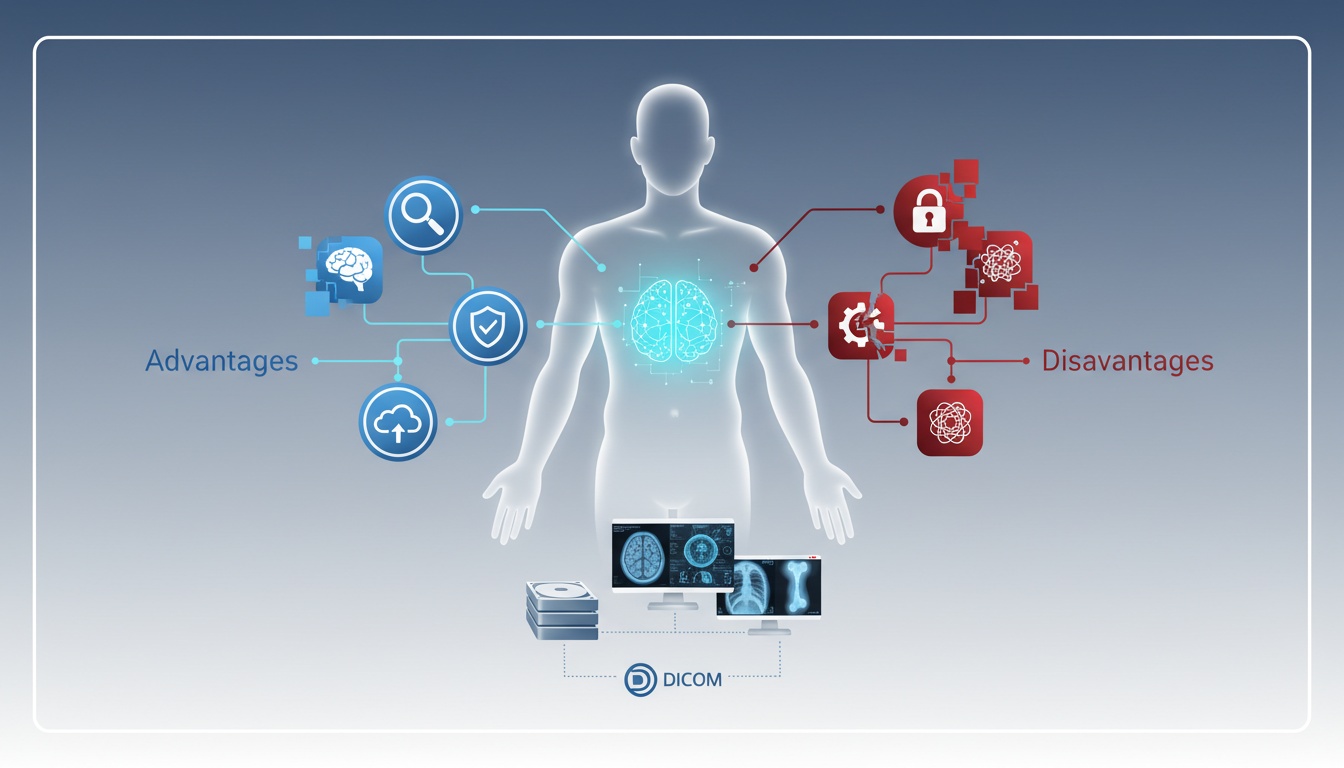
Electronic health records (EHRs) are digital systems that store and manage patient health information. They have become increasingly popular in recent years as a way to improve the efficiency and accuracy of healthcare delivery.
However, like any technology, EHRs have their advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will explore 10 key advantages and disadvantages of EHRs to help you better understand their impact on the healthcare industry.
PostDICOM offers medical data storage and display facilities for various industries. You can get the most updated and secured data transmission and presentation solution at an affordable cost. Check the solution page for more details.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) have numerous benefits that can make patient and data management easy. We have rounded up the ten most essential ones.
Electronic health records (EHRs) provide easy access to complete and up-to-date patient information, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions and provide more effective care.
EHRs can streamline managing patient records, reducing the time and effort required to enter, retrieve, and share information.
EHRs facilitate communication between healthcare providers, enabling them to collaborate more effectively and share important patient information in real-time.
EHRs can help reduce the risk of errors and improve patient safety by providing alerts for potential drug interactions, allergies, and other important information.
EHRs can be used to track and analyze population health data, allowing healthcare providers to identify trends and patterns that can inform the development of more effective interventions.
EHRs can provide patients access to their health information and tools to manage their care, empowering them to take a more active role in their health and wellness.
EHRs can be designed with robust security measures to protect patient privacy and sensitive health information.
EHRs can reduce healthcare costs by increasing efficiency and reducing the risk of errors.
EHRs can help healthcare providers track and monitor patient progress, allowing them to identify opportunities for improvement and make necessary changes to treatment plans.
EHRs can provide a wealth of data that can be used for research and public health reporting, helping to advance our understanding of diseases and health outcomes.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
Initial implementation and setup costs can be high.
There may be a learning curve for healthcare providers to use the system.
The systems may require ongoing maintenance and updates.
The systems may be prone to technical problems or downtime.
The systems may not be compatible with all devices or software.
There may be issues with data security and privacy.
It may be difficult to fully transition to electronic records, especially if some healthcare providers resist change.
Electronic record systems may not be user-friendly.
It may be challenging to accurately and completely transfer all relevant patient information into the electronic record system.
The electronic record system may not be accessible to all healthcare providers, which can impact the patient's quality of care.
Electronic health records (EHRs) and electronic medical records (EMRs) are digital systems that store and manage patient health information. However, there are some key differences between the two:
EHRs are a more comprehensive system that includes a patient's complete medical history, while EMRs generally focus on a specific episode of care or treatment.
EHRs are owned and managed by healthcare organizations, while EMRs are typically owned and managed by individual healthcare providers.
EHRs are designed to be accessible to all authorized healthcare providers within a healthcare organization or system. At the same time, EMRs are typically only accessible to the healthcare provider or practice that owns the system.
EHRs generally have more advanced functionality and capabilities, such as generating population health reports, support for clinical decision support tools, and integration with other healthcare systems. EMRs may have more basic functionality and are primarily used for documentation and billing purposes.
In general, hospitals tend to use EHRs rather than EMRs because of the comprehensive nature of EHRs and the ability to access and share patient information across the entire healthcare organization.
However, some hospitals may also use EMRs in addition to EHRs, particularly for specialty care or in cases where the hospital contracts with external healthcare providers.
Electronic health records (EHRs) have significantly impacted the healthcare industry. Some of the key ways that EHRs have impacted healthcare include:
EHRs allow healthcare providers to access a patient's complete medical history and treatment information in a single, centralized location, which can help to improve the accuracy and quality of care.
EHRs can streamline many administrative tasks associated with healthcare, such as scheduling appointments, prescribing medications, and billing.
EHRs make it easier for healthcare providers to share patient information with other healthcare organizations, which can improve care coordination.
EHRs can help reduce the risk of medical errors, such as incorrect dosages or diagnoses, by providing healthcare providers with access to accurate and up-to-date patient information.
EHRs often include patient portals that allow patients to access their health information and communicate with their healthcare providers, which can encourage patients to be more proactive in their healthcare.
Electronic health records (EHRs) have significantly impacted the healthcare industry, offering numerous advantages such as improved patient care, increased efficiency, enhanced collaboration, reduced errors, and increased patient engagement.
While there are also some disadvantages to EHRs, such as initial implementation and maintenance costs and the potential for technical issues, the benefits of EHRs far outweigh the drawbacks.
|
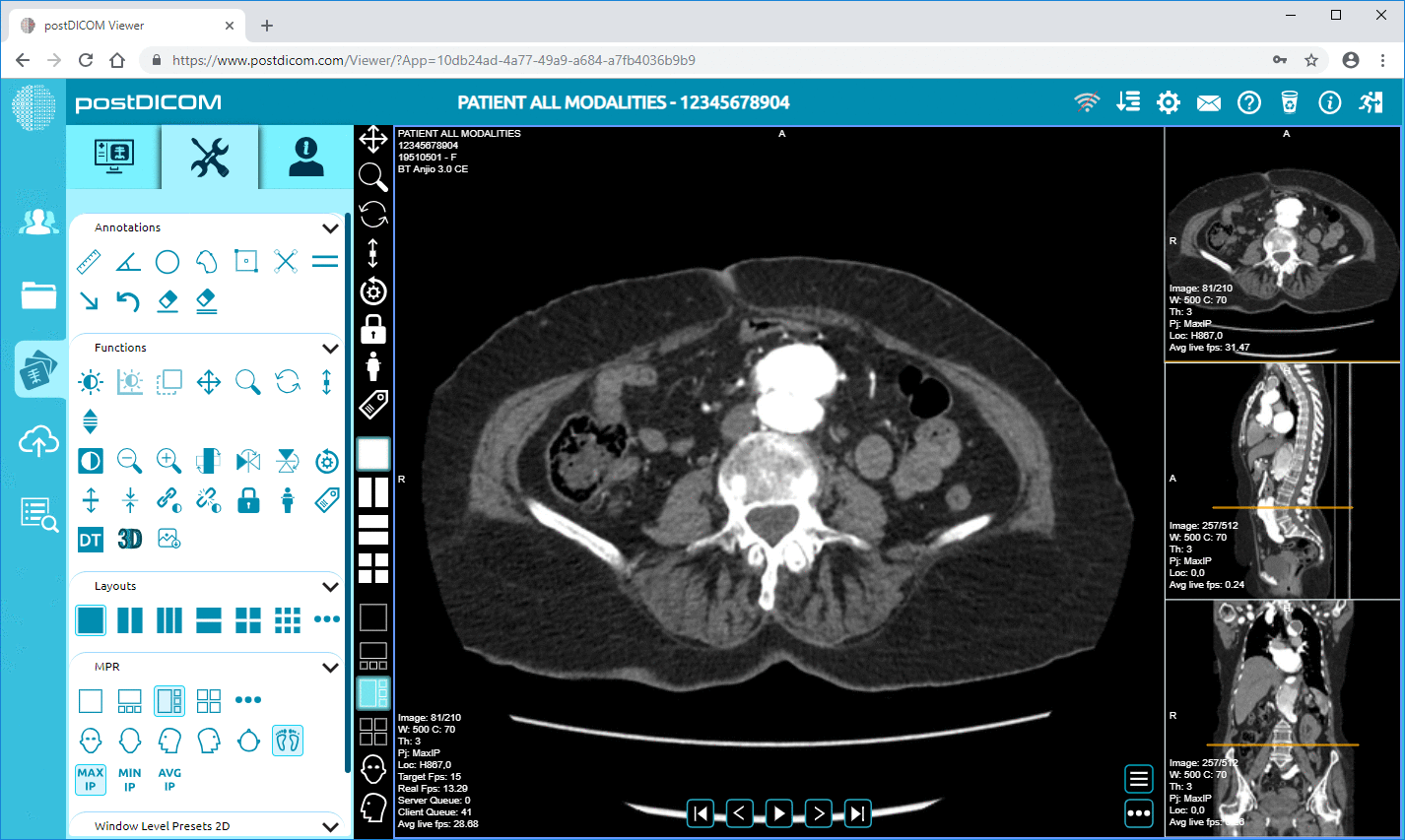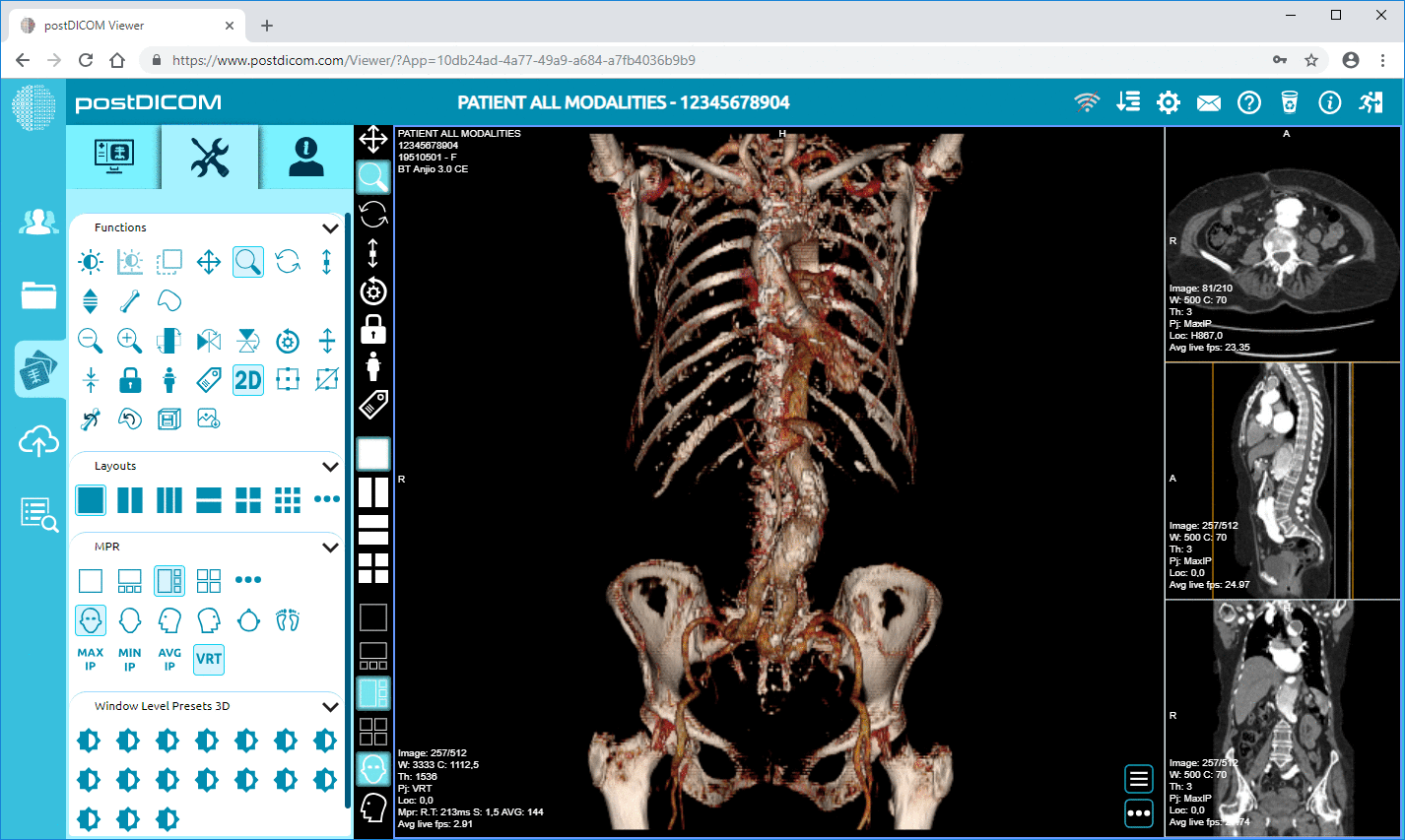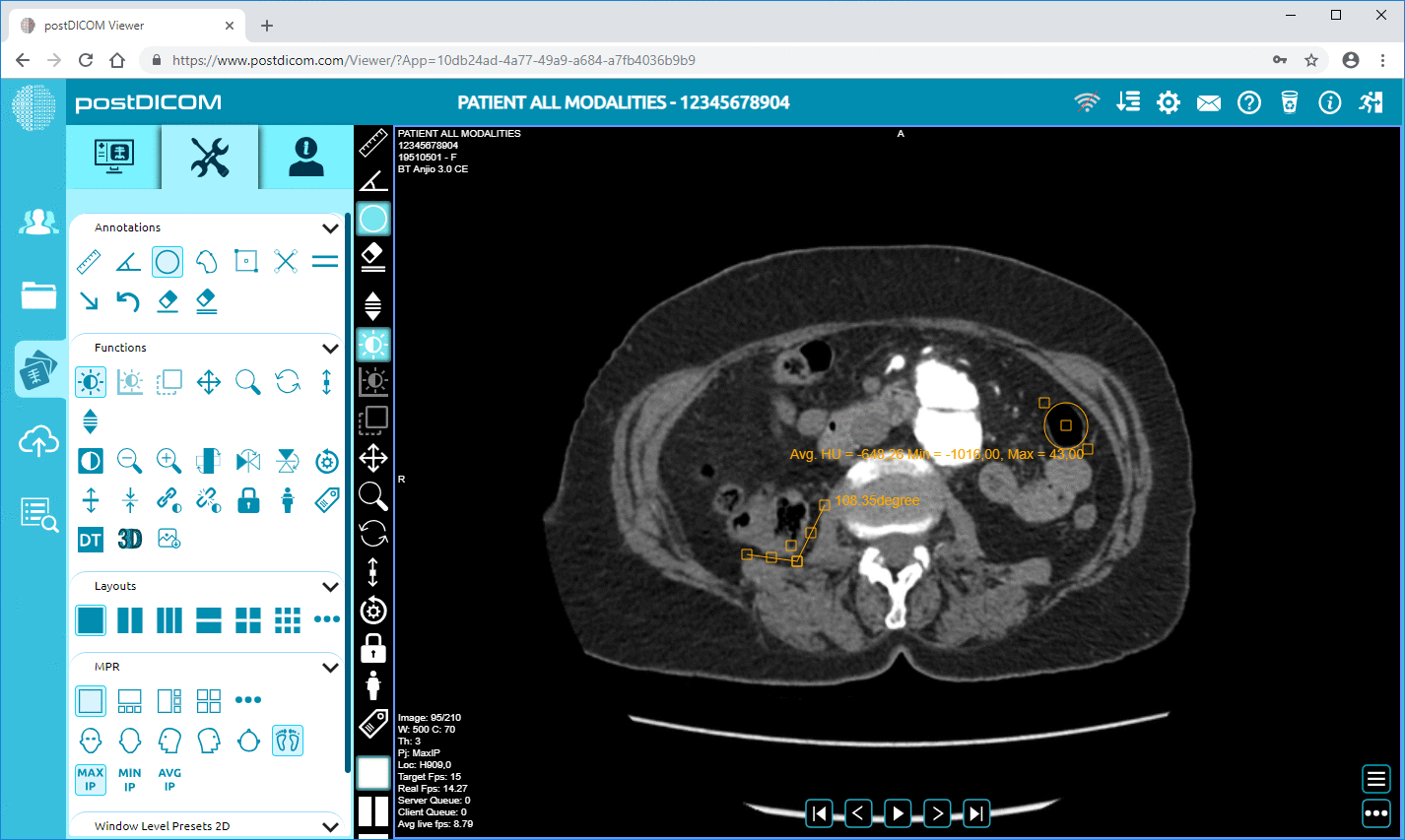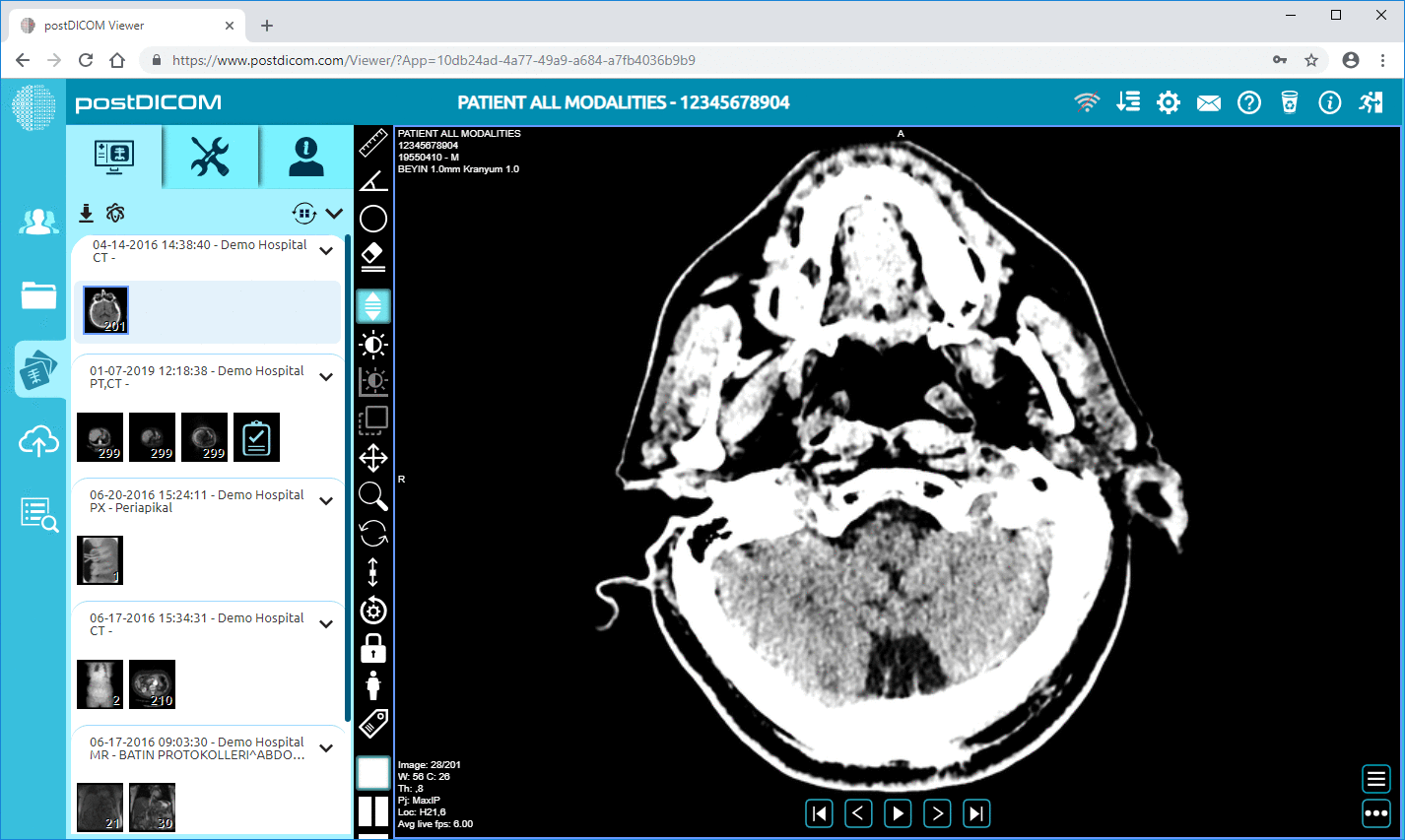
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |