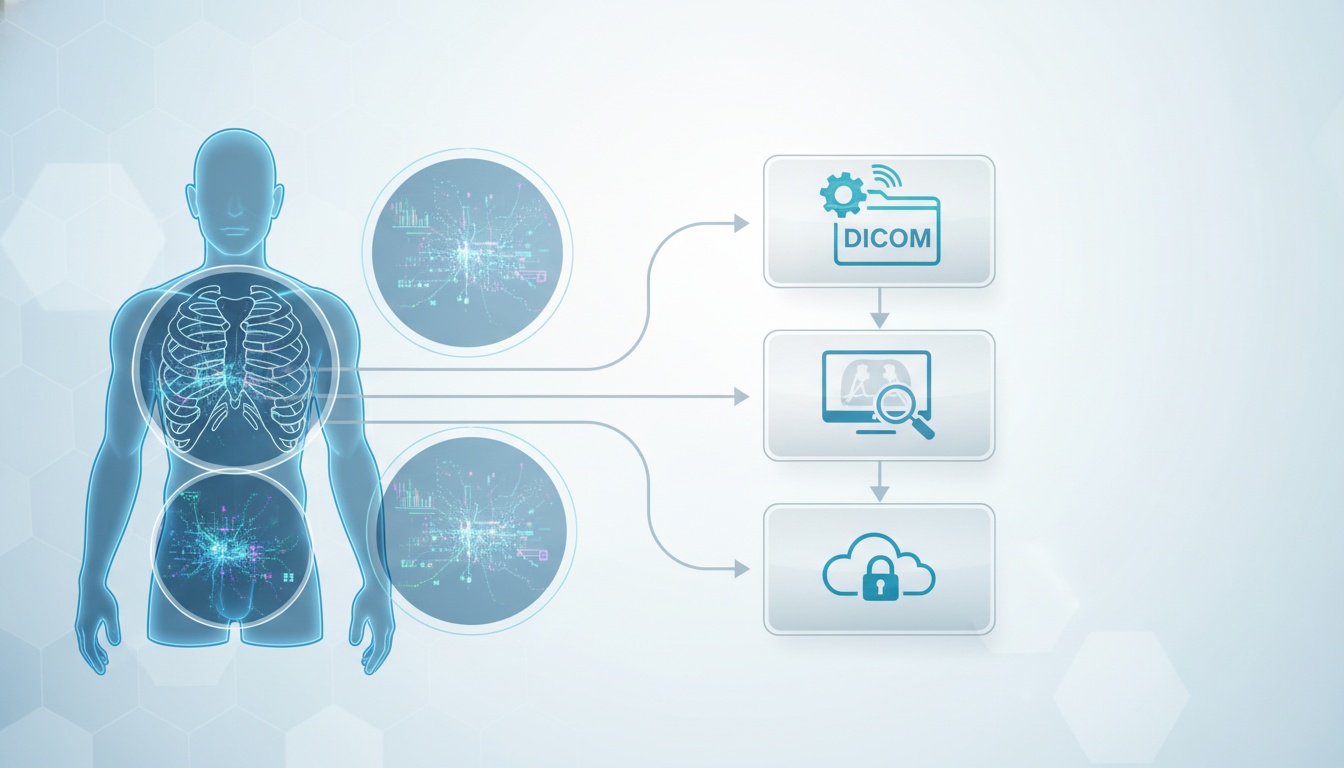
Medical imaging technology has come a long way from simple radiographs and is now represented by advanced, digitalized modalities such as CT and MRI. As the use of medical imaging becomes more widespread, there is a need to improve on other aspects of the workflow associated with imaging—reading the images and forming diagnostic reports as well as proper storage and retrieval of medical images. One of the major advances in improving the medical imaging workflow has been the introduction of DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine).
Since medical technology needs to meet exacting requirements, a certain standard is expected of images that are obtained from patients. The DICOM format is a high standard, internationally accepted format for viewing, storing and sharing medical images. You will not be able to see images acquired through a CT scan, MRI or other imaging techniques with the regular picture viewing software available on your computer. Specialized software that supports the DICOM format is required for these purposes.
Microsoft Windows is one of the most common operating systems in use worldwide, with an estimated 78% of desktop and laptop users preferring it over other systems. Therefore, it makes sense to choose a DICOM viewing application that works best with Windows. A simple search on Google will open out a world of options showcasing the best DICOM viewer for Windows. It may be difficult, however, for the uninitiated to choose from these options and to understand the various features offered by DICOM viewers. The tips below will tell you what to look for when deciding on a DICOM viewer for Windows 10, and other versions.
The kind of DICOM software that you should choose depends on several criteria. The most important being the primary purpose of the software. You should also consider commercial and legal aspects, technical features, and the cost.
Simple viewing of DICOM images: Are you a patient, and just want to be able to see your own scans? A simple viewer with minimum functionality will do. A viewer that offers sharing functions may help you send the DICOM file easily to physicians for a second opinion. Even for simple viewing, however, some applications have tweaks that let you make minor adjustments in the images—like brightness and contrast enhancements—that allow for better visualization.
Advanced diagnosis and treatment planning: If you’re a radiologist and want to use the software primarily for diagnosis, you should look at viewers that offer features that not only enhance the quality of the image but also allow you to get maximum information from the image files. Some advanced features that radiologists should definitely look for include the following:
3D reconstruction — A software that allows 3D imaging can help radiologists orient themselves to the body’s anatomy, which makes it easier to form a diagnosis. Look specifically for a 3D DICOM viewer for Windows.
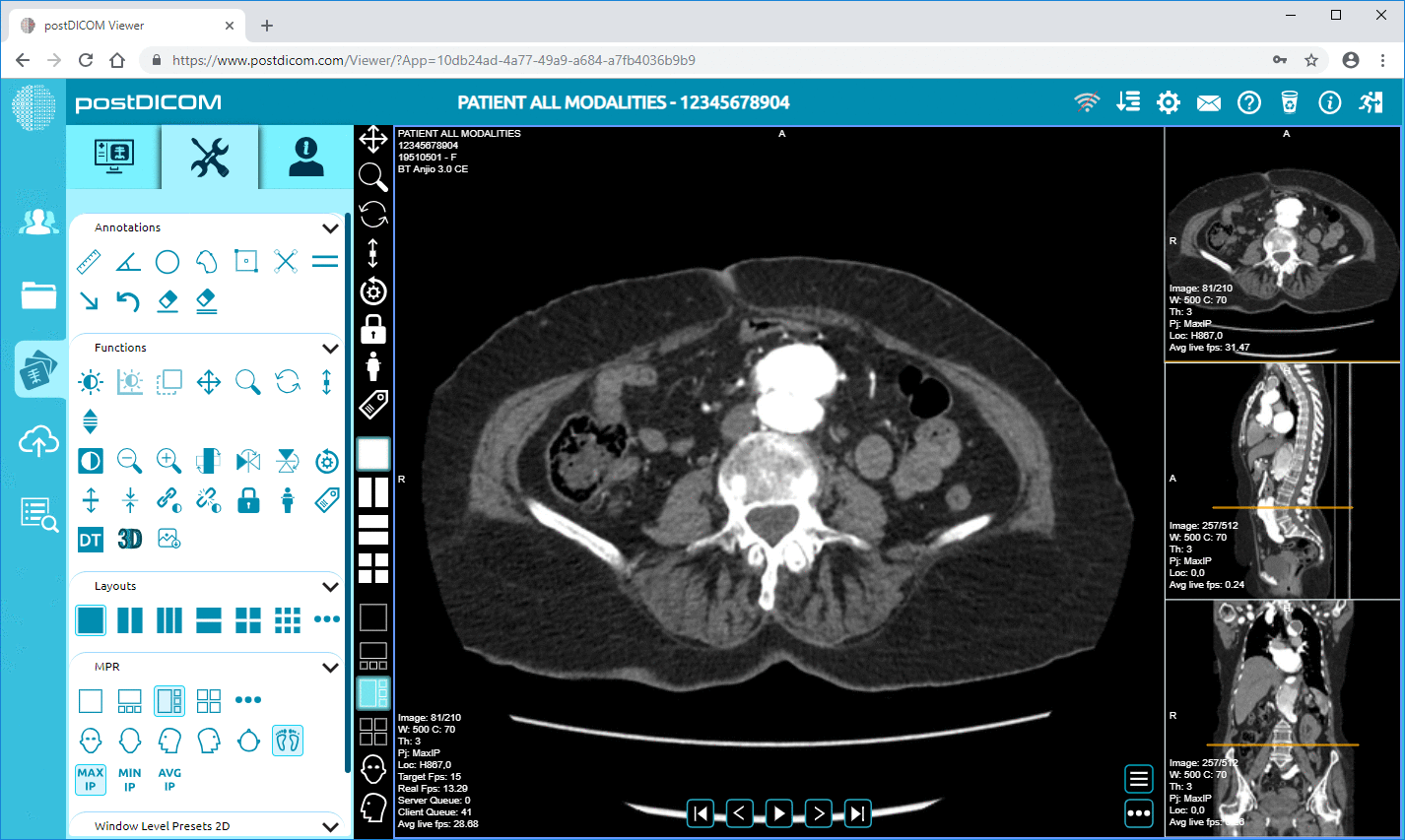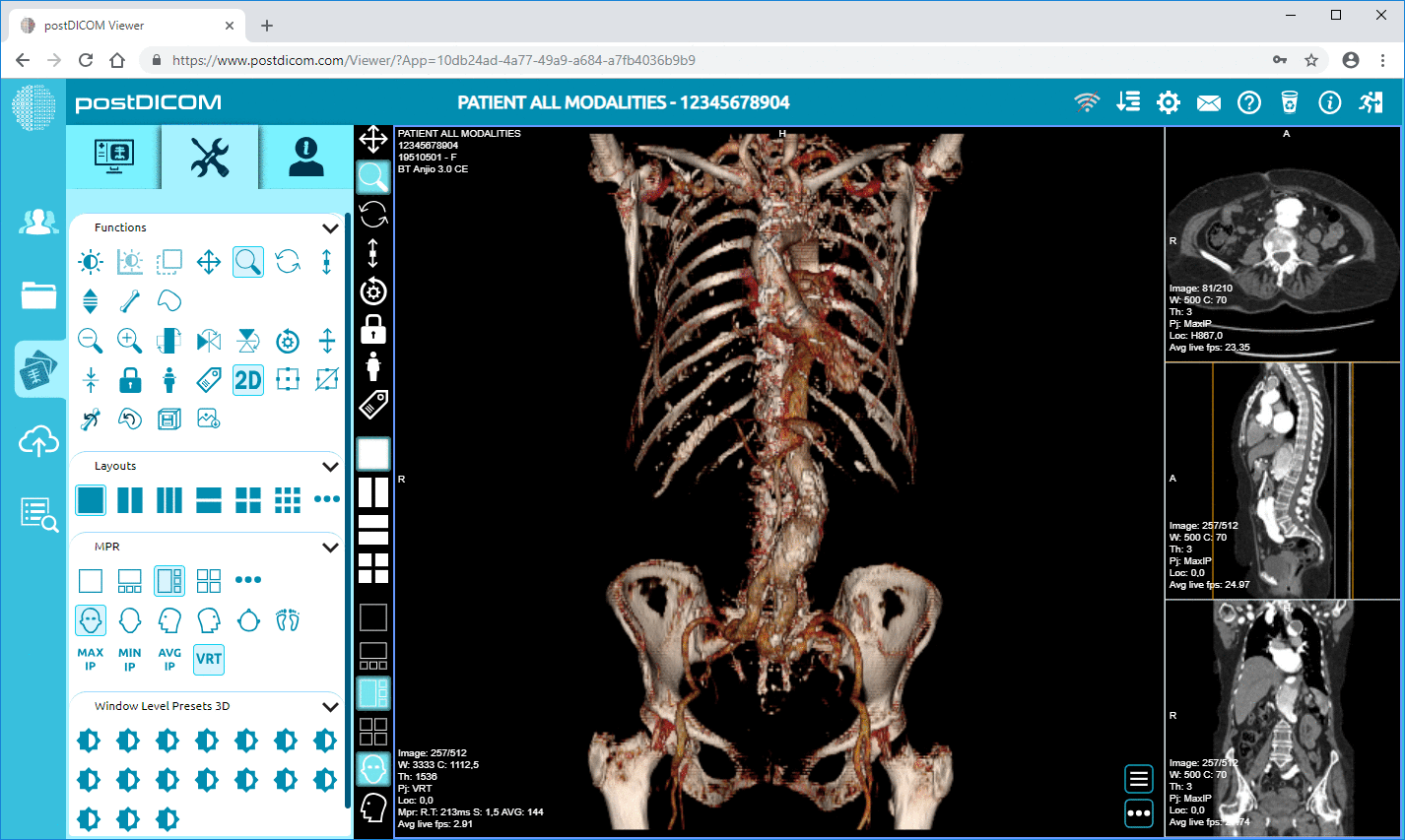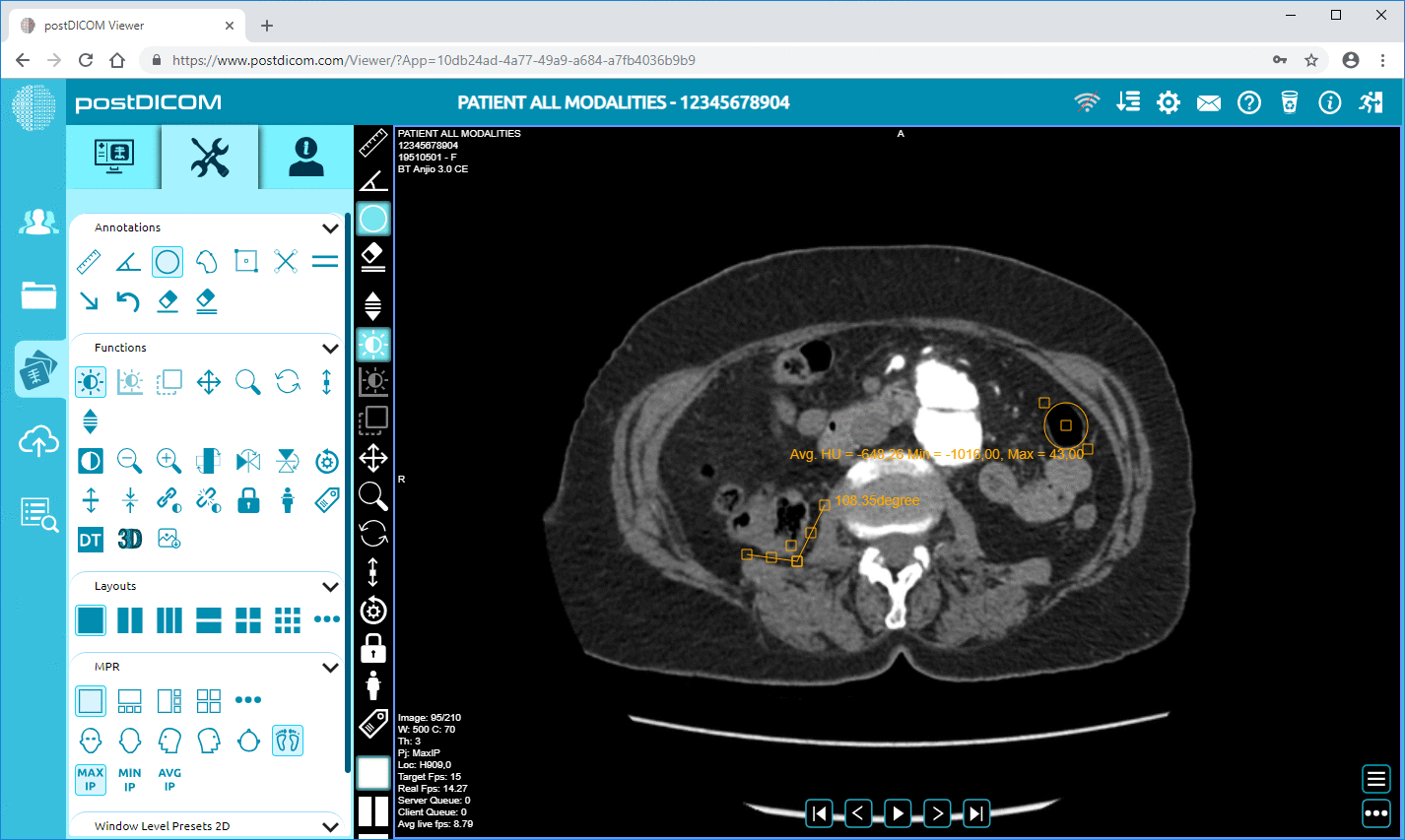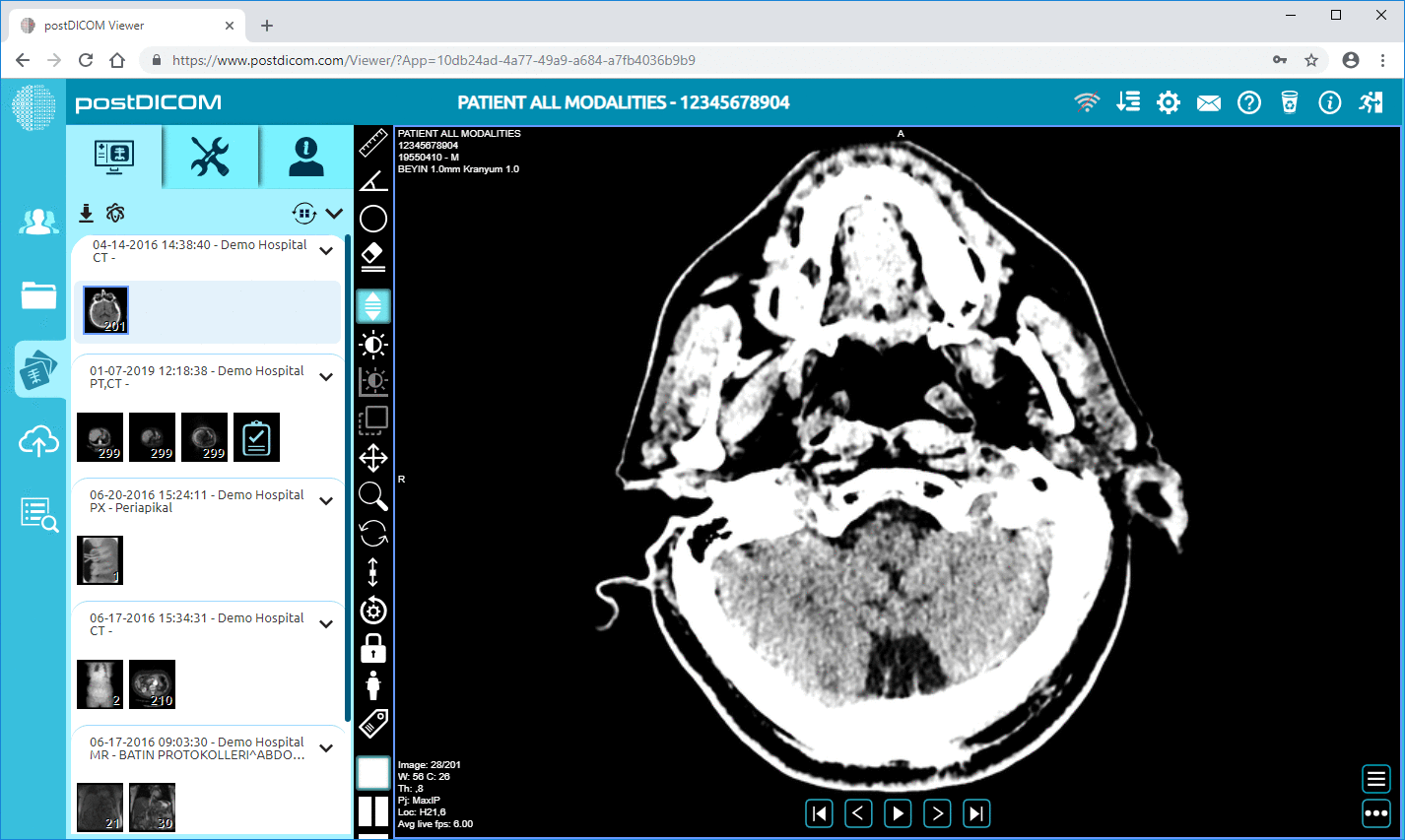
Multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) — This technology requires software that is capable of 3D imaging. This advanced feature allows radiologists to obtain new slices of images from the 3D constructed model. These new slices would be different from the original slices obtained at the time of imaging and can reduce the possibility of missing a key abnormality. MPR is also useful when the radiologist wants to track the course of a structure, such as a major blood vessel.
Maximum and Minimum Intensity Projections (MIP and MINIP) — These allow radiologists to selectively view regions that have either maximum or minimum intensity values. It enables greater focus on areas of interest by increasing the contrast between these areas and the surrounding normal tissue.
Image fusion — It allows radiologists to merge images taken through two different modalities such as PET and CT, or PET and MRI. This technique therefore encompasses the advantages of both modalities and enables greater accuracy in diagnosis.
Real-time imaging — This feature in the DICOM software allows radiologists to view the image as and when it is being acquired. This is useful when the functionality of a particular body part must be assessed.
If you’re a surgeon, most of the above features can aid in treatment planning. 3D imaging gives a good idea of normal anatomical structures. Real-time imaging is useful peri-operatively to make decisions prior to closure. It should also be possible to import DICOM files into CAD/CAM or similar software, so that stents and other body prostheses can be constructed with ease of workflow.
Research: As a researcher, you would need to collect information from multiple sets of DICOM files for data analysis. A key ethical component in research is patient confidentiality. You would need to choose a DICOM software that allows you to anonymize patient data. A researcher would also benefit from a DICOM software that has access to or comes with a PACS (Picture Archiving and Communications System) server. The server can either be part of an internal server, as in hospital databases, or it can be a cloud-based server which can be accessed from anywhere using the internet. This will help the researcher locate, access and store multiple files for data analysis.
Teaching and learning: Smart teaching methods today require you to make presentations to share information with students. As a student yourself, you may need to incorporate DICOM images into your reports and case presentations. For these purposes, it can be useful if the DICOM software allows you to export images easily in common file formats such as JPEG, PNG, or even to office applications. As a student, you may also find it convenient to share and receive DICOM files from other students or mentors. A software that allows for convenient sharing would be an added bonus.
It is quite possible that you may intend to use the DICOM software for more than one of the above listed reasons. In that case, identify the uses that would be the most important for you and prioritize accordingly.
If the use of DICOM images is going to directly impact patient health, it should be considered as commercial use. Just studying images, using them for teaching, or obtaining information from the images for research does not constitute commercial use. For commercial use, the software must have a CE mark and should be labeled either 2a (software that aids in diagnosis) or 2b (software that directs diagnosis). In addition, any DICOM software that is used commercially in the United States must have the FDA seal of approval.
Most DICOM software is available free to use, but for a certain trial period or with limited features. As a radiologist selecting a software for hospital use, you may want a version with all advanced features even if it is available at a cost. Most of the DICOM viewers for Windows offer all advanced features for a limited trial period, with an option to buy at the end of the period. Some of the DICOM applications offer free software as long as you do not require technical support.
Once you have determined your needs, you can check the features of different DICOM viewers to see which one meets your requirements.
To help you choose wisely, we have compiled a list of the five most recommended DICOM viewers for Windows. We’ve selected them based on ease of use and features available.
PostDICOM ranks as the best DICOM viewer for Windows. It has advanced imaging options, including 3D rendering, MPR, MIP and image fusion. Radiologists may find this DICOM viewer for Windows particularly useful, because it offers a user-friendly interface as well, that helps clinicians upload patient data to the PACS and generate reports. The software is compatible with most versions of Windows, and also with other operating systems such as Mac OS, iOS and android interfaces.
The best part about PostDICOM is that it offers all the advanced features at no cost to the user. You can use the cloud-based PACS to store your files. Data can be accessed through one user account and two files can be shared with other users every month. If you have a high volume of cases or would like more sharing and account options, paid subscriptions are available with these features.
All in all, PostDICOM can be used for clinical as well as teaching and learning purposes. Researchers and clinicians who see several cases a day can benefit from the paid version of this software.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |
RadiANT is an easy to use DICOM viewer for Windows that has multiple features, including MPR, MIP and image fusion. Image files can be easily exported to other formats. Multiple image files can be opened at the same time for comparison. This software is fast and easy to use, and does not require installation—it can directly open files from a CD or DVD. It has a multilingual interface and is available in over 20 languages.
It does not come with a PACS server. However, it does allow you to search and retrieve studies from other PACS locations. It does not have CE certification, and it comes with a disclaimer stating that it is meant strictly for non-commercial use.
RadiANT has been found useful by researchers. It is useful for students and residents studying radiology.
The main advantage of Navegatium is that it is one of the easiest applications to operate. This software also carries advanced features like MPR and MIP. It does not allow for image fusion. However, the software can be used to generate reports, which is useful for clinicians. One feature of this application that makes it particularly attractive to surgeons is that it can be linked to the Navegatium 3D printing service, which allows printing of three-dimensional models of body parts. This is useful for surgical planning and designing stents and guides for use during surgery.
Navegatium does not have an inbuilt PACS server. However, it does allow integration to PACS for retrieving files. It also has a database of stored image files, called the Navegatium knowledge base. These files can be used for comparing with your current images, for learning purposes.
This application is ideal for students and for teaching. It has good features that enable limited use by clinicians. Although it is completely free, the application does not have FDA approval and this must be considered before using it commercially. This free DICOM viewer is ideally meant for Windows 10, but works on versions 8.1 and higher.
As the name suggests, this software was designed with surgeons in mind. It is fast and can open DICOM files directly from PACS, a CD/DVD, or even from a USB drive. Apart from 3D reconstruction, MPR and MIP, it also allows oblique slicing of images. It allows side-by-side comparison of pre- and post-operative images. One unique feature of this software is that it allows images to be exported in the STL format. The STL format is needed for stereolithography, or 3D printing of surgical models. This is extremely useful in treatment planning and preparing guides and stents. ProSurgical DICOM viewer can also anonymize patient data, so it is also useful for researchers. Prosurgical 3D DICOM viewer for Windows works only on Windows 8.1 or higher versions.
This is a fast and powerful DICOM viewer that is compatible even with older versions of Windows such as Windows Vista. It has limited features like single oblique MPR, and the ability to export images to different formats. The free version is limited to a database of 15 patients. The paid version has additional features, which include anonymization of patient data, use from multiple monitors, and ‘on-demand’ or direct opening of files from the source (PACS, USB or CD drive) without downloading the file into the local system. Features like double oblique MPR, MIP rendering and image calibration are available only in the paid version.
Since this free DICOM viewer for Windows 10 is not licensed, it is mainly for students. Clinicians can opt to try this version first before switching to the paid version that has more features.
In the end, of the five top applications, PostDICOM appears to suit multiple purposes and if you are uncertain what your primary use will be, this is your best bet. Since it is free to use with all the advanced features, you can’t go wrong. Try this free DICOM viewer for Windows today!