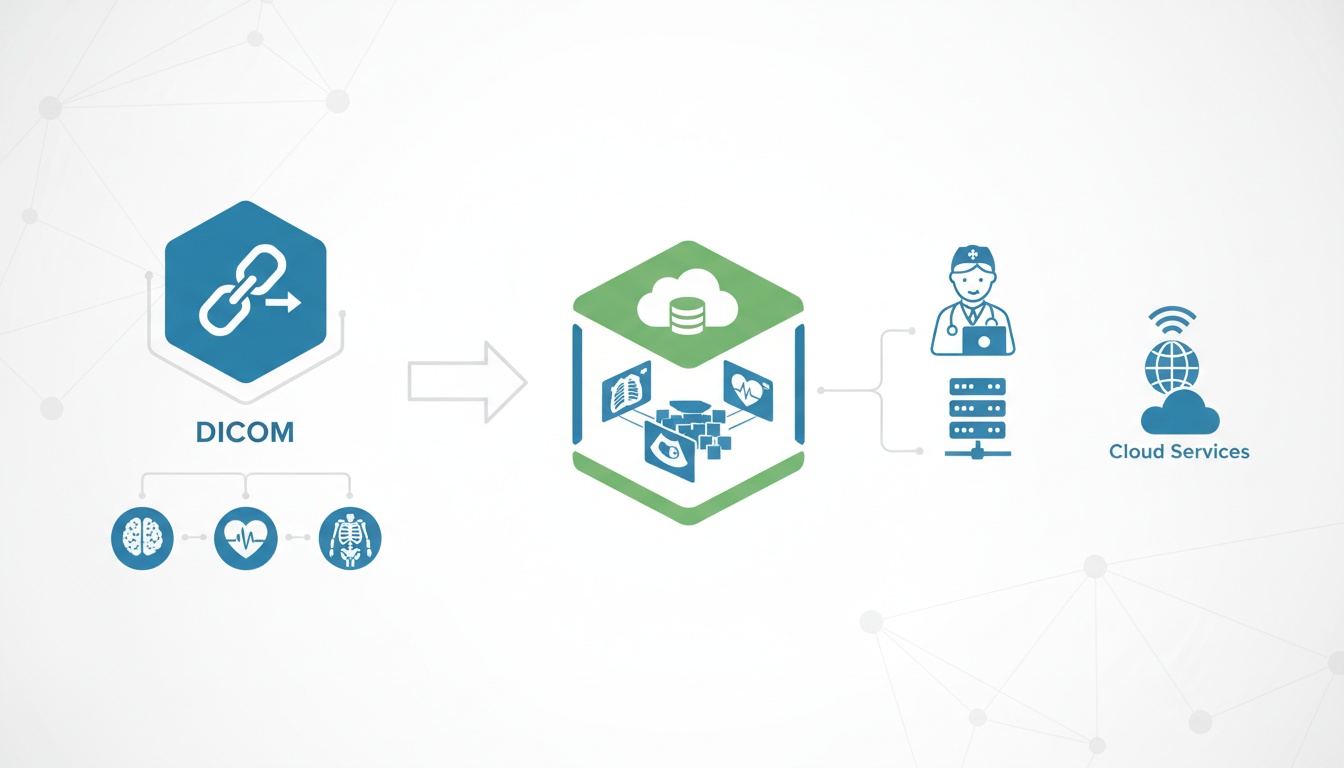
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) and PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) are two essential technologies used in the healthcare industry for managing and accessing medical images.
While they are often used together, there are some crucial differences between them. DICOM is a standard for storing, transmitting, and communicating medical images and data, while PACS is a system that uses the DICOM standard to store and manage medical images.
This article will explore the differences between DICOM and PACS and how they are used in the healthcare industry. And don’t forget to check the most updated cloud PACS services of postDICOM. We are here to meet all your medical data storage, transmission, and presentation needs.
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) is a medical imaging technology for storing, retrieving, presenting, and communicating medical images.
It is a computer-based system that provides electronic access to images and reports from various modalities such as CT, MRI, and ultrasound.
The modality: This is the medical imaging device, such as a CT scanner or an MRI machine, that is used to acquire the images.
The PACS server: This is a computer-based system that stores and manages medical images and data. It includes a database for storing the images and data and the software and hardware needed to process and transmit the images.
The workstation: This is a computer used by healthcare providers to view and manipulate medical images. It typically includes a PACS client, a software application allowing users to access the images stored on the PACS server.
The network: This is the infrastructure that connects the modalities, PACS server, and workstations. It can be a local area network (LAN) within a single facility or a wide area network (WAN) that connects multiple facilities over a larger geographic area. The network allows the various components of the PACS system to communicate and exchange data.
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is a standard for storing, transmitting, and communicating medical images and related data
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is a standard for storing, transmitting, and communicating medical images and related data. It is widely used in the healthcare industry to facilitate the exchange of medical images and data between devices such as computers, scanners, and printers.
Some of the primary uses of DICOM include:
Storing medical images: DICOM provides a standard format for storing medical images such as CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays. This allows images to be easily shared and accessed by authorized healthcare providers.
Transmitting medical images: DICOM includes a set of communication protocols that allow medical images and data to be transmitted between devices over a network. This enables healthcare providers to access images from multiple locations, such as from a hospital to a clinic or from one hospital to another.
Displaying medical images: DICOM provides guidelines for displaying medical images on computer monitors and other devices. This ensures that the images are displayed consistently and accurately across different systems.
Printing medical images: DICOM includes a set of standards for printing medical images on a film or other media. This allows images to be printed in a way consistent with their appearance on a computer screen.
Describing medical images: DICOM includes standardized data elements that you can use to describe the images and related information, such as patient demographics, image acquisition parameters, and diagnostic reports. This allows healthcare providers to access a comprehensive overview of a patient's medical history and imaging studies.
While PACS and DICOM are often used together, they are different. PACS refers to the overall system used to manage medical images, while DICOM refers to the specific standard encoded and transmitted images and data.
In other words, PACS is a system that uses the DICOM standard to store and communicate medical images.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
PACS uses DICOM to store, transmit, and communicate medical images and data. When a medical image is acquired using a device such as a CT scanner, the image is typically saved in the DICOM format. The DICOM image is then transferred to a PACS server, a central repository for storing and managing medical images.
Once the DICOM image is stored on the PACS server, it can be accessed by authorized healthcare providers using a PACS client. This software application allows users to view, manipulate, and share images. The PACS client communicates with the PACS server using the DICOM standard to retrieve and display the images.
In addition to storing and transmitting images, DICOM includes standardized data elements describing the images and related information, such as patient demographics, image acquisition parameters, and diagnostic reports. This allows healthcare providers to access a comprehensive overview of a patient's medical history and imaging studies.
HL7 (Health Level Seven) is a standard for exchanging electronic health information between healthcare organizations. It defines a set of standards, protocols, and guidelines for the structured exchange, integration, sharing, and retrieval of electronic health information.
HL7 is often used in conjunction with PACS and DICOM to enable the exchange of patient information and medical images between systems.
| PACS | RIS | CIS | DICOM | |
| Definition | A computer-based system for storing, retrieving, presenting, and communicating medical images. | A computer-based system for managing and processing a radiology department's administrative, financial, and clinical data. | A computer-based system for managing and processing the clinical data of a healthcare organization. | A standard for storing, transmitting, and communicating medical images and related data. |
| Key features | Provide electronic access to medical images and reports. | Manages the scheduling, reporting, and billing of radiology exams. | Manages and processes clinical data for a healthcare organization. | Standardized format for storing and transmitting medical images and data. |
| Examples of use | Storing and accessing medical images from various modalities (e.g., CT, MRI, ultrasound). | Scheduling and managing appointments for radiology exams. | Managing patient records and clinical data for a healthcare organization. | Transmitting medical images between devices (e.g., computers, scanners, printers). |
| Commonly used with | DICOM | PACS | HL7 (Health Level Seven) | PACS, HL7 (Health Level Seven) |
Understanding the differences between DICOM and PACS is essential for healthcare professionals working with medical images and data. By using these technologies effectively, healthcare providers can improve the accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of medical imaging and patient care.
|
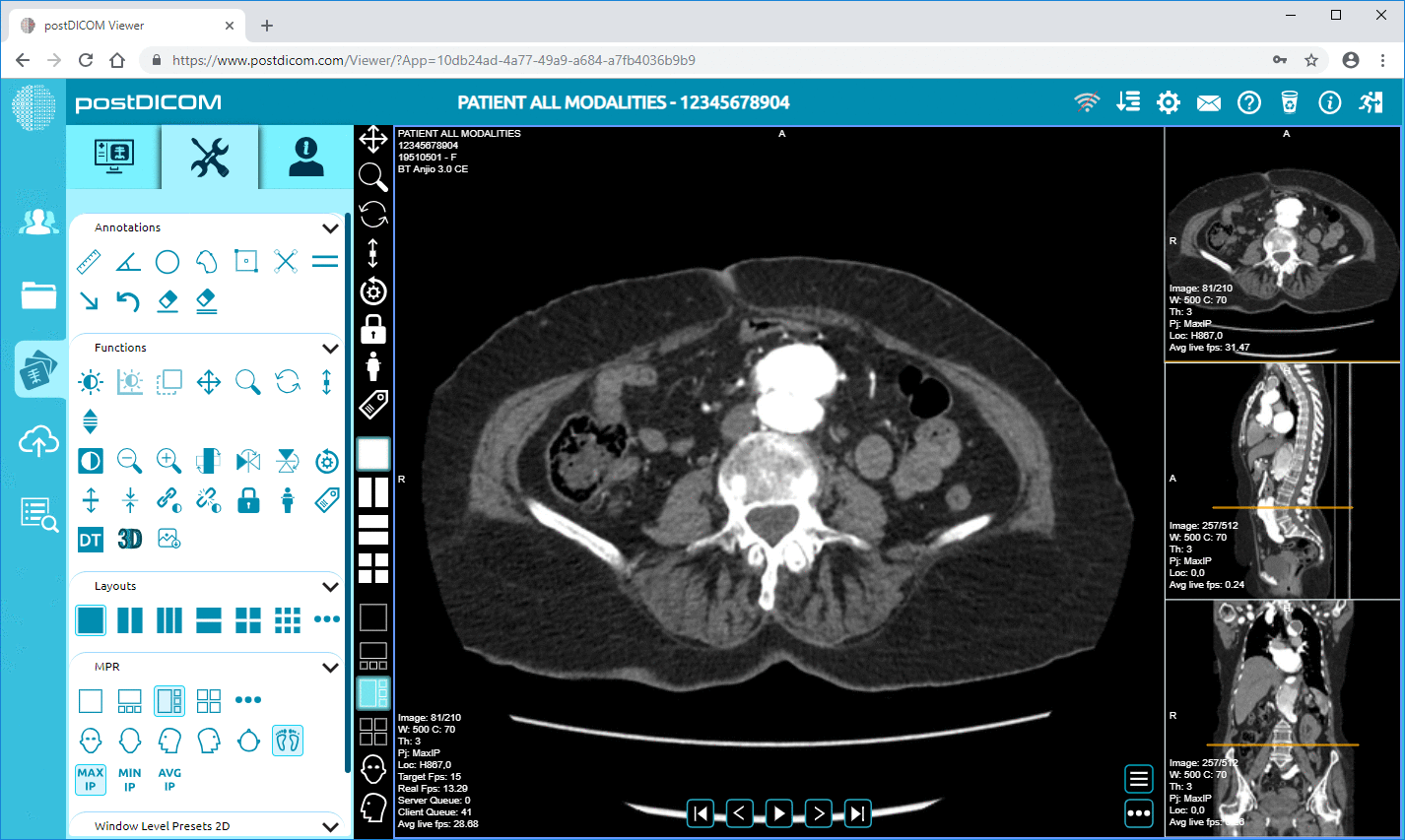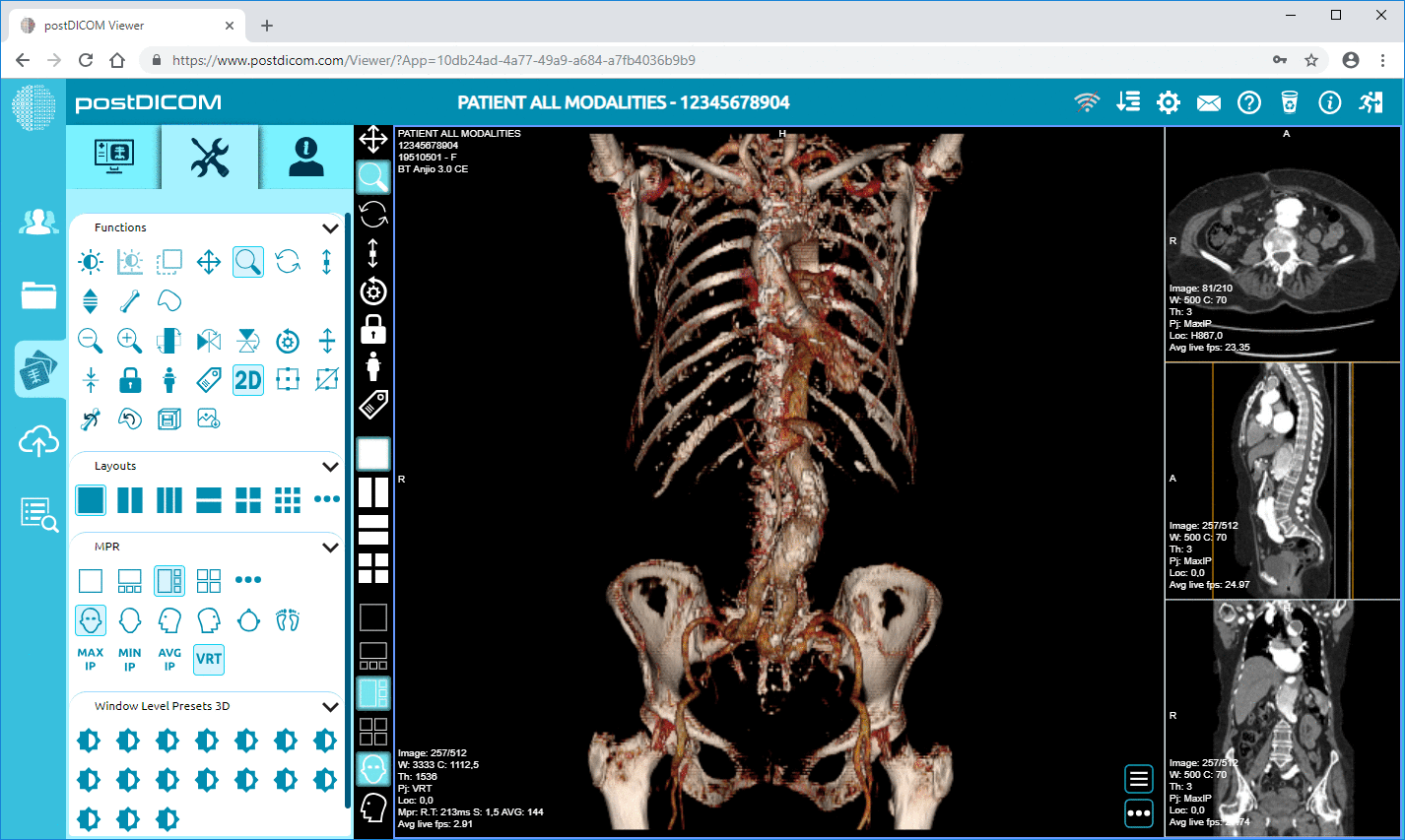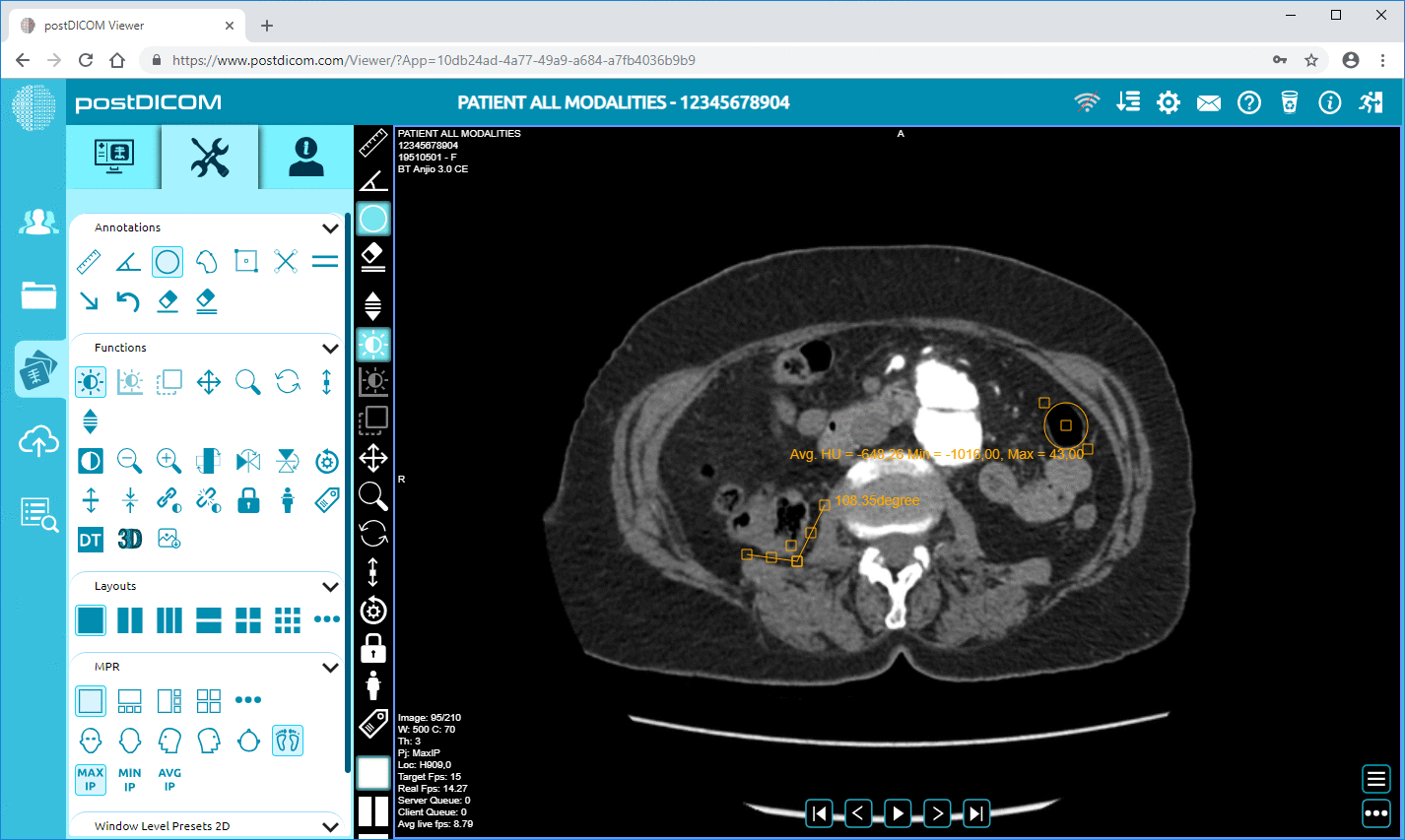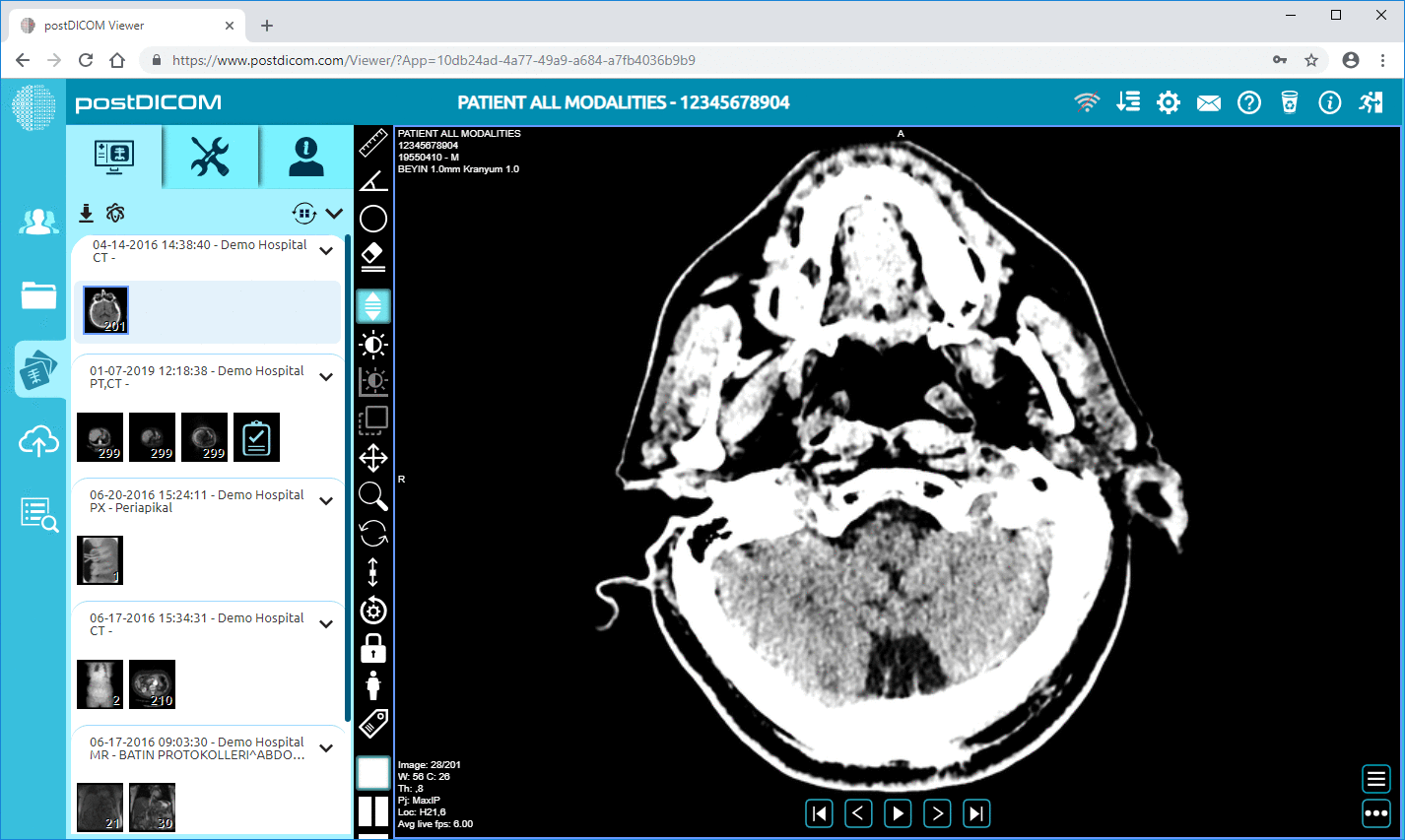
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |