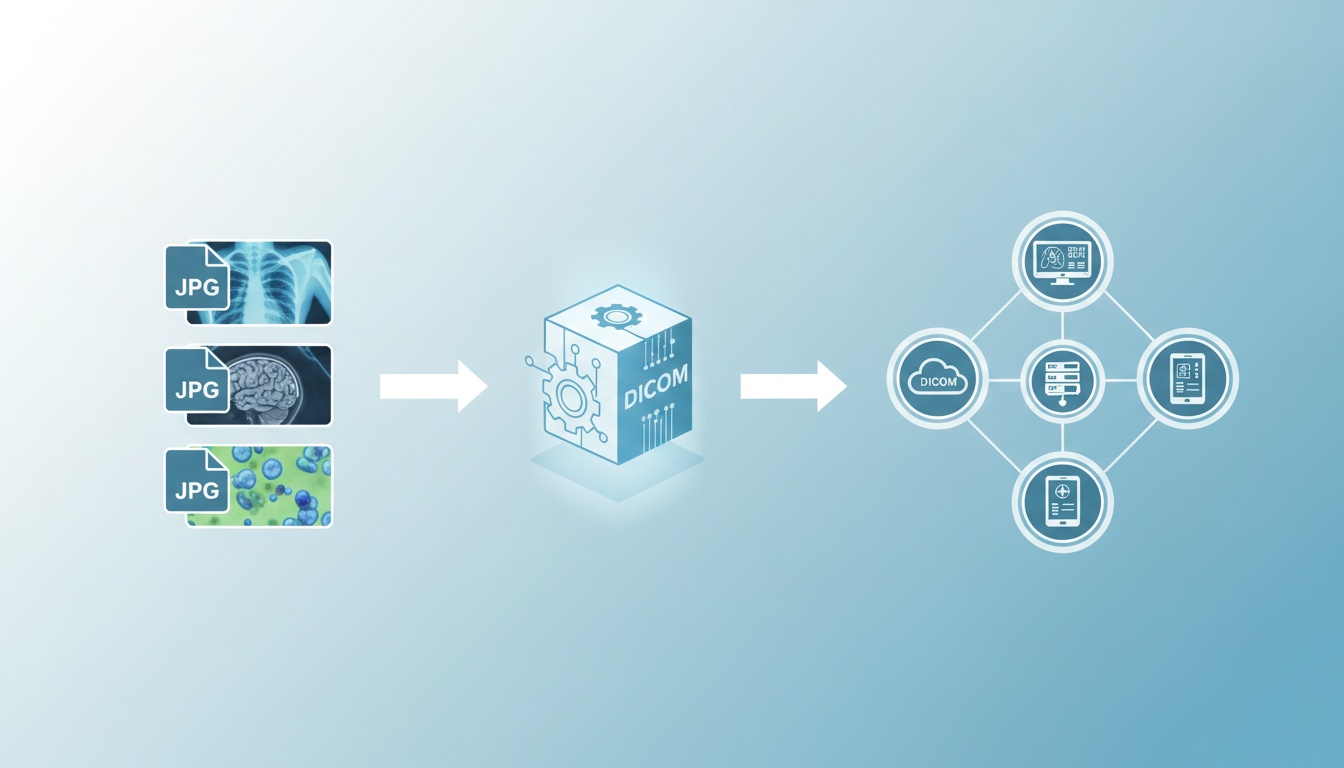
Today, the ability to seamlessly integrate different types of medical data is crucial in the modern healthcare system.
For medical facilities, converting JPEG images to DICOM format is more than a technical necessity—it’s about ensuring that every piece of patient information can be accessed within the sophisticated digital systems used in modern medicine.
This guide explains converting multiple JPEG files into DICOM format, enhancing compatibility and compliance with medical standards.
Doing so can streamline your diagnostic and treatment processes, ensuring that patient care remains efficient and effective. Whether you're a tech specialist at a hospital or a manager at a small clinic, understanding this conversion process will help you maintain the integrity and utility of your medical imaging data.
When delving into medical imaging and digital records, two file formats often come into play: JPEG and DICOM. Each serves distinct purposes in healthcare settings, and understanding their roles and capabilities is crucial for effective data management and usage.
JPEG, which stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group, is a widely used image format recognized for its efficient compression methods. In general photography and digital imaging, JPEG is king due to its ability to balance image quality with file size, making it ideal for web usage and storing large quantities of photos.
However, JPEG’s use in medical imaging is typically confined to non-diagnostic purposes such as medical reports, client communications, or educational materials. The reason is its lossy compression, which, while reducing file size, can diminish subtle details crucial for accurate medical diagnosis.
DICOM stands apart as the gold standard specifically designed for medical imaging. Unlike JPEG, DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is not just a file format but a comprehensive network communications protocol. It ensures that images and associated patient information can be stored, exchanged, and viewed across various medical imaging equipment and systems.
A DICOM file goes beyond storing an image; it also encapsulates detailed metadata about the patient’s information, the type of scan, imaging parameters, and contextual data that might influence diagnostic decisions. This aspect is vital in clinical environments, where the integrity and richness of data can directly impact patient outcomes.
While JPEG might suffice for general purposes within a medical facility, its limitations become apparent when precision and data fidelity are paramount. This necessitates converting JPEG images to DICOM in scenarios where images need to be integrated into electronic health records or used for diagnostic purposes.
The conversion not only preserves the quality during the transition but also embeds necessary metadata, ensuring that the images are viewable and analyzable within the comprehensive medical systems used in hospitals and clinics.
The transition from JPEG to DICOM in a medical setting is not just about changing file formats but upgrading to a system that can support the nuanced needs of medical diagnostics. It highlights a facility’s commitment to maintaining high patient care and data management standards.
As medical facilities continue to advance digitally, understanding and implementing the correct image formats becomes crucial for ensuring they can offer the best patient diagnostics and treatment plans.
Transitioning from JPEG to DICOM requires thoughtful preparation to ensure that the conversion process enhances the utility of the images in a medical setting without compromising data integrity or patient confidentiality. This section provides a practical guide to preparing for an effective conversion process.
Assessing the quality of the JPEG images before initiating the conversion process is essential. Since JPEG is a lossy format, evaluating whether the image resolution and detail have been significantly compromised during initial compression is crucial.
High-quality source images are pivotal for medical diagnosis, so verify that the JPEGs retain sufficient quality to be useful once converted to DICOM. If the images are of poor quality, consider acquiring new ones, especially for critical diagnostic purposes.
Choosing the right software tools for the conversion is essential. The market offers various DICOM conversion tools, both commercial and open-source. When selecting a conversion tool, look for features such as:
Compatibility with Existing Systems: Ensure the conversion software is compatible with your existing PACS or other medical imaging systems.
Support for Metadata: The tool should not only convert image formats but also allow for the insertion of relevant DICOM metadata. This metadata is critical for later retrieval and association of images with the correct patient and clinical context.
Batch Processing Capabilities: The tool should support batch processing to handle multiple conversions efficiently, allowing multiple JPEGs to be converted simultaneously.
Compliance and Security Features: Ensure the tool adheres to medical data handling standards, including security measures that protect patient data during conversion.
Before converting any data, make a full backup of all JPEG images. This precaution protects against the loss of information through corruption or during the conversion process. Store backups in a secure, compliant manner to ensure they remain accessible and intact if needed for recovery or audit purposes.
Outline a clear workflow for the conversion process, including:
Scheduling: Plan the conversion during off-peak hours if the process impacts system performance or when image access is less critical to avoid disrupting clinical operations.
Roles and Responsibilities: Assign specific roles to team members, such as who performs the conversion, who checks the quality of the converted images, and who manages data backup and security.
Quality Checks: Establish a procedure for checking the quality of converted images and their associated metadata to ensure they meet clinical and technical standards.
Conduct a pilot test with a small set of images before rolling out the conversion process on a large scale. This test helps identify any unexpected issues with image quality, metadata accuracy, or software compatibility. Based on the outcomes, you can refine the workflow and address issues before processing a larger batch of images.
Converting JPEG images to DICOM format is critical for medical facilities aiming to integrate imaging data more seamlessly into their diagnostic systems. Here’s a detailed guide on how to carry out this conversion efficiently and effectively.
First, select a conversion software that suits your facility’s needs. This software should support the inclusion of DICOM metadata and be compatible with your existing PACS system. Options vary from free tools with basic functionality to advanced software offering comprehensive customization options.
Before conversion, organize the JPEG images you intend to convert. It’s important to verify that these images are of sufficient quality and are correctly labeled and sorted. This step prevents errors during the conversion process and ensures that all necessary images are included.
Install and configure your chosen conversion software according to the manufacturer’s instructions. During setup, specify the default settings for DICOM metadata that will be applied to all images. These settings include patient ID, study dates, and modality. Customizing these settings correctly is crucial for maintaining the integrity and traceability of the converted images.
Most conversion software offers a batch processing feature, allowing you to convert multiple images simultaneously. To use this feature:
Load all JPEG files into the software.
Confirm the metadata settings for each batch, adjusting any details specific to certain images or groups of images.
Start the conversion process and monitor its progress. The software should provide a status update for each image, highlighting any errors or files that require attention.
After all images have been converted to DICOM format, conduct a thorough check to ensure no data has been lost or corrupted. Open several new DICOM files in your PACS viewer to check for image quality and correct metadata. This verification step is vital for catching any issues before the images are used clinically.
Once converted and verified, the new DICOM files should be properly archived in your PACS system. Ensure that your facility’s data management policies back up all files. Regular backups prevent data loss and ensure that all images are available for future retrieval.
Finally, document the conversion process, including details about the software used, the settings chosen, and any issues encountered. This documentation can be invaluable for troubleshooting future conversions and training new staff.

Converting JPEG images to DICOM is not just about changing file formats—it's about ensuring that these images are properly integrated into medical imaging systems while maintaining high quality and compliance standards.
Here are some best practices to guide facilities through the conversion process effectively and securely.
Maintaining the integrity of the image during conversion is crucial. Ensure that the conversion process does not compromise the image quality, which is vital for accurate diagnosis.
Always use conversion software that preserves the original image resolution and detail and avoids unnecessary re-compression of images, which can lead to loss of valuable diagnostic information.
One of the significant advantages of DICOM files is their ability to store extensive metadata along with the image. When converting JPEGs to DICOM, including as much relevant metadata as possible is essential.
This includes patient identification, imaging parameters, and any clinical notes relevant to the image. Proper metadata helps in categorizing and retrieving images more efficiently and ensures compliance with medical documentation standards.
Security is paramount when handling patient data. During the conversion process, ensure that all DICOM files are handled and stored securely to prevent unauthorized access. Use encryption where possible, especially if images need to be transmitted over a network.
Additionally, the conversion software and processes must comply with HIPAA or other relevant data protection regulations to safeguard patient privacy.
Technology and standards in digital imaging continue to evolve, and keeping your conversion software updated is crucial to ensure compatibility and efficiency.
Regular updates can also fix security vulnerabilities, enhance functionality, and improve the overall reliability of the conversion process. Choose a software provider that offers regular updates and support.
After converting images from JPEG to DICOM, it’s essential to validate the process to ensure that the converted files meet the necessary medical and technical standards.
Review a sample of the converted images in your DICOM viewer to check for any anomalies in image quality or metadata inaccuracies. Validation helps in catching issues early and can prevent problems down the line in clinical settings.
Ensure that staff involved in the conversion process are well-trained not only in using the conversion software but also in understanding the importance of DICOM standards and compliance requirements.
Training should cover handling file errors, managing data securely, and maintaining the images' quality throughout the process.
Implement a system to monitor the conversion process and conduct regular audits to ensure all procedures are followed correctly. Monitoring can help identify recurring issues or bottlenecks, while auditing ensures compliance with internal and external standards and regulations.
When converting JPEG images to DICOM, various challenges can arise that may complicate the process. Addressing these issues promptly and effectively is crucial to maintaining the integrity and usefulness of medical images.
Problem: During conversion, some JPEG images may appear to lose quality, which is critical for diagnostic purposes.
Solution: Ensure the conversion settings are optimized for the highest possible quality. Avoid unnecessary re-compression during conversion and choose conversion software that supports lossless data compression techniques. If quality issues persist, it may be necessary to source higher-quality JPEGs or initially adjust the imaging equipment settings to capture higher-resolution images.
Problem: DICOM files rely heavily on metadata for image categorization and retrieval. Sometimes, metadata may need to be correctly transferred or entered during conversion.
Solution: Set up a metadata validation step post-conversion to check for completeness and accuracy. Use software that allows for easy editing of metadata fields before finalizing the conversion. Training staff on the importance of metadata and how to accurately input it during the conversion process can also reduce errors.
Problem: Conversion software may not be fully compatible with existing PACS systems, leading to errors in uploading or displaying converted images.
Solution: Conduct a trial run with the chosen conversion software before full-scale implementation to ensure compatibility with your PACS. Check with software vendors for any necessary patches or updates that improve compatibility. If issues persist, consider consulting with IT specialists who can create custom solutions to bridge compatibility gaps.
Problem: Handling sensitive medical images requires strict adherence to data protection regulations, which might be compromised during conversion.
Solution: Use conversion software that includes robust security features such as encryption and secure user authentication. Regularly update all software to protect against vulnerabilities and ensure all data transfers are conducted over secure networks during the conversion process.
Problem: When converting large batches of images, errors may occur, such as system crashes or failed conversions for some files.
Solution: Regularly update and maintain conversion software to handle large volumes efficiently. Divide large batches into smaller segments to reduce system strain and make errors easier to identify and rectify. Additionally, ensure that the hardware can handle the required processing load.
Effective troubleshooting in JPEG to DICOM conversion is as crucial as the initial setup and execution of the conversion process. By anticipating potential issues and preparing solutions, medical facilities can ensure a smoother transition to DICOM standards, enhancing the quality of medical imaging practices and patient care.
Each challenge addressed not only improves the conversion process but also deepens the understanding and capabilities of the medical imaging team.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |