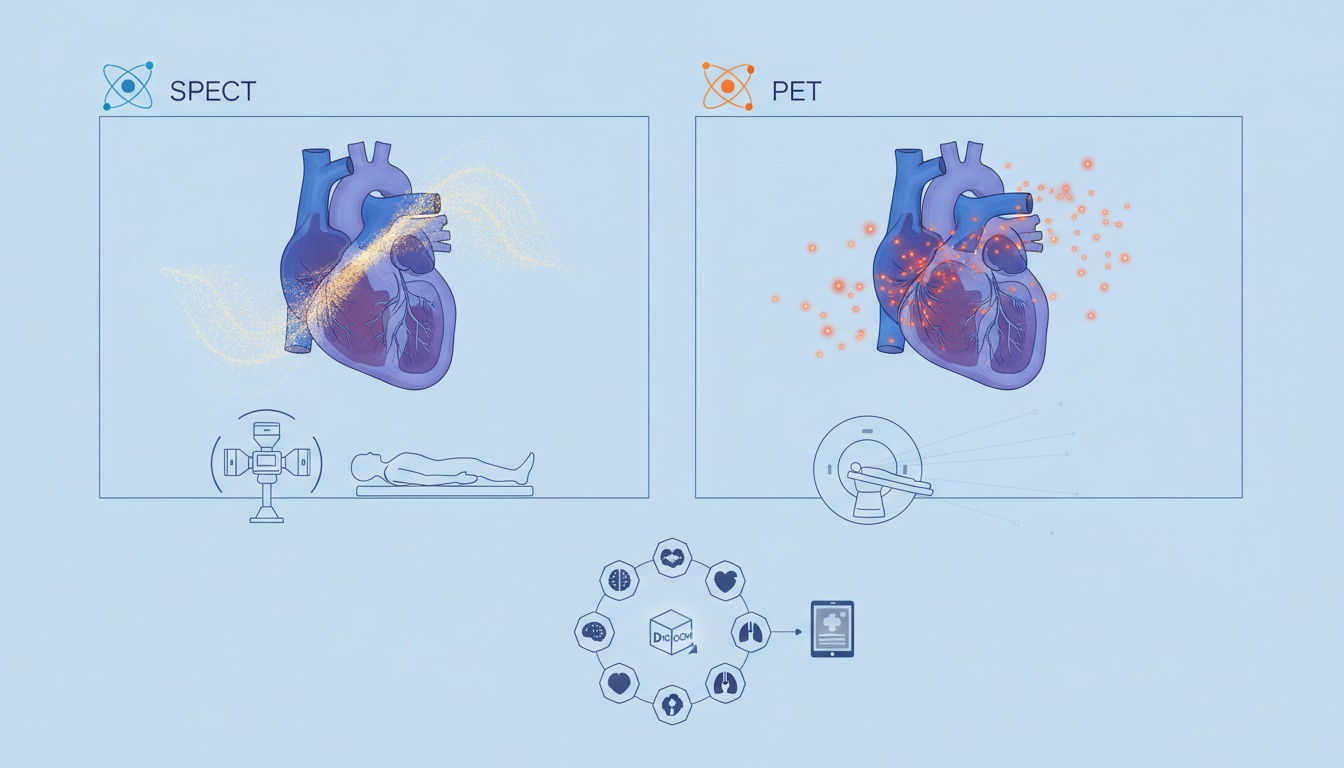
Cardiovascular diseases have been one of the leading reasons for mortality, even the most developed nations. In order to identify certain diseases, cardiac imaging becomes a vital technology for every health organization. SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) and PET (Positron Emission Tomography) are both highly efficient cardio imaging technologies that various facilities use. SPECT still manages to be the leading choice for cardiac images, although PET is also attracting considerable interest.
In the end, the choice is made by the patients or technicians depending on the advantages and shortcomings of both procedures. Keep reading to know the distinction between PET and SPECT in terms of utility for cardiology.
This sort of imaging provides metabolic and functional information about the cardiac organ. It involves injecting radiotracers into the bloodstream which depicts the images as and when it flows through various organs. Through this technique, it is able to determine whether or not a patient has any cardiovascular disease. It can ideally be performed when the patient is at rest or during a nuclear stress test.
The procedure also includes a Perfusion imaging which is generally done once at rest and the second time after cardiac stress. The radiotracer used has a half-life of six hours, giving plenty of time for the technologists to perform the imaging. The decay of the radiotracer combines into thousands of gamma-ray which results in forming an appropriate image suitable for diagnosis.
SPECT has a wider range of circulation than PET which also makes it more affordable with an average cost of $500,000.
The worldwide usage of technology also indicates that there is more trained personnel available.
Ideal ford cardiac stress testing with the expectation to boost image quality.
Images of sometimes prove to be weakening in the older cameras.
Quite similar to SPECT, PET that also uses injections of radiopharmaceuticals to aid the camera in creating images of the desired diagnosis. It can be used to study the blood flow of the heart along with pinpointing any damage such as scar tissue from a heart attack. The radiotracer used has a short half-life of 75 seconds which leaves very little time for the technicians to get the images acquired. The decay system is more complex when it comes to PET and each positron decay produces two gamma rays detectable by a camera.
Less widely available and a little heavy on the pockets as compared to the implementation of SPECT.
The short life of the radiopharmaceuticals is a drawback which is expected to be resolved in the future.
Bet standing delivers high-quality images which tend to have fewer artifacts. The high-speed should resolution provided hopes in quantitative estimates of blood flow.
Want to know more about healthcare technologies and how you can improve your hospital or facility using such advanced functionality? Think no more and contact Post DICOM. We provide cloud-based services that are affordable, reliable and easily maintained just to cater to your needs.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |